
The working principle of the spring balance is
A). Newton’s laws of motion
B). Hooke's law
C). Ohm’s law
D). None of the above
Answer
603.9k+ views
Hint: Imagine a spring is expanding or compressing due to the presence of external force. We will feel an opposition to obtain the equilibrium state of the spring. This opposing force is exactly equal to the external force on the spring. Using this concept, we measure with the help of spring balance.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The spring can either be extended or compressed by applying an external force on it. When we apply an external force on spring it will produce an opposite balancing force to keep the spring in stable condition. For the same distance of extension and compression, the balancing force produced by the spring will be the same.
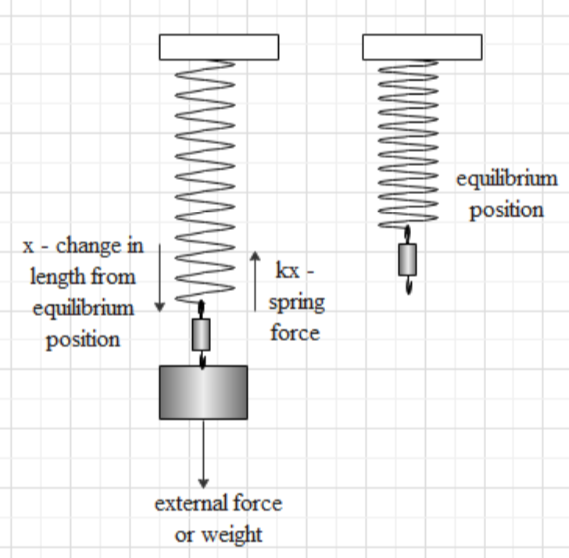
Suppose to extend the spring at X distance and external force applied is ${{\text{F}}_{\text{ext}}}$. The spring will produce an opposite balancing force to keep the spring stable is ${{\text{F}}_{\text{bal}}}$.
${{F}_{bal}}\propto X$
${{F}_{bal}}=kX$
A balanced condition
${{\text{F}}_{\text{ext}}}\text{=}{{\text{F}}_{\text{bal}}}$
${{F}_{ext}}=k{{X}^{{}}}$ ………..(i)
Where, $k=$ proportionality constant called the spring constant.
The last equation is called the hooke's equation. For various, the distance applied force should be varied too.
Note: In this question, students will be confused between two option (A) newton’s laws of motion and option (B) hooke's laws. Because spring is part of the mechanics of physics and in the mechanics part mainly newton’s laws of motion are used. But, if you remember the equation of the spring balance you can eliminate the option(A).
The option(C) ohm’s laws, we know that this law is part of electrical physics so we will eliminate this because our question is from mechanics physics.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The spring can either be extended or compressed by applying an external force on it. When we apply an external force on spring it will produce an opposite balancing force to keep the spring in stable condition. For the same distance of extension and compression, the balancing force produced by the spring will be the same.

Suppose to extend the spring at X distance and external force applied is ${{\text{F}}_{\text{ext}}}$. The spring will produce an opposite balancing force to keep the spring stable is ${{\text{F}}_{\text{bal}}}$.
${{F}_{bal}}\propto X$
${{F}_{bal}}=kX$
A balanced condition
${{\text{F}}_{\text{ext}}}\text{=}{{\text{F}}_{\text{bal}}}$
${{F}_{ext}}=k{{X}^{{}}}$ ………..(i)
Where, $k=$ proportionality constant called the spring constant.
The last equation is called the hooke's equation. For various, the distance applied force should be varied too.
Note: In this question, students will be confused between two option (A) newton’s laws of motion and option (B) hooke's laws. Because spring is part of the mechanics of physics and in the mechanics part mainly newton’s laws of motion are used. But, if you remember the equation of the spring balance you can eliminate the option(A).
The option(C) ohm’s laws, we know that this law is part of electrical physics so we will eliminate this because our question is from mechanics physics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




