
The type of hybridisation and number of lone pair(s) of electrons of Xe in \[XeO{F_{4}}\;\] respectively, are:
A.\[s{p^3}d\,\]and 1
B.\[s{p^3}d\,\]and 2
C.\[s{p^3}{d^2}\,\]and 1
D.\[s{p^3}{d^2}\,\]and 2
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you should recall that Xenon is a noble gas and when bonding it will have the tendency to use all the eight electrons in the outermost shell to form bond pairs. We know fluorine is a halogen and can form one sigma bond with the central atom and oxygen can form a double bond with the central atom. Now, use this information to answer the question.
Complete step by step answer:
Hybridization is defined as the concept of mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a degenerated new type of orbitals. This intermixing is based on quantum mechanics. \[XeO{F_{4}}\;\]has square pyramidal geometry. The central \[{\text{Xe}}\]atom has one lone pair electrons and five bonding domains where it donates its outermost eight electrons to four sigma bonded fluorine and one double-bonded oxygen. This results in \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridisation. The geometry or shape is octahedral and the arrangement of electrons around the central atom in the molecule is square pyramidal. The structure can be drawn as:
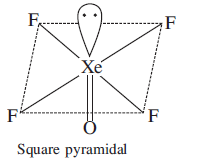
Hence, the correct answer to this question is option C.
Note:
Even if you are not able to calculate the hybridisation using the above-mentioned you can find the hybridization $(X)$ using the formula: \[\frac{1}{2}(V + H - C + A)\] where
$V$= Number of valence electrons in the central atom
$H$= Number of surrounding monovalent atoms
$C$= Cationic charge
$A$= Anionic charge. The value of X will determine the hybridisation of the molecule. If $X$is 2 then $sp$; is 3 then $s{p^2}$ ; is 4 then $s{p^3}$; is 5 then $s{p^3}d$ ; is 6 then $s{p^3}{d^2}$ ; is 7 then $s{p^3}{d^3}$ hybridization.
Complete step by step answer:
Hybridization is defined as the concept of mixing two atomic orbitals with the same energy levels to give a degenerated new type of orbitals. This intermixing is based on quantum mechanics. \[XeO{F_{4}}\;\]has square pyramidal geometry. The central \[{\text{Xe}}\]atom has one lone pair electrons and five bonding domains where it donates its outermost eight electrons to four sigma bonded fluorine and one double-bonded oxygen. This results in \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] hybridisation. The geometry or shape is octahedral and the arrangement of electrons around the central atom in the molecule is square pyramidal. The structure can be drawn as:

Hence, the correct answer to this question is option C.
Note:
Even if you are not able to calculate the hybridisation using the above-mentioned you can find the hybridization $(X)$ using the formula: \[\frac{1}{2}(V + H - C + A)\] where
$V$= Number of valence electrons in the central atom
$H$= Number of surrounding monovalent atoms
$C$= Cationic charge
$A$= Anionic charge. The value of X will determine the hybridisation of the molecule. If $X$is 2 then $sp$; is 3 then $s{p^2}$ ; is 4 then $s{p^3}$; is 5 then $s{p^3}d$ ; is 6 then $s{p^3}{d^2}$ ; is 7 then $s{p^3}{d^3}$ hybridization.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




