
The well known compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid, have the same molecular formula, \[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]. The correct relationship between them is:
A. Constitutional isomerism
B. Geometrical isomerism
C. Identicalness
D. Optical isomerism
Answer
577.5k+ views
Hint: Compounds having the same molecular formula but different physical and chemical properties due to different arrangements of atoms within their molecules are called isomers of each other. Draw the structures of compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid. Determine the type of isomerism based on the arrangement of the atom.
Step by step answer: The structures of compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid are as follows:
The molecular formula of lactic acid given to us is
\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\].
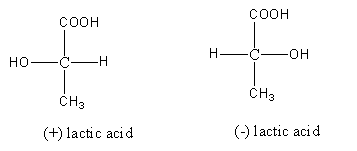
Constitutional isomers are the type of isomers having the same molecular formula but different connectivity of bonded atoms.
So, compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid are not constitutional isomers as in both the structure the same groups (\[{\text{OH, H, C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ and COOH}}\]) are bonded to the same carbon.
So, option (A) Constitutional isomerism is an incorrect answer.
The isomers which possess the same structural formula but differ in the spatial arrangement of the groups around the double bond are called geometrical isomerism. As lactic acid does not have a double bond so it can not show geometrical isomerism.
So, option (B) Geometrical isomerism is an incorrect answer.
As compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid are not identical they are mirror images of each other so option (C) Identicalness is an incorrect answer
Isomerism arises from the different arrangements of atoms or groups in three-dimensional spaces resulting in two isomers which are mirror images of each other known as optical isomers of each other.
Optical isomers have similar physical and chemical properties but differ in their behavior towards plane polarised light. The isomer which rotates the plane polarized light towards the left is denoted by a negative sign and the isomer which rotates the plane polarized light towards the right is denoted by a positive sign.
So, compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid are optical isomers.
Thus, the correct option is (D) Optical isomerism
Note: Only compounds containing double bonds show geometrical isomerism. Due to different connectivity of atoms or group constitutional isomers have different physical and chemical properties. Physical and chemical properties optical isomers are the same only they rotate plane polarised light in a different direction.
Step by step answer: The structures of compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid are as follows:
The molecular formula of lactic acid given to us is
\[{{\text{C}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\].

Constitutional isomers are the type of isomers having the same molecular formula but different connectivity of bonded atoms.
So, compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid are not constitutional isomers as in both the structure the same groups (\[{\text{OH, H, C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ and COOH}}\]) are bonded to the same carbon.
So, option (A) Constitutional isomerism is an incorrect answer.
The isomers which possess the same structural formula but differ in the spatial arrangement of the groups around the double bond are called geometrical isomerism. As lactic acid does not have a double bond so it can not show geometrical isomerism.
So, option (B) Geometrical isomerism is an incorrect answer.
As compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid are not identical they are mirror images of each other so option (C) Identicalness is an incorrect answer
Isomerism arises from the different arrangements of atoms or groups in three-dimensional spaces resulting in two isomers which are mirror images of each other known as optical isomers of each other.
Optical isomers have similar physical and chemical properties but differ in their behavior towards plane polarised light. The isomer which rotates the plane polarized light towards the left is denoted by a negative sign and the isomer which rotates the plane polarized light towards the right is denoted by a positive sign.
So, compounds (+) –lactic acid and (-) –lactic acid are optical isomers.
Thus, the correct option is (D) Optical isomerism
Note: Only compounds containing double bonds show geometrical isomerism. Due to different connectivity of atoms or group constitutional isomers have different physical and chemical properties. Physical and chemical properties optical isomers are the same only they rotate plane polarised light in a different direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




