
Thermolabile protein part of enzyme is?
A.Apoenzyme
B.Proenzyme
C.Holoenzyme
D.Isoenzyme
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Enzymes are biological molecules (typically proteins) that significantly speed up the rate of virtually all of the chemical reactions that take place within cells. They are indispensable forever and serve a wide scope of significant capacities in the body, for example, helping in absorption and digestion.
Complete answer:
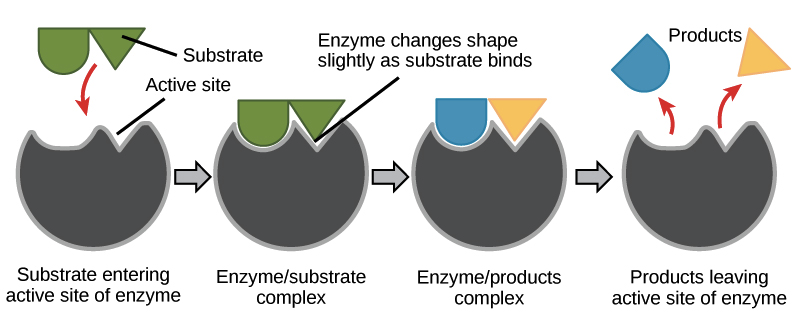
Some enzymes help break large molecules into smaller pieces that are more easily absorbed by the body. Other enzymes help bind two molecules together to produce a new molecule Different compounds help tie two atoms together to create another particle. Proteins are profoundly particular impetuses, implying that every compound just accelerates a particular response to the atoms that a catalyst works with are called substrates.
The substrates tie to a locale on the catalyst called the dynamic site. Two hypotheses are clarifying the compound substrate collaboration. In the lock-and-key model, the dynamic site of a catalyst is correctly formed to hold explicit substrates. In the actuated fit model, the dynamic site and substrate don't fit entirely together; rather, the two of them modify their shape to an interface.
Whatever the case, the responses that happen quicken significantly — over a million-fold — when the substrates tie to the dynamic site of the protein. The compound responses bring about another item or particle that at that point isolates from the chemical, which proceeds to catalyze different responses.
Hence the correct answer is OPTION(A)
Note: When the point when the protein part of the form protein or holoenzyme. It is composed of amino acids. It participates in the reactant movement of the protein. It is heat touchy. It works just at the ideal temperature. It gets latent at high temperature or low temperature.
Complete answer:
Some enzymes help break large molecules into smaller pieces that are more easily absorbed by the body. Other enzymes help bind two molecules together to produce a new molecule Different compounds help tie two atoms together to create another particle. Proteins are profoundly particular impetuses, implying that every compound just accelerates a particular response to the atoms that a catalyst works with are called substrates.
The substrates tie to a locale on the catalyst called the dynamic site. Two hypotheses are clarifying the compound substrate collaboration. In the lock-and-key model, the dynamic site of a catalyst is correctly formed to hold explicit substrates. In the actuated fit model, the dynamic site and substrate don't fit entirely together; rather, the two of them modify their shape to an interface.
Whatever the case, the responses that happen quicken significantly — over a million-fold — when the substrates tie to the dynamic site of the protein. The compound responses bring about another item or particle that at that point isolates from the chemical, which proceeds to catalyze different responses.

Hence the correct answer is OPTION(A)
Note: When the point when the protein part of the form protein or holoenzyme. It is composed of amino acids. It participates in the reactant movement of the protein. It is heat touchy. It works just at the ideal temperature. It gets latent at high temperature or low temperature.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




