
The value of the bond order of the C-O bond in ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ ion is:
(A.) 1.25
(B.) 1.33
(C.) 1.5
(D.) 1.0
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: To find the bond order of this ion, first, you need to figure out the bond formed by carbon atom in the general case and then divide it by the number of surrounding atoms. Now you have to figure out the correct answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Now let’s fiend the bond order of ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$
In the structure of ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ carbon is the least electronegative element, we place it in the central position:
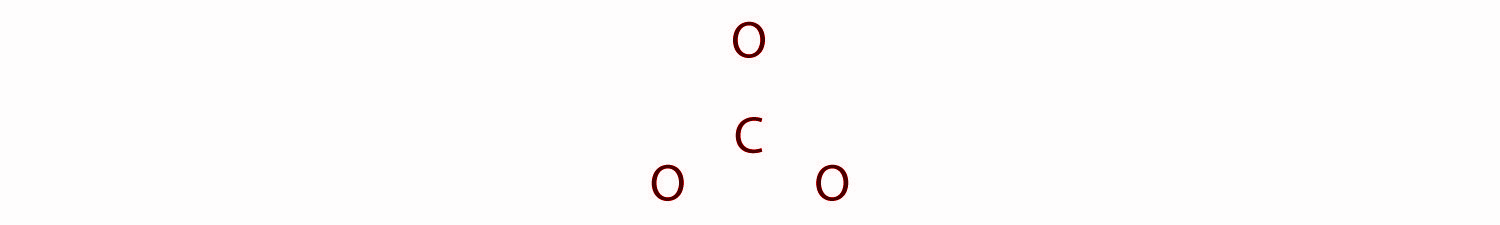
Here the Carbon atom has 4 valence electrons, each oxygen has 6 valence electrons, and there are 2 more for the −2 charge. This gives a total 4 + (3 × 6) + 2 = 24 valence electrons.
In this structure, six electrons are used to form three bonding pairs between the oxygen atoms and the carbon.
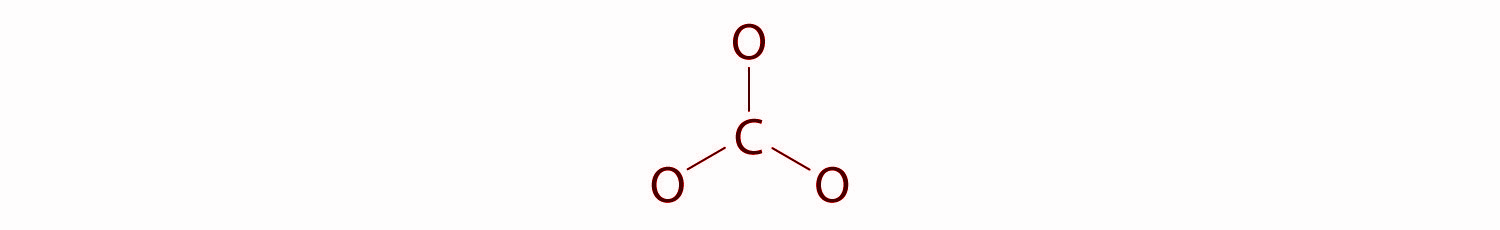
We will divide the remaining 18 electrons equally among the three oxygen atoms by placing three lone pairs on each and indicating the −2 charge on the complete structure.
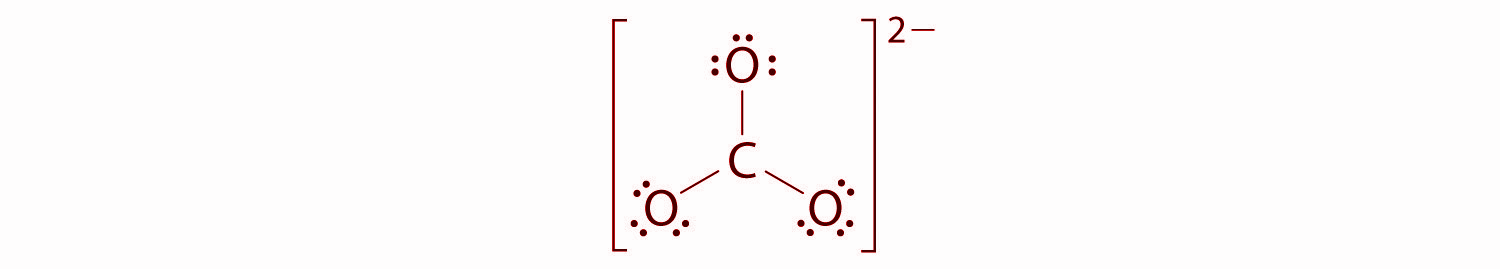
Hence, there are no electrons left for the central atom.
At this point, the carbon atom has only 6 valence electrons, so we must take one lone pair from oxygen and use it to form a carbon-oxygen double bond. There are three possible choices -
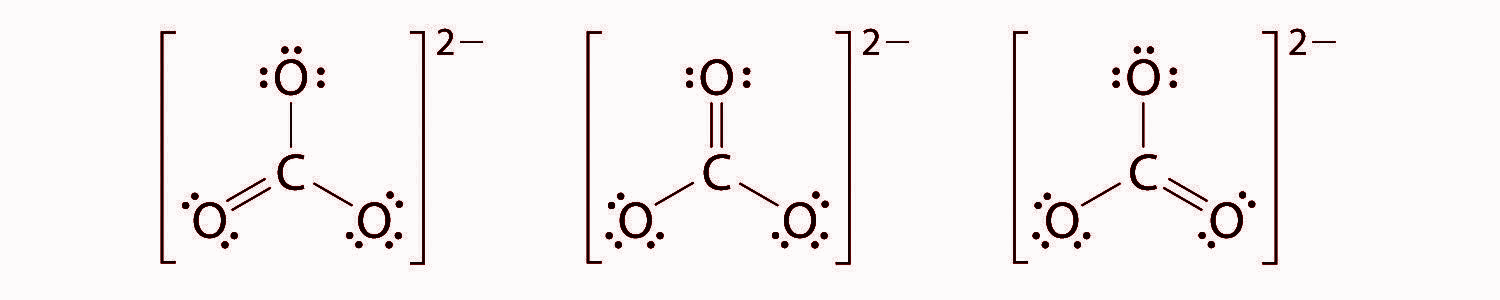
${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ has a total of three resonating structures and it has 4 bonds, The way to calculate the bond order for most compounds having resonating structures is to divide the Number of bonds by the Number of resonating structures. Thus the final answer will be 4/3 or 1.3333.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option B.
