
Triangle ABC is right angled at A. The points P and Q are on the hypotenuse BC such that \[BP=PQ=QC\] and if \[AP=3\] and \[AQ=4\] then the value of BC equal to
(a) \[3\sqrt{5}\]
(b) \[5\sqrt{3}\]
(c) \[4\sqrt{5}\]
(d) 7
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: We solve this problem by using the cosine rule and Pythagoras theorem of a triangle.
We have the formula of cosine rule of the following triangle as
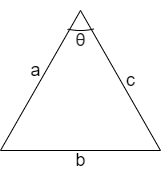
The cosine rule of above triangle is given as
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{2ac}\]
The Pythagoras Theorem states that the square of hypotenuse is equal to sum of squares of other two sides that is for the triangle shown below
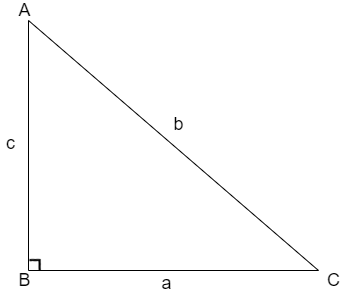
The Pythagoras theorem is given as\[{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}\].
Complete step by step answer:
Let us take the figure that represents the given information of triangle ABC as follows
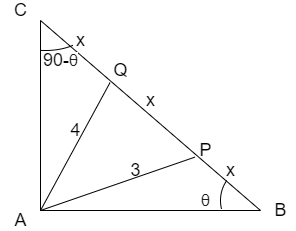
Let us assume that length of BP, PQ and QC as
\[\Rightarrow BP=PQ=QC\]
Now, let us take the value of BC as
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow BC=BP+PQ+QC \\
& \Rightarrow BC=x+x+x=3x \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the triangle \[\Delta ABC\]
We know that the Pythagoras Theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides that is for the triangle shown below
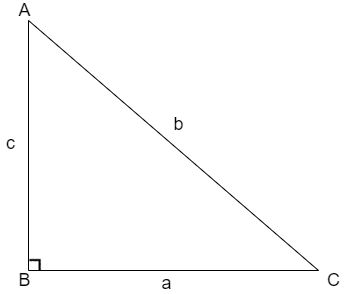
The Pythagoras theorem is given as\[{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}\].
By using the Pythagoras theorem for triangle \[\Delta ABC\] then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=9{{x}^{2}}.......equation(i) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the triangle \[\Delta APB\]
We know that the formula of cosine rule of a following triangle as
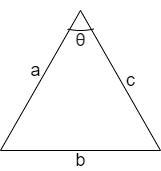
The cosine rule of above triangle is given as
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{2ac}\]
By using the cosine rule to angle \[\angle ABP\] of triangle \[\Delta APB\] then we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}+B{{P}^{2}}-A{{P}^{2}}}{2AB\times BP}......equation(ii)\]
We know that the cosine ratio of right angled triangle is given as
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{Adjacent}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
By using this cosine ratio to triangle \[\Delta ABC\] then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{AB}{3x} \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the required values in equation (ii) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{3x}=\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-9}{2\times AB\times x} \\
& \Rightarrow 2A{{B}^{2}}=3A{{B}^{2}}+3{{x}^{2}}-27 \\
& \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}=27-3{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the triangle \[\Delta ACQ\]
By using the cosine rule at the angle of vertex C then we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}+C{{Q}^{2}}-A{{Q}^{2}}}{2\times AC\times CQ}.....equation(iii)\]
By using the cosine ratio of right angled triangle \[\Delta ABC\] we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\dfrac{AC}{BC}\]
By substituting the required values in equation (iii) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AC}{3x}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-16}{2\times AC\times x} \\
& \Rightarrow 2A{{C}^{2}}=3A{{C}^{2}}+3{{x}^{2}}-48 \\
& \Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}=48-3{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by substituting the required values in the equation (i) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( 27-3{{x}^{2}} \right)+\left( 48-3{{x}^{2}} \right)=9{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 15{{x}^{2}}=75 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us find the value of BC as follows
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow BC=3x \\
& \Rightarrow BC=3\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore we can conclude that the value of side BC is \[3\sqrt{5}\]
So, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note:
We need to note that any of the line segments AP and AQ is not perpendicular to side BC.
Students may do a mistake and consider that
\[\Rightarrow AP\bot BC\text{ or }AQ\bot BC\]
This gives the wrong answer because we cannot judge by seeing the figure.
Considering anyone is also wrong.
So, we need to use the properties of triangles that are cosine rule or sine rule to get the required answer.
We have the formula of cosine rule of the following triangle as

The cosine rule of above triangle is given as
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{2ac}\]
The Pythagoras Theorem states that the square of hypotenuse is equal to sum of squares of other two sides that is for the triangle shown below

The Pythagoras theorem is given as\[{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}\].
Complete step by step answer:
Let us take the figure that represents the given information of triangle ABC as follows

Let us assume that length of BP, PQ and QC as
\[\Rightarrow BP=PQ=QC\]
Now, let us take the value of BC as
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow BC=BP+PQ+QC \\
& \Rightarrow BC=x+x+x=3x \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the triangle \[\Delta ABC\]
We know that the Pythagoras Theorem states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides that is for the triangle shown below

The Pythagoras theorem is given as\[{{b}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}\].
By using the Pythagoras theorem for triangle \[\Delta ABC\] then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=9{{x}^{2}}.......equation(i) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the triangle \[\Delta APB\]
We know that the formula of cosine rule of a following triangle as

The cosine rule of above triangle is given as
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}}{2ac}\]
By using the cosine rule to angle \[\angle ABP\] of triangle \[\Delta APB\] then we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}+B{{P}^{2}}-A{{P}^{2}}}{2AB\times BP}......equation(ii)\]
We know that the cosine ratio of right angled triangle is given as
\[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{Adjacent}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
By using this cosine ratio to triangle \[\Delta ABC\] then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \theta =\dfrac{AB}{3x} \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the required values in equation (ii) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AB}{3x}=\dfrac{A{{B}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-9}{2\times AB\times x} \\
& \Rightarrow 2A{{B}^{2}}=3A{{B}^{2}}+3{{x}^{2}}-27 \\
& \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}=27-3{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us consider the triangle \[\Delta ACQ\]
By using the cosine rule at the angle of vertex C then we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}+C{{Q}^{2}}-A{{Q}^{2}}}{2\times AC\times CQ}.....equation(iii)\]
By using the cosine ratio of right angled triangle \[\Delta ABC\] we get
\[\Rightarrow \cos \left( {{90}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)=\dfrac{AC}{BC}\]
By substituting the required values in equation (iii) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{AC}{3x}=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}-16}{2\times AC\times x} \\
& \Rightarrow 2A{{C}^{2}}=3A{{C}^{2}}+3{{x}^{2}}-48 \\
& \Rightarrow A{{C}^{2}}=48-3{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by substituting the required values in the equation (i) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( 27-3{{x}^{2}} \right)+\left( 48-3{{x}^{2}} \right)=9{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 15{{x}^{2}}=75 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us find the value of BC as follows
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow BC=3x \\
& \Rightarrow BC=3\sqrt{5} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore we can conclude that the value of side BC is \[3\sqrt{5}\]
So, option (a) is the correct answer.
Note:
We need to note that any of the line segments AP and AQ is not perpendicular to side BC.
Students may do a mistake and consider that
\[\Rightarrow AP\bot BC\text{ or }AQ\bot BC\]
This gives the wrong answer because we cannot judge by seeing the figure.
Considering anyone is also wrong.
So, we need to use the properties of triangles that are cosine rule or sine rule to get the required answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




