
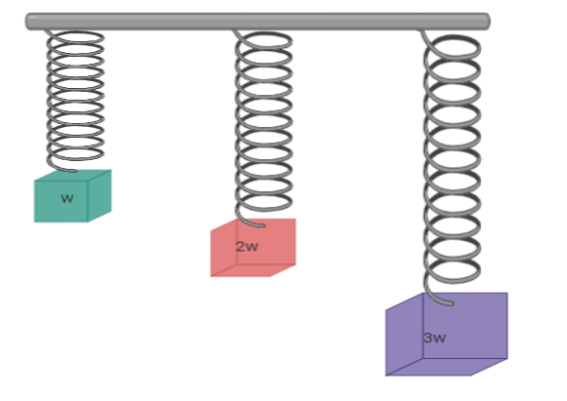
Three weights $w$, $2w$, \[3w\] are connected to identical springs suspended from a rigid horizontal rod. The assembly of the rod and weights falls freely. The positions of the weight from the rod are such that
A. $3w$ will be farthest
B. $w$ will be farthest
C. All will be at the same distance
D. $2w$ will be farthest
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint:When a body freely falls, It’s apparent weight becomes zero. This is due to the Pseudo force. This effect was first explained by Newton.
Pseudo Force:- A Pseudo force is an apparent force that acts on all masses whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of the reference frame.
Pseudo Force ${F_p}$ = m (mass of object) $\times$ a(acceleration of noninertial frame)
Non-Inertial Frame:-A non-inertial reference frame is a frame of reference that is undergoing acceleration with respect to an inertial frame. An accelerometer at rest in a non-inertial frame will, in general, detect a non-zero acceleration.

Complete step by step solution:
When the whole assembly is in rest, springs will be in the stretched position.
$Spring{\text{ }}Force{F_s} = kx$
Where , $k = $ Stiffness of springs
$x = $ Elongation in spring
As we can see,
$x \propto {F_s}$
In our case
${F_s} = $ Weight of body
So $x\left( {elongation} \right)$ will be more for $3w$.
Now when assembly falls freely with gravitational acceleration. A pseudo force will act on all bodies.
So, the
Pseudo Force ${F_p}$ = m(mass of body) $\times g$
(Note:- Assembly is falling with gravitational acceleration)
And
$m\left( {mass{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}body} \right) = \dfrac{{weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}body}}{g}$
So,
${F_p} = \left( {\dfrac{{weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}body}}{g} \times g} \right)$
Finally
${F_p} = $ Weight of body
From Free body diagram of the body
The resultant force on spring
${F_s} = \left( {Weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}body - {F_p}} \right)$
${F_s} = 0$
So there will be no force acting on spring. Spring will come in an unstretched position.
Now when all the springs are identical. So all springs will be at the same level and all the weights will be at equal distances from the rod.
So our option (C) is the right answer.
Note:The whole assembly is falling freely. So all weights are weightless during free fall. As there is no weight and also there will be no force on springs. Springs will be unstretched and all weights will be at the same level.
Pseudo Force:- A Pseudo force is an apparent force that acts on all masses whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of the reference frame.
Pseudo Force ${F_p}$ = m (mass of object) $\times$ a(acceleration of noninertial frame)
Non-Inertial Frame:-A non-inertial reference frame is a frame of reference that is undergoing acceleration with respect to an inertial frame. An accelerometer at rest in a non-inertial frame will, in general, detect a non-zero acceleration.

Complete step by step solution:
When the whole assembly is in rest, springs will be in the stretched position.
$Spring{\text{ }}Force{F_s} = kx$
Where , $k = $ Stiffness of springs
$x = $ Elongation in spring
As we can see,
$x \propto {F_s}$
In our case
${F_s} = $ Weight of body
So $x\left( {elongation} \right)$ will be more for $3w$.
Now when assembly falls freely with gravitational acceleration. A pseudo force will act on all bodies.

So, the
Pseudo Force ${F_p}$ = m(mass of body) $\times g$
(Note:- Assembly is falling with gravitational acceleration)
And
$m\left( {mass{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}body} \right) = \dfrac{{weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}body}}{g}$
So,
${F_p} = \left( {\dfrac{{weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}body}}{g} \times g} \right)$
Finally
${F_p} = $ Weight of body
From Free body diagram of the body
The resultant force on spring
${F_s} = \left( {Weight{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}body - {F_p}} \right)$
${F_s} = 0$
So there will be no force acting on spring. Spring will come in an unstretched position.
Now when all the springs are identical. So all springs will be at the same level and all the weights will be at equal distances from the rod.
So our option (C) is the right answer.
Note:The whole assembly is falling freely. So all weights are weightless during free fall. As there is no weight and also there will be no force on springs. Springs will be unstretched and all weights will be at the same level.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