Note: We also know that CO has triple bonds, ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ will have two double bonds in case of ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ the bond character lies between single and double bond due to resonance.
Hence the order of bond order will be ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ < ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ < CO.
Complete step by step solution:
Now let’s fiend the bond order of ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$
In the structure of ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ carbon is the least electronegative element, we place it in the central position:

Here the Carbon atom has 4 valence electrons, each oxygen has 6 valence electrons, and there are 2 more for the −2 charge. This gives a total 4 + (3 × 6) + 2 = 24 valence electrons.
In this structure, six electrons are used to form three bonding pairs between the oxygen atoms and the carbon.

We will divide the remaining 18 electrons equally among the three oxygen atoms by placing three lone pairs on each and indicating the −2 charge on the complete structure.

Hence, there are no electrons left for the central atom.
At this point, the carbon atom has only 6 valence electrons, so we must take one lone pair from oxygen and use it to form a carbon-oxygen double bond. There are three possible choices -

${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ has a total of three resonating structures and it has 4 bonds, The way to calculate the bond order for most compounds having resonating structures is to divide the Number of bonds by the Number of resonating structures. Thus the final answer will be 4/3 or 1.3333.
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option B.
Note: We also know that CO has triple bonds, ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ will have two double bonds in case of ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ the bond character lies between single and double bond due to resonance.
Hence the order of bond order will be ${ CO }_{ 3 }^{ 2- }$ < ${ CO }_{ 2 }$ < CO.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




