
The T-wave in an ECG represents
A) Electrical excitation of atria
B) Return of the ventricles from excited state
C) Depolarization of ventricles.
D) Beginning of systole
Answer
524.1k+ views
Hint: An ECG is an electrical signal from the heart to check the different heart conditions. ECG stands for electrocardiogram which describes the heart conditions, whether it functions well or not. Electrodes are placed on the chest of the human body to record the heart’s electrical signal, which causes the heart to beat. The machine that records the heart rate or beat of the person is called an electrocardiograph.
Complete answer:
Option A) Electrical excitation of atria.
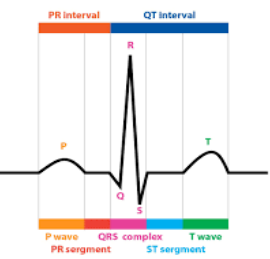
The waves on electrocardiogram include four types of waves- P wave, Q wave, R wave, S wave, T wave and U wave. The P wave represents the electrical excitation of atria or depolarization, which leads to contraction of both atria. As we know how important electrical signals are to the heart. The electrical signal travels through the network of conducting cell pathways which stimulate the upper and lower chambers of the heart which are atria and ventricles respectively. The AV node sends impulse into ventricles and ventricles contract or pump.
So, option A is not correct
Option B) Return of the ventricles from excited state- as we know that heart activity cannot go on a straight line. So, the return of the ventricles from the excited state represents the T wave on the electrocardiogram. It represents the repolarization which returns ventricular myocardium from its excited state. This state denotes when the heart returns back to normal state and starts preparing for contraction again. The T wave has a positive deflection since the cells in the ventricles that depolarize are the first to repolarize.
So, option B is correct.
Option C) Depolarization of ventricles- Depolarization of ventricles are denoted by a series of three deflections that reflect in the right and left ventricles. It denotes the QRS complex or wave in the electrocardiogram. The first deflection in the complex is known as Q wave as its negative. The first positive deflection in the complex is called the R wave. Then, a negative deflection after an R wave is called an S wave. And if there is another positive deflection after the S wave, we call it the R' wave.
So, option c is not correct.
Option D) Beginning of systole- Isovolumetric ventricular contraction marks the beginning of systole and starts with the appearance of the QRS complex. Beginning of systole marks the ventricles to fill during ventricular diastole. After tracing the P wave of the ECG, atria begin to contract. That is known as systole, pulsing blood into ventricles.
There are two phases in systole,
a) Atrial systole which lasts \[0.1\] second, both atria contract and force blood back to ventricles.
b) Ventricular systole- lasts about \[0.3\] seconds, both ventricles contract, blood is forced to the lungs via the pulmonary trunk and rest of the body by aorta.
So, option D is not correct.
So the correct answer is option B i.e., return of the ventricles from excited state.
Note:
The waves of ECG have some time intervals which are denoted by QT and PR intervals. The PR interval runs from the start of the P wave to the start of the QRS. The QT interval is the distance between the start of the QRS and the end of the T wave. It indicates the point at which the ventricles depolarize and repolarize. It is a ventricular action potential measurement (AP).
Complete answer:

Option A) Electrical excitation of atria.
The waves on electrocardiogram include four types of waves- P wave, Q wave, R wave, S wave, T wave and U wave. The P wave represents the electrical excitation of atria or depolarization, which leads to contraction of both atria. As we know how important electrical signals are to the heart. The electrical signal travels through the network of conducting cell pathways which stimulate the upper and lower chambers of the heart which are atria and ventricles respectively. The AV node sends impulse into ventricles and ventricles contract or pump.
So, option A is not correct
Option B) Return of the ventricles from excited state- as we know that heart activity cannot go on a straight line. So, the return of the ventricles from the excited state represents the T wave on the electrocardiogram. It represents the repolarization which returns ventricular myocardium from its excited state. This state denotes when the heart returns back to normal state and starts preparing for contraction again. The T wave has a positive deflection since the cells in the ventricles that depolarize are the first to repolarize.
So, option B is correct.
Option C) Depolarization of ventricles- Depolarization of ventricles are denoted by a series of three deflections that reflect in the right and left ventricles. It denotes the QRS complex or wave in the electrocardiogram. The first deflection in the complex is known as Q wave as its negative. The first positive deflection in the complex is called the R wave. Then, a negative deflection after an R wave is called an S wave. And if there is another positive deflection after the S wave, we call it the R' wave.
So, option c is not correct.
Option D) Beginning of systole- Isovolumetric ventricular contraction marks the beginning of systole and starts with the appearance of the QRS complex. Beginning of systole marks the ventricles to fill during ventricular diastole. After tracing the P wave of the ECG, atria begin to contract. That is known as systole, pulsing blood into ventricles.
There are two phases in systole,
a) Atrial systole which lasts \[0.1\] second, both atria contract and force blood back to ventricles.
b) Ventricular systole- lasts about \[0.3\] seconds, both ventricles contract, blood is forced to the lungs via the pulmonary trunk and rest of the body by aorta.
So, option D is not correct.
So the correct answer is option B i.e., return of the ventricles from excited state.
Note:
The waves of ECG have some time intervals which are denoted by QT and PR intervals. The PR interval runs from the start of the P wave to the start of the QRS. The QT interval is the distance between the start of the QRS and the end of the T wave. It indicates the point at which the ventricles depolarize and repolarize. It is a ventricular action potential measurement (AP).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




