
Triangle with side 2cm, 3cm, 4cm is similar to the triangle of following measures
(a).4, 5, 6
(b).5, 6, 7
(c).12, 13, 14
(d).6, 9, 12
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: Here in this question given the sides of the triangle. We have to check or find the similar triangle of given length of triangle and from the given option by using the some conditions for the similarity of two triangles. And observing the triangles we can easily say the similar triangle.
Complete answer:
Triangle is also a polygon. So we have some conditions for the similarity of two triangles. That is: Two triangles are similar, if
their corresponding angles are equal and
their corresponding sides are in the same ratio (or proportion).
if corresponding angles of two triangles are equal, then they are known as equiangular triangles.
A famous Greek mathematician Thales gave an important truth relating to two equiangular triangles which is as follows:
“The ratio of any two corresponding sides in two equiangular triangles is always the same”
i.e., \[\dfrac{{AB}}{{DE}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{EF}} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{DF}}\]
By using the Thales theorem we can find easily the similar triangle
Consider the given length of the triangle with side 2cm, 3cm, 4cm is:
Option (a) The triangle of length 4, 5 and 6 is comparing with the given triangle of length 2, 3 and 4
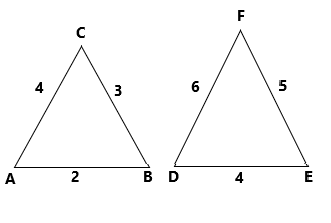
By the Thales theorem
\[\dfrac{2}{4} = \dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{4}{6}\]
On simplification
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \ne \dfrac{3}{5} \ne \dfrac{2}{3}\]
The Thales theorem does not satisfy. hence the option (a) is not correct one
Option (b) The triangle of length 5, 6 and 7 is comparing with the given triangle of length 2, 3 and 4
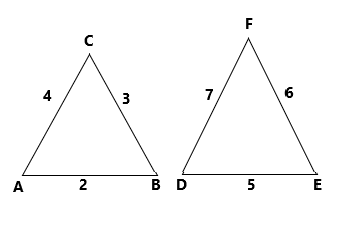
By the Thales theorem
\[\dfrac{2}{5} = \dfrac{3}{6} = \dfrac{4}{7}\]
On simplification
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{5} \ne \dfrac{1}{2} \ne \dfrac{4}{7}\]
The Thales theorem does not satisfy. hence the option (b) is not correct one
Option (c) The triangle of length 12, 13 and 14 is comparing with the given triangle of length 2, 3 and 4
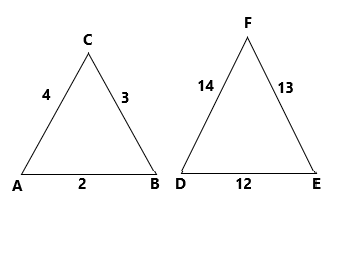
By the Thales theorem
\[\dfrac{2}{{12}} = \dfrac{3}{{13}} = \dfrac{4}{{14}}\]
On simplification
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{6} \ne \dfrac{3}{{13}} \ne \dfrac{2}{7}\]
The Thales theorem does not satisfy. hence the option (c) is not correct one
Option (d) The triangle of length 6, 9 and 12 is comparing with the given triangle of length 2, 3 and 4
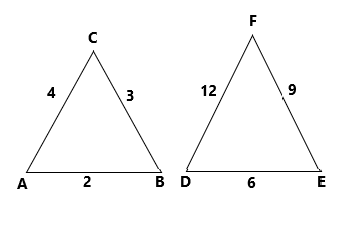
By the Thales theorem
\[\dfrac{2}{6} = \dfrac{3}{9} = \dfrac{4}{{12}}\]
On simplification
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3} = \dfrac{1}{3} = \dfrac{1}{3}\]
The Thales theorem satisfies. Hence the option (d) is a correct one .
Note:
The condition of a triangle must know that their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are in the same ratio (or proportion). The Thales theorem is stated on the similar triangles, considering the theorem we have solved the given question and got the solution.
Complete answer:
Triangle is also a polygon. So we have some conditions for the similarity of two triangles. That is: Two triangles are similar, if
their corresponding angles are equal and
their corresponding sides are in the same ratio (or proportion).
if corresponding angles of two triangles are equal, then they are known as equiangular triangles.
A famous Greek mathematician Thales gave an important truth relating to two equiangular triangles which is as follows:
“The ratio of any two corresponding sides in two equiangular triangles is always the same”
i.e., \[\dfrac{{AB}}{{DE}} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{EF}} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{DF}}\]
By using the Thales theorem we can find easily the similar triangle
Consider the given length of the triangle with side 2cm, 3cm, 4cm is:
Option (a) The triangle of length 4, 5 and 6 is comparing with the given triangle of length 2, 3 and 4

By the Thales theorem
\[\dfrac{2}{4} = \dfrac{3}{5} = \dfrac{4}{6}\]
On simplification
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \ne \dfrac{3}{5} \ne \dfrac{2}{3}\]
The Thales theorem does not satisfy. hence the option (a) is not correct one
Option (b) The triangle of length 5, 6 and 7 is comparing with the given triangle of length 2, 3 and 4

By the Thales theorem
\[\dfrac{2}{5} = \dfrac{3}{6} = \dfrac{4}{7}\]
On simplification
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{5} \ne \dfrac{1}{2} \ne \dfrac{4}{7}\]
The Thales theorem does not satisfy. hence the option (b) is not correct one
Option (c) The triangle of length 12, 13 and 14 is comparing with the given triangle of length 2, 3 and 4

By the Thales theorem
\[\dfrac{2}{{12}} = \dfrac{3}{{13}} = \dfrac{4}{{14}}\]
On simplification
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{6} \ne \dfrac{3}{{13}} \ne \dfrac{2}{7}\]
The Thales theorem does not satisfy. hence the option (c) is not correct one
Option (d) The triangle of length 6, 9 and 12 is comparing with the given triangle of length 2, 3 and 4

By the Thales theorem
\[\dfrac{2}{6} = \dfrac{3}{9} = \dfrac{4}{{12}}\]
On simplification
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3} = \dfrac{1}{3} = \dfrac{1}{3}\]
The Thales theorem satisfies. Hence the option (d) is a correct one .
Note:
The condition of a triangle must know that their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are in the same ratio (or proportion). The Thales theorem is stated on the similar triangles, considering the theorem we have solved the given question and got the solution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




