
Thiosulfuric acid is ______________
(a)- ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
(b)- ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
(c)- ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$
(d)- ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}$
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Thiosulfuric acid is an oxoacid of the element of sulfur. There are 2 sulfur atoms in thiosulfuric acid. One sulfur atom is +6 oxidation state and the other is in -2 oxidation state.
Complete step by step answer:
Sulfur is the element of group 16 and it forms several oxoacids. Some oxoacids of sulphur are ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$, ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$, ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}$ etc. Some of the oxoacids are unstable and hence cannot be isolated. They are known only in aqueous solutions or in the form of their salts.
Thiosulfuric acid is an oxoacid of sulfur. Its formula is ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$. There are 2 sulfur atoms in the thiosulfuric acid.
The structure of thiosulfuric acid is given below:
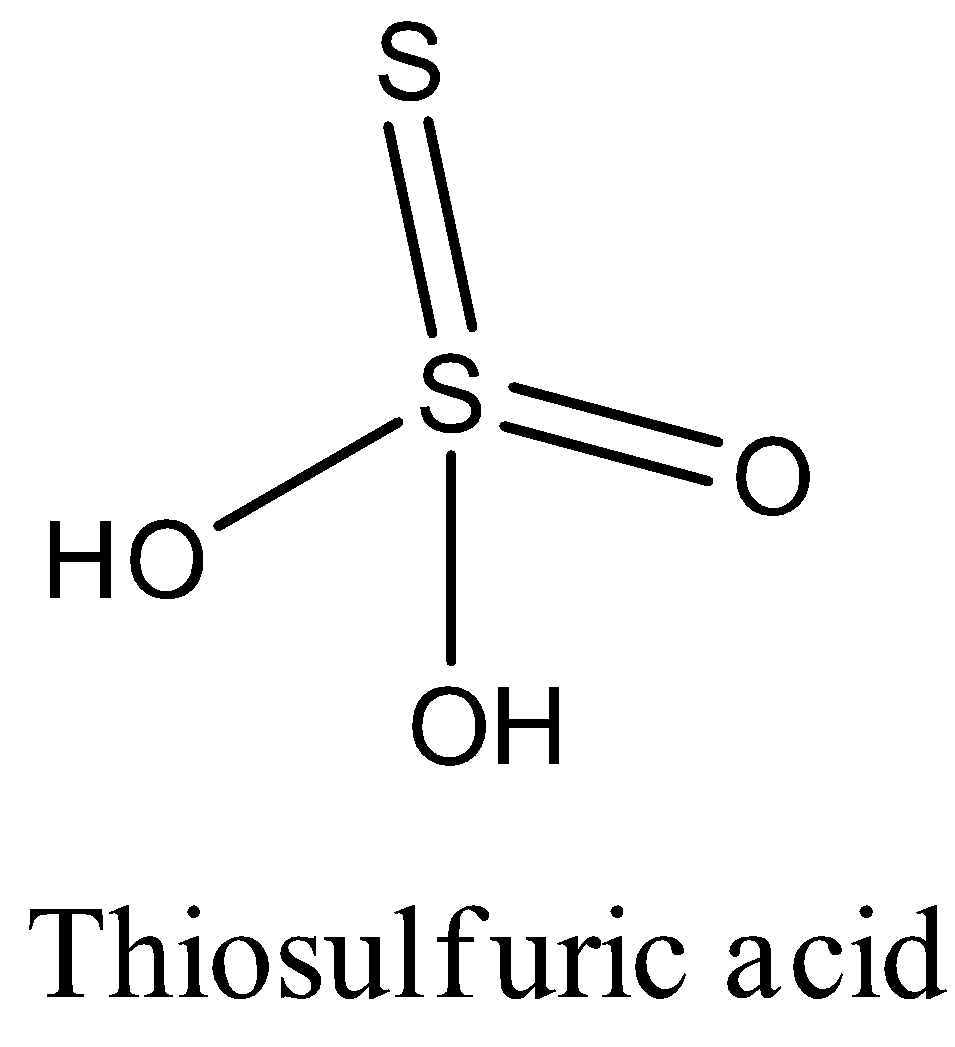
Since, there are two sulfur atoms in thiosulfuric acid, the oxidation state of both the sulfur atoms is different.
The sulfur atom which is in the middle has an oxidation state +6. And the sulfur which is attached to the central sulfur atom has a -2 oxidation state.
It readily decomposes in water.
The molecular mass of thiosulfuric acid is $114.14\text{ g/mol}$
Based on the exact reaction conditions, there are several products formed, these are sulfur, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, polysulfanes, sulfuric acid, and polythionates.
The different methods of formation of thiosulfuric acid are as follows:
(i)- By reacting ${{H}_{2}}S$ and $S{{O}_{3}}$.
${{H}_{2}}S+S{{O}_{3}}\to {{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
(ii)- By the action of hydrochloric acid on $N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
$N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
(iii)- By reacting hydrogen sulfide with $HS{{O}_{3}}Cl$
$HS{{O}_{3}}Cl+{{H}_{2}}S\to HCl+{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The thiosulfuric acid is kept at a very low temperature because it decomposes readily. It even decomposes at -5 degrees Celsius. On decomposition, it forms hydrogen sulfide and sulfur trioxide.
${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}\to {{H}_{2}}S+S{{O}_{3}}$
Complete step by step answer:
Sulfur is the element of group 16 and it forms several oxoacids. Some oxoacids of sulphur are ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$, ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$, ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{5}}$ etc. Some of the oxoacids are unstable and hence cannot be isolated. They are known only in aqueous solutions or in the form of their salts.
Thiosulfuric acid is an oxoacid of sulfur. Its formula is ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$. There are 2 sulfur atoms in the thiosulfuric acid.
The structure of thiosulfuric acid is given below:

Since, there are two sulfur atoms in thiosulfuric acid, the oxidation state of both the sulfur atoms is different.
The sulfur atom which is in the middle has an oxidation state +6. And the sulfur which is attached to the central sulfur atom has a -2 oxidation state.
It readily decomposes in water.
The molecular mass of thiosulfuric acid is $114.14\text{ g/mol}$
Based on the exact reaction conditions, there are several products formed, these are sulfur, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, polysulfanes, sulfuric acid, and polythionates.
The different methods of formation of thiosulfuric acid are as follows:
(i)- By reacting ${{H}_{2}}S$ and $S{{O}_{3}}$.
${{H}_{2}}S+S{{O}_{3}}\to {{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
(ii)- By the action of hydrochloric acid on $N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
$N{{a}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+2HCl\to 2NaCl+{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
(iii)- By reacting hydrogen sulfide with $HS{{O}_{3}}Cl$
$HS{{O}_{3}}Cl+{{H}_{2}}S\to HCl+{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The thiosulfuric acid is kept at a very low temperature because it decomposes readily. It even decomposes at -5 degrees Celsius. On decomposition, it forms hydrogen sulfide and sulfur trioxide.
${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}\to {{H}_{2}}S+S{{O}_{3}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




