
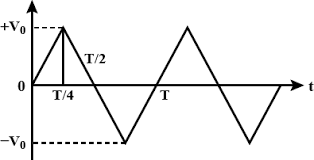
The voltage time (V-t) graph for triangular waves having peak value ${V}_{0}$ is as shown in figure. The rms value of V in time interval from t=0 to $\dfrac { T }{ 4 }$ is:
A. $\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \sqrt { 3 } }$
B. $\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ 2 }$
C. $\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \sqrt { 2 } }$
D. None of these

Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: We have to calculate rms value of voltage. As the name itself explains, rms voltage is calculated by taking the square root of the mean average of the square of the voltage in an appropriately chosen time interval which is already mentioned in the question. Substitute the values in the rms formula and calculate the rms value of V in a time interval from t=0 to $\dfrac { T }{ 4 }$.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Peak value of the triangular wave is ${V}_{0}$
For t=0 to $\dfrac { T }{ 4 }$,
$\dfrac { V }{ t } =\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 }-0 }{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } -0 }$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac { V }{ t } =\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }$
$\Rightarrow V=\dfrac { 4{ { V }_{ 0 } } }{ { T }_{ 0 } } t$
RMS value is given by,
${ V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { \int _{ 0 }^{ T }{ { V }^{ 2 }dt } }{ T } }$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
${ V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { \int _{ 0 }^{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }{ { \left( \dfrac { 4{ V }_{ 0 } }{ T } t \right) }^{ 2 }dt } }{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } } }$
$\Rightarrow { V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { \dfrac { 16{ V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ { T }^{ 2 } } \int _{ 0 }^{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }{ { t }^{ 2 }dt } }{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } } }$
$\Rightarrow { V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { 64{ V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ { T }^{ 3 } } \int _{ 0 }^{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }{ { t }^{ 2 }dt } }$
$\Rightarrow { V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { 64{ V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ { T }^{ 3 } } \int _{ 0 }^{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }{ \cfrac { { t }^{ 3 } }{ 3 } } }$
${ \Rightarrow V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { 64{ V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ { T }^{ 3 } } \times \dfrac { 1 }{ 3 } \left( \dfrac { { T }^{ 3 } }{ 64 } \right) }$
${ \Rightarrow V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { { V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ 3 } }$
${ \therefore V }_{ rms }=\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \sqrt {3} }$
Thus, the rms value of V in time interval from t=0 to $\dfrac { T }{ 4 }$ is $\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \sqrt { 3 } }$
Hence, the correct answer is option A i.e. $\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \sqrt { 3 } }.$
Note:
RMS value of a half wave rectifier wave is the least as compared to other waveforms with the same peak value. RMS value for triangular, saw-tooth and sinusoidal waveforms is greater as compared to half-wave rectifiers but lesser than that of the square wave. Square wave has the highest RMS value as compared to all the other waveforms.
Complete step by step answer:
Given: Peak value of the triangular wave is ${V}_{0}$
For t=0 to $\dfrac { T }{ 4 }$,
$\dfrac { V }{ t } =\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 }-0 }{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } -0 }$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac { V }{ t } =\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }$
$\Rightarrow V=\dfrac { 4{ { V }_{ 0 } } }{ { T }_{ 0 } } t$
RMS value is given by,
${ V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { \int _{ 0 }^{ T }{ { V }^{ 2 }dt } }{ T } }$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
${ V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { \int _{ 0 }^{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }{ { \left( \dfrac { 4{ V }_{ 0 } }{ T } t \right) }^{ 2 }dt } }{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } } }$
$\Rightarrow { V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { \dfrac { 16{ V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ { T }^{ 2 } } \int _{ 0 }^{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }{ { t }^{ 2 }dt } }{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } } }$
$\Rightarrow { V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { 64{ V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ { T }^{ 3 } } \int _{ 0 }^{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }{ { t }^{ 2 }dt } }$
$\Rightarrow { V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { 64{ V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ { T }^{ 3 } } \int _{ 0 }^{ \dfrac { T }{ 4 } }{ \cfrac { { t }^{ 3 } }{ 3 } } }$
${ \Rightarrow V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { 64{ V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ { T }^{ 3 } } \times \dfrac { 1 }{ 3 } \left( \dfrac { { T }^{ 3 } }{ 64 } \right) }$
${ \Rightarrow V }_{ rms }=\sqrt { \dfrac { { V }_{ 0 }^{ 2 } }{ 3 } }$
${ \therefore V }_{ rms }=\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \sqrt {3} }$
Thus, the rms value of V in time interval from t=0 to $\dfrac { T }{ 4 }$ is $\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \sqrt { 3 } }$
Hence, the correct answer is option A i.e. $\dfrac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ \sqrt { 3 } }.$
Note:
RMS value of a half wave rectifier wave is the least as compared to other waveforms with the same peak value. RMS value for triangular, saw-tooth and sinusoidal waveforms is greater as compared to half-wave rectifiers but lesser than that of the square wave. Square wave has the highest RMS value as compared to all the other waveforms.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




