
Why is the tosylate anion a good leaving group?
Answer
490.8k+ views
Hint: Tosylate is the anion formed from tosylic acid. The other name of tosylic acid is p-toluenesulfonic acid. The conjugate base of tosylic acid is tosylate. It is toluene with a sulfonate group attached to it on the fourth position.
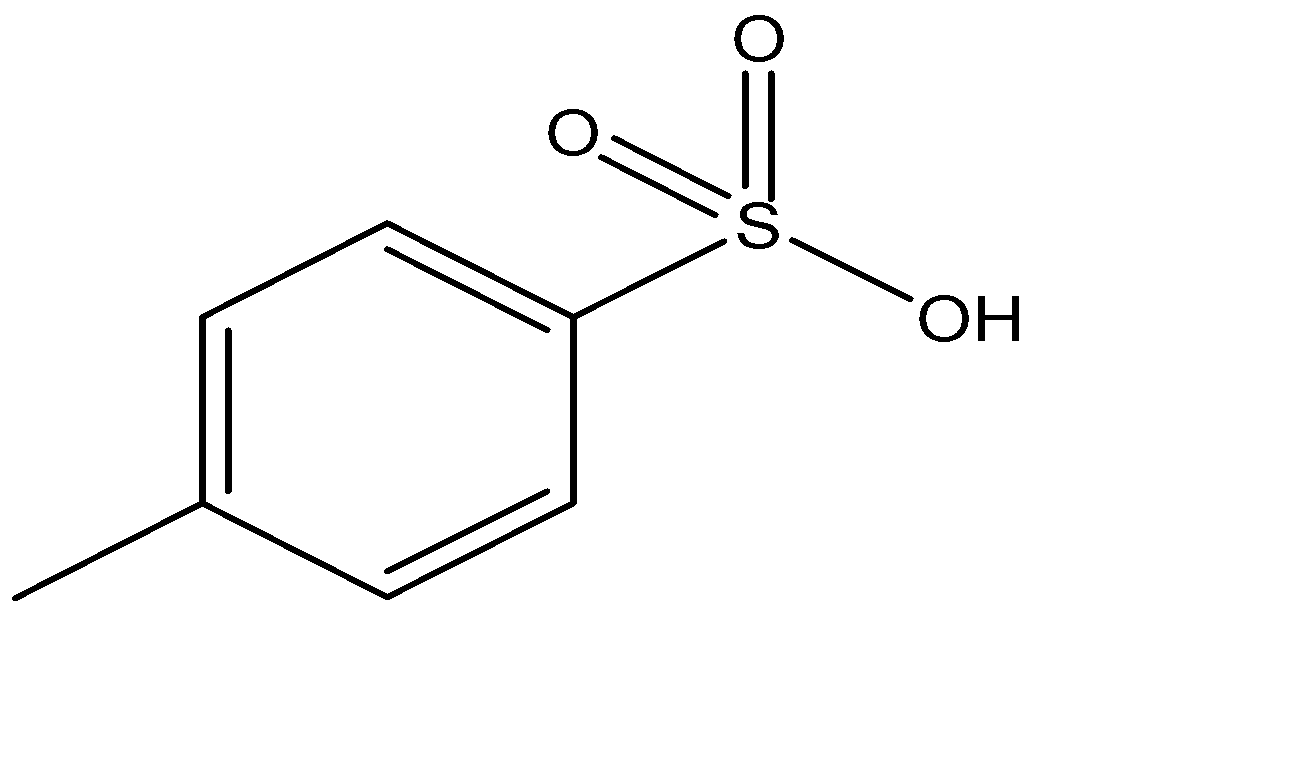
The tosylate group is large and has low $pK_a$ values, making it a good leaving group. A common tosyl compound is tosyl chloride.
Complete answer:
We have learnt earlier that; resonance stabilized structures are weak bases. Therefore, the leaving groups that form resonance stabilized structures upon leaving form excellent leaving groups. Alkyl sulphates and sulphonates make excellent leaving groups because of this. Tosylate anion also forms stabilized resonance structure on leaving and hence is an excellent leaving group.
