
How many triangles can be formed by joining the vertices of a hexagon?
A. 31
B. 25
C. 20
D. 60
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: As we know that hexagon has \[6\] vertices means \[6\] points and the triangle has \[3\] points means a triangle need \[3\] vertices to be formed. Then, the numbers of triangles that can be formed by joining the vertices of a hexagon can be calculated by applying the concept of combination.
Complete step by step solution:
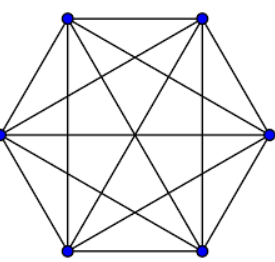
The number of vertices in a hexagon is \[6\].
The number of vertices in a triangle is \[3\].
That means to make a triangle we need \[3\] vertices.
So,\[6\]is the total number of vertices in hexagons, and out of those 6 vertices, 3 vertices that being chosen at a time to make a triangle.
By applying the formula of combination:
\[{}^n{C_r} = \dfrac{{n!}}{{r! \times \left( {n - r} \right)!}}\] where, n is the total numbers of objects and r is the number of objects to be chosen as a time.
Therefore,
\[{}^6{C_3} = \dfrac{{6!}}{{3! \times \left( {6 - 3} \right)!}} = \dfrac{{6!}}{{3! \times \left( 3 \right)!}}\]
By using the values of factorial terms:
We have, \[6!\] can be written as \[6 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1\] and \[3!\] can be written as \[3 \times 2 \times 1.\]
Replace \[6!\] = \[6 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1\] and \[3!\]= \[3 \times 2 \times 1\] in the following equation,
\[
{}^6{C_3} = \dfrac{{6!}}{{3! \times \left( 3 \right)!}} \\
= \dfrac{{6 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1}}{{3 \times 2 \times 1\left( {3 \times 2 \times 1} \right)}} = \dfrac{{120}}{6} = 20 \\
\]
$\therefore$ The number of triangles that can be formed by joining the vertices of a hexagon is \[20\]. Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
These types of questions always use a combination concept for solving the problem.
Some important definitions you should know
Vertices mean the point where \[2\] or more lines meet.
Combination: Any of the ways we can combine things when the order does not matter.
Combination formula: The formula of combination is \[{}^n{C_r} = \dfrac{{n!}}{{r! \times \left( {n - r} \right)!}}\], where \[n\] represents the number of items and \[r\] represents the number of the items that being chosen at a time.
The factorial function\[(!)\]: The factorial function means to multiply all whole numbers from the chosen numbers down to \[1\].
The representation of factorial is \[n!\].
Alternatively, you can draw the figure and count the triangles but it becomes complicated.
Complete step by step solution:

The number of vertices in a hexagon is \[6\].
The number of vertices in a triangle is \[3\].
That means to make a triangle we need \[3\] vertices.
So,\[6\]is the total number of vertices in hexagons, and out of those 6 vertices, 3 vertices that being chosen at a time to make a triangle.
By applying the formula of combination:
\[{}^n{C_r} = \dfrac{{n!}}{{r! \times \left( {n - r} \right)!}}\] where, n is the total numbers of objects and r is the number of objects to be chosen as a time.
Therefore,
\[{}^6{C_3} = \dfrac{{6!}}{{3! \times \left( {6 - 3} \right)!}} = \dfrac{{6!}}{{3! \times \left( 3 \right)!}}\]
By using the values of factorial terms:
We have, \[6!\] can be written as \[6 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1\] and \[3!\] can be written as \[3 \times 2 \times 1.\]
Replace \[6!\] = \[6 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1\] and \[3!\]= \[3 \times 2 \times 1\] in the following equation,
\[
{}^6{C_3} = \dfrac{{6!}}{{3! \times \left( 3 \right)!}} \\
= \dfrac{{6 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3 \times 2 \times 1}}{{3 \times 2 \times 1\left( {3 \times 2 \times 1} \right)}} = \dfrac{{120}}{6} = 20 \\
\]
$\therefore$ The number of triangles that can be formed by joining the vertices of a hexagon is \[20\]. Hence, option (C) is correct.
Note:
These types of questions always use a combination concept for solving the problem.
Some important definitions you should know
Vertices mean the point where \[2\] or more lines meet.
Combination: Any of the ways we can combine things when the order does not matter.
Combination formula: The formula of combination is \[{}^n{C_r} = \dfrac{{n!}}{{r! \times \left( {n - r} \right)!}}\], where \[n\] represents the number of items and \[r\] represents the number of the items that being chosen at a time.
The factorial function\[(!)\]: The factorial function means to multiply all whole numbers from the chosen numbers down to \[1\].
The representation of factorial is \[n!\].
Alternatively, you can draw the figure and count the triangles but it becomes complicated.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




