
The vertices of a triangle are \[A=(0,0)\] , \[B=(0,2)\] and \[C=(2,0)\] then find the distance between its orthocenter and circumcenter.
1. \[0\]
2. \[\sqrt{2}\]
3. \[\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
4. None of these
Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: First of all we will make a figure with the help of the vertices of the triangle \[ABC\] then we will find out the midpoint \[X\] of \[BC\] as \[X\] is the circumcenter of the triangle and \[A\] is the orthocenter of the triangle after that find the distance between orthocenter and circumcenter to check the correct option.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that a closed figure formed by three intersecting lines is called a triangle where tri means three as the triangle has three sides, three angles and three vertices.
The orthocenter is the point of intersection of three heights of a triangle and the circumcenter is the point of intersection of the three perpendicular bisectors. The circumcenter is the center of a triangle’s circumcircle.
In a triangle the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the third angle and a triangle is a two dimensional figure.
To calculate the midpoint find the exact centre point between two defined points in a line segment. We may use the following formula to calculate the midpoint that bisects the line segment
\[\text{Midpoint=( }\dfrac{{{\text{x}}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2})\]
When we know the horizontal and vertical distance between two points we can calculate the distance of the straight line as the distance formula is based on Pythagoras theorem.
Now according to the question:
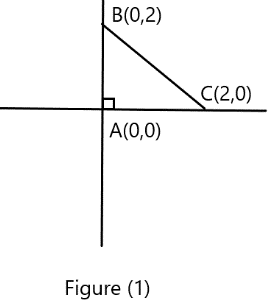
In the figure \[(1)\] we have given a right angle triangle \[ABC\] in which \[A=(0,0)\] , \[B=(0,2)\] and \[C=(2,0)\]
In right angle triangle circumcenter is the midpoint of hypotenuse hence our hypotenuse is \[BC\] according to figure \[(1)\]
Thus we will find out the midpoint of \[BC\] , shown in figure \[(2)\] :
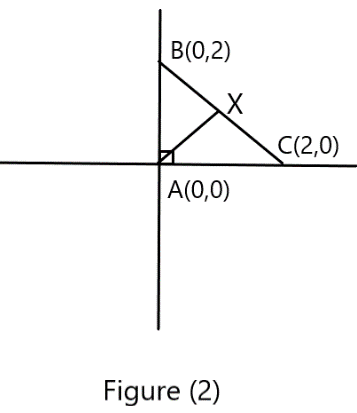
As we know that midpoint equals to \[(\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}),(\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2})\]
Here \[{{x}_{1}}=0,{{x}_{2}}=2\] and \[{{y}_{1}}=2,{{y}_{2}}=0\]
\[\Rightarrow (\dfrac{0+2}{2}),(\dfrac{2+0}{2})\]
\[\Rightarrow (1,1)\]
Hence \[X=(1,1)\]
Now we will find out the distance between orthocenter and circumcenter
In figure \[(2)\] you can see that \[A\] is the orthocenter because orthocenter is that point from which the right angle is made and \[X\] is the circumcenter.
Distance between orthocenter and circumcenter will be:
\[\Rightarrow XA=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}}\]
Where \[{{x}_{1}}=0,{{x}_{2}}=1\] and \[{{y}_{1}}=0,{{y}_{2}}=1\]
\[\Rightarrow XA=\sqrt{{{(1-0)}^{2}}+{{(1-0)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow XA=\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow XA=\sqrt{2}\]
Hence option \[(3)\] is correct as the distance between circumcenter and orthocenter is \[\sqrt{2}\] .
Note: Students must remember that no matter how the triangle is constructed, the sum of all the internal angles of a triangle is always \[{{180}^{\circ }}\] and you can split a triangle into two right triangles and the length of any side of a triangle is shorter than sum of the other two sides.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We know that a closed figure formed by three intersecting lines is called a triangle where tri means three as the triangle has three sides, three angles and three vertices.
The orthocenter is the point of intersection of three heights of a triangle and the circumcenter is the point of intersection of the three perpendicular bisectors. The circumcenter is the center of a triangle’s circumcircle.
In a triangle the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the third angle and a triangle is a two dimensional figure.
To calculate the midpoint find the exact centre point between two defined points in a line segment. We may use the following formula to calculate the midpoint that bisects the line segment
\[\text{Midpoint=( }\dfrac{{{\text{x}}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2})\]
When we know the horizontal and vertical distance between two points we can calculate the distance of the straight line as the distance formula is based on Pythagoras theorem.
Now according to the question:

In the figure \[(1)\] we have given a right angle triangle \[ABC\] in which \[A=(0,0)\] , \[B=(0,2)\] and \[C=(2,0)\]
In right angle triangle circumcenter is the midpoint of hypotenuse hence our hypotenuse is \[BC\] according to figure \[(1)\]
Thus we will find out the midpoint of \[BC\] , shown in figure \[(2)\] :

As we know that midpoint equals to \[(\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}),(\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2})\]
Here \[{{x}_{1}}=0,{{x}_{2}}=2\] and \[{{y}_{1}}=2,{{y}_{2}}=0\]
\[\Rightarrow (\dfrac{0+2}{2}),(\dfrac{2+0}{2})\]
\[\Rightarrow (1,1)\]
Hence \[X=(1,1)\]
Now we will find out the distance between orthocenter and circumcenter
In figure \[(2)\] you can see that \[A\] is the orthocenter because orthocenter is that point from which the right angle is made and \[X\] is the circumcenter.
Distance between orthocenter and circumcenter will be:
\[\Rightarrow XA=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}}\]
Where \[{{x}_{1}}=0,{{x}_{2}}=1\] and \[{{y}_{1}}=0,{{y}_{2}}=1\]
\[\Rightarrow XA=\sqrt{{{(1-0)}^{2}}+{{(1-0)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow XA=\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}+{{1}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow XA=\sqrt{2}\]
Hence option \[(3)\] is correct as the distance between circumcenter and orthocenter is \[\sqrt{2}\] .
Note: Students must remember that no matter how the triangle is constructed, the sum of all the internal angles of a triangle is always \[{{180}^{\circ }}\] and you can split a triangle into two right triangles and the length of any side of a triangle is shorter than sum of the other two sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Which are the three major ports of Tamil Nadu A Chennai class 10 social science CBSE

The highest dam in India is A Bhakra dam B Tehri dam class 10 social science CBSE

Describe the process of Unification of Italy class 10 social science CBSE




