
The working of a common balance and physical balance is used on the basis of "Principle of moments". A meter scale of uniform density is being balanced at the centre. If a mass of $2kg$ is suspended at an edge of the scale, then what should be suspended on other side at ${{\dfrac{1}{4}}^{th}}$ length of the scale to maintain the horizontal position of the scale?
$\begin{align}
& A.400kg \\
& B.40kg \\
& C.4kg \\
& D.2kg \\
\end{align}$
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: A beam balance is working on basis of the principle of moments according to which in the equilibrium, the anti-clockwise moment because of the weight of an object on left pan of the beam is similar to the clockwise moment because of to the standard weights on the right pan of the beam.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all let us discuss the principle of moments at first. The principle of moments states that if in equilibrium the total sum of the anti-clockwise moment is equivalent to the total sum of the clockwise moment.
The equation of the principle of moment is given as,
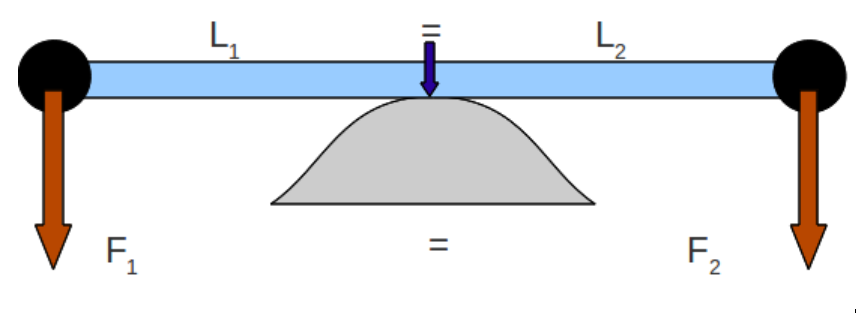
${{F}_{1}}\times {{L}_{1}}={{F}_{2}}\times {{L}_{2}}$
In which the force is given as the gravitational force,
Therefore,
${{w}_{1}}\times {{L}_{1}}={{w}_{2}}\times {{L}_{2}}$
That is,
${{m}_{1}}\times g\times {{L}_{1}}={{m}_{2}}\times g\times {{L}_{2}}$
Simplifying,
${{m}_{1}}\times {{L}_{1}}={{m}_{2}}\times {{L}_{2}}$
Here $m$ is the mass and $L$is the length of the scale in which equilibrium is attained.
${{L}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Substituting the values will give,
$\begin{align}
& 2\times \dfrac{1}{2}={{m}_{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{4} \\
& {{m}_{2}}=4kg \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
When a system is in stability or balance, then it is said to be in equilibrium as all the forces experiencing on the system cancel each other out. Common balance is defined as the balance which is having each arm as suspended. The unknown mass is kept in one arm and the known mass in another until they both become equivalent. Therefore this balance is working on the principle of moment of weights. When the weights are being balanced, equilibrium is attained.
Complete step by step answer:
First of all let us discuss the principle of moments at first. The principle of moments states that if in equilibrium the total sum of the anti-clockwise moment is equivalent to the total sum of the clockwise moment.
The equation of the principle of moment is given as,
${{F}_{1}}\times {{L}_{1}}={{F}_{2}}\times {{L}_{2}}$
In which the force is given as the gravitational force,
Therefore,
${{w}_{1}}\times {{L}_{1}}={{w}_{2}}\times {{L}_{2}}$
That is,
${{m}_{1}}\times g\times {{L}_{1}}={{m}_{2}}\times g\times {{L}_{2}}$
Simplifying,
${{m}_{1}}\times {{L}_{1}}={{m}_{2}}\times {{L}_{2}}$
Here $m$ is the mass and $L$is the length of the scale in which equilibrium is attained.
${{L}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Substituting the values will give,
$\begin{align}
& 2\times \dfrac{1}{2}={{m}_{2}}\times \dfrac{1}{4} \\
& {{m}_{2}}=4kg \\
\end{align}$

So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
When a system is in stability or balance, then it is said to be in equilibrium as all the forces experiencing on the system cancel each other out. Common balance is defined as the balance which is having each arm as suspended. The unknown mass is kept in one arm and the known mass in another until they both become equivalent. Therefore this balance is working on the principle of moment of weights. When the weights are being balanced, equilibrium is attained.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