The transformation of alcohol to sulfonic ester using para-toluene sulphonyl chloride (Ts-Cl), creates an organic tosylate ion. The reaction can be shown as:
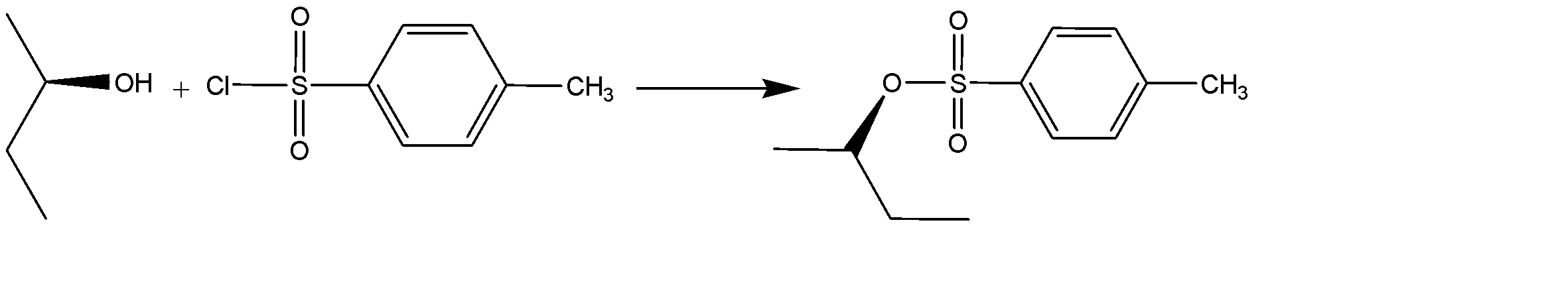
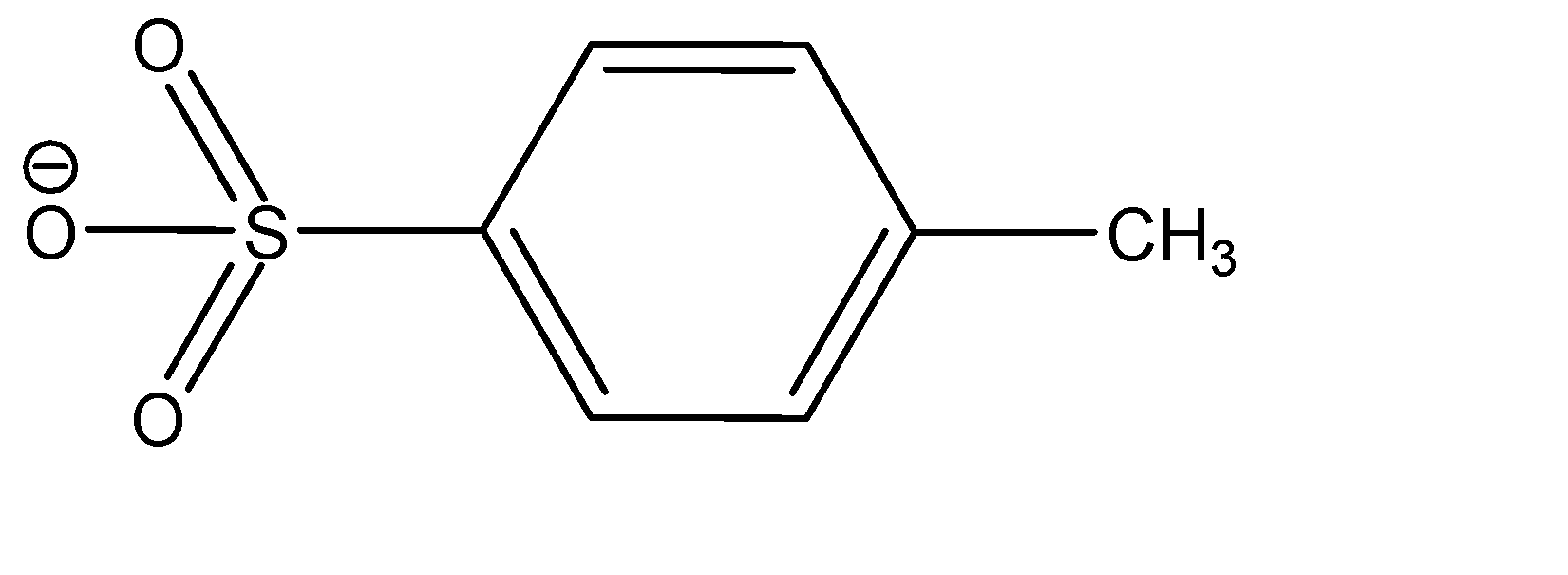
Notice that the conversion of alcohol to alcohol to tosylate proceeds via a retention of configuration. The tosylates/mesylates are excellent leaving groups in Nucleophilic substitution reactions, because of the resonance delocalization due to development of negative charge on the leaving oxygen. The tosylate ion formed during nucleophilic substitution reaction is:
The resonance stabilization can be shown as:
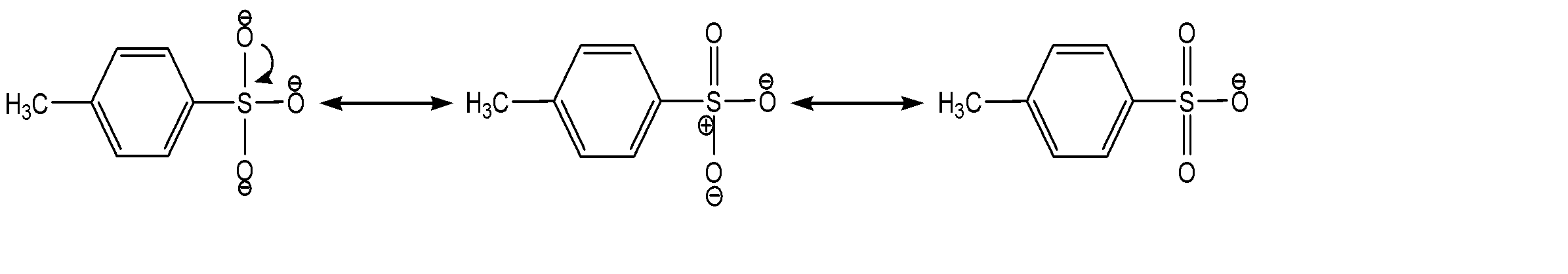
Therefore, due to resonance stabilization, it becomes an excellent leaving group.
Note:
The laboratory synthesis of isopentyl diphosphate, the building block of the molecule used for constructing isoprenoid molecules such as cholesterol, etc was accomplished by conversion of alcohol to organic tosylate, and then displacing the tosylate group with inorganic pyrophosphate nucleophile.

The tosylate group is large and has low $pK_a$ values, making it a good leaving group. A common tosyl compound is tosyl chloride.
Complete answer:
We have learnt earlier that; resonance stabilized structures are weak bases. Therefore, the leaving groups that form resonance stabilized structures upon leaving form excellent leaving groups. Alkyl sulphates and sulphonates make excellent leaving groups because of this. Tosylate anion also forms stabilized resonance structure on leaving and hence is an excellent leaving group.
The transformation of alcohol to sulfonic ester using para-toluene sulphonyl chloride (Ts-Cl), creates an organic tosylate ion. The reaction can be shown as:

Notice that the conversion of alcohol to alcohol to tosylate proceeds via a retention of configuration. The tosylates/mesylates are excellent leaving groups in Nucleophilic substitution reactions, because of the resonance delocalization due to development of negative charge on the leaving oxygen. The tosylate ion formed during nucleophilic substitution reaction is:

The resonance stabilization can be shown as:

Therefore, due to resonance stabilization, it becomes an excellent leaving group.
Note:
The laboratory synthesis of isopentyl diphosphate, the building block of the molecule used for constructing isoprenoid molecules such as cholesterol, etc was accomplished by conversion of alcohol to organic tosylate, and then displacing the tosylate group with inorganic pyrophosphate nucleophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




