
The upper part of a broken tree by the wind makes an angle of $30^\circ $with the ground and the distance from the foot to the point where the top of the tree meets the ground is 8 meters. What was the height of the tree?
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint:
We can draw a figure showing the details given in the question and label the sides. Then we can take the cosine of the given angle to get the length of the hypotenuse which is the length of the broken part. Then we can take the cosine ratio to get the length of the other side which is the height at which the tree is broken. Then we can take the sum of the height at which the tree is broken and height of the broken part to get the height of the tree.
Complete step by step solution:
We can represent the given details in a diagram
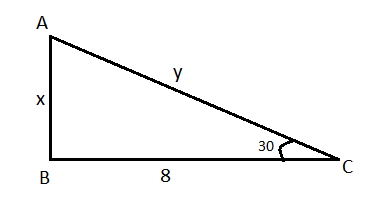
Let BC be the tree which is broken at B.
Let the height at which the tree is broken be x.
$ \Rightarrow AB = x$
Let the length of the broken part be y.
$ \Rightarrow AC = y$
It is given that the distance from the foot of the tree to the point where the top meets the ground is 8m
$ \Rightarrow BC = 8m$
It is also given that the tree meets the ground at an angle of $30^\circ $ .
$ \Rightarrow \angle ACB = 30^\circ $
Now consider the right-angled triangle ABC.
We know that $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{adj}}{\text{. side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \angle ACB = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \cos 30^\circ = \dfrac{8}{y}$
We know that $\cos 30^\circ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ ,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = \dfrac{8}{y}$
On cross multiplication, we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{8 \times 2}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
We know that $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opp}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \angle ACB = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{x}{y}$
We know that $\sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{2}$ and $y = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{x \times \sqrt 3 }}{{16}}$
On cross multiplication, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{16}}{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Let h be the height of the tree
From the figure, height of the tree is,
$h = AC + AB$
That is,
$ \Rightarrow h = y + x$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }} + \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
As the denominators are equal, we can add the numerators.
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{16 + 8}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
So, we have,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{24}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
We can write the numerator as,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{3 \times 8}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = 8\sqrt 3 $
Therefore, the height of the tree is $8\sqrt 3 \,m$.
Note:
Alternate method to solve this problem is by,
Now consider the right-angled triangle ABC.
We know that $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opp}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{adj}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{side}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \angle ACB = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{x}{8}$
We know that $\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ ,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{x}{8}$
On cross multiplication, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Now we can apply Pythagoras theorem.
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
As $AB = x$ and $AC = y$ , on substituting the values we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {x^2} + {8^2}$
On substituting the value of x we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} + {8^2}$
On taking ${8^2}$ common we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {8^2}\left( {\dfrac{1}{3} + 1} \right)$
On taking LCM we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {8^2}\left( {\dfrac{{1 + 3}}{3}} \right)$
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {8^2}\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)$
On taking square root, we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = 8\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)} $
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{8 \times 2}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Hence, we have,
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
From the figure, height of the tree is,
$h = AC + AB$
$ \Rightarrow h = y + x$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }} + \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
As the denominators are equal, we can add the numerators.
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{16 + 8}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On adding we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{24}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
We can write the numerator as,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{3 \times 8}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = 8\sqrt 3 $
Therefore, the height of the tree is $8\sqrt 3 \,m$.
We can draw a figure showing the details given in the question and label the sides. Then we can take the cosine of the given angle to get the length of the hypotenuse which is the length of the broken part. Then we can take the cosine ratio to get the length of the other side which is the height at which the tree is broken. Then we can take the sum of the height at which the tree is broken and height of the broken part to get the height of the tree.
Complete step by step solution:
We can represent the given details in a diagram

Let BC be the tree which is broken at B.
Let the height at which the tree is broken be x.
$ \Rightarrow AB = x$
Let the length of the broken part be y.
$ \Rightarrow AC = y$
It is given that the distance from the foot of the tree to the point where the top meets the ground is 8m
$ \Rightarrow BC = 8m$
It is also given that the tree meets the ground at an angle of $30^\circ $ .
$ \Rightarrow \angle ACB = 30^\circ $
Now consider the right-angled triangle ABC.
We know that $\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{adj}}{\text{. side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \angle ACB = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \cos 30^\circ = \dfrac{8}{y}$
We know that $\cos 30^\circ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$ ,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = \dfrac{8}{y}$
On cross multiplication, we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{8 \times 2}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
We know that $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opp}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \sin \angle ACB = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{x}{y}$
We know that $\sin 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{2}$ and $y = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{{x \times \sqrt 3 }}{{16}}$
On cross multiplication, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{16}}{{2\sqrt 3 }}$
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Let h be the height of the tree
From the figure, height of the tree is,
$h = AC + AB$
That is,
$ \Rightarrow h = y + x$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }} + \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
As the denominators are equal, we can add the numerators.
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{16 + 8}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
So, we have,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{24}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
We can write the numerator as,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{3 \times 8}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = 8\sqrt 3 $
Therefore, the height of the tree is $8\sqrt 3 \,m$.
Note:
Alternate method to solve this problem is by,
Now consider the right-angled triangle ABC.
We know that $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{opp}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{adj}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{side}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \tan \angle ACB = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{x}{8}$
We know that $\tan 30^\circ = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$ ,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{x}{8}$
On cross multiplication, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Now we can apply Pythagoras theorem.
$ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
As $AB = x$ and $AC = y$ , on substituting the values we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {x^2} + {8^2}$
On substituting the value of x we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}} \right)^2} + {8^2}$
On taking ${8^2}$ common we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {8^2}\left( {\dfrac{1}{3} + 1} \right)$
On taking LCM we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {8^2}\left( {\dfrac{{1 + 3}}{3}} \right)$
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow {y^2} = {8^2}\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)$
On taking square root, we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = 8\sqrt {\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)} $
On simplification we get,
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{8 \times 2}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Hence, we have,
$ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
From the figure, height of the tree is,
$h = AC + AB$
$ \Rightarrow h = y + x$
On substituting the values, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{16}}{{\sqrt 3 }} + \dfrac{8}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
As the denominators are equal, we can add the numerators.
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{16 + 8}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On adding we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{24}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
We can write the numerator as,
$ \Rightarrow h = \dfrac{{3 \times 8}}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
On simplification, we get,
$ \Rightarrow h = 8\sqrt 3 $
Therefore, the height of the tree is $8\sqrt 3 \,m$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




