
The variation of radial probability density ${R^2}\left( r \right)$ as a function of distance r of the electron from the nucleus for 3p- orbital.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall radial probability curves for various orbitals. Radial probability density curve helps us in finding the points in space with respect to the nucleus where the probability of finding electrons is maximum and also tells the points where the probability is zero. The points where the probability density of electrons is zero are known as nodes.
Formula used:
Number of radial nodes $ = n - l - 1$
Where, $n$ is the principal quantum number
And $l$ is the azimuthal quantum number
Complete step by step answer:
Probability density of finding an electron at a point can be defined as the probability per unit volume, with the limit that the volume is infinitesimally. Knowing this, we can define the radial probability distribution at a certain radius as the probability density of electrons in an infinitesimally thin spherical shell. Thus, we can say that radial probability distribution is a function of radial distance from the nucleus. The points where radial probability distribution is zero are called radial nodes.
We know that radial nodes in a given orbital are given by the formula,
Number of radial nodes$ = n - l - 1$.
We need to find the radial nodes for the $3p$orbital, which has the principal quantum number $n = 3$ and the azimuthal quantum number, $l = 1$
Using the formula, we get the number of radial nodes$ = 3 - 1 - 1 = 1$.
Thus, the variation of the radial probability density for $3p$ orbital can be given as,
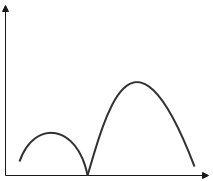
Note:
Apart from radial nodes, there is another type of node that exists in an atom. This is known as angular node. While radial nodes are spherical and at a fixed radius, the angular nodes are flat and at a fixed angle.
Formula used:
Number of radial nodes $ = n - l - 1$
Where, $n$ is the principal quantum number
And $l$ is the azimuthal quantum number
Complete step by step answer:
Probability density of finding an electron at a point can be defined as the probability per unit volume, with the limit that the volume is infinitesimally. Knowing this, we can define the radial probability distribution at a certain radius as the probability density of electrons in an infinitesimally thin spherical shell. Thus, we can say that radial probability distribution is a function of radial distance from the nucleus. The points where radial probability distribution is zero are called radial nodes.
We know that radial nodes in a given orbital are given by the formula,
Number of radial nodes$ = n - l - 1$.
We need to find the radial nodes for the $3p$orbital, which has the principal quantum number $n = 3$ and the azimuthal quantum number, $l = 1$
Using the formula, we get the number of radial nodes$ = 3 - 1 - 1 = 1$.
Thus, the variation of the radial probability density for $3p$ orbital can be given as,

Note:
Apart from radial nodes, there is another type of node that exists in an atom. This is known as angular node. While radial nodes are spherical and at a fixed radius, the angular nodes are flat and at a fixed angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




