
The total number of diprotic acids among the following is
${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}},{{H}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}},{{H}_{2}}Cr{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}$
(A) 6
(B) 5
(C) 4
(D) 2
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Acid continuing oxygen, those compounds are known as oxoacids of oxyacids. More specifically, these oxoacids are containing oxygen and contain at least another element. Oxoacids have at least one hydrogen atom bonded to oxygen and in which forms ions in solution by loss of one more proton.
Complete answer:
The general formula of oxoacids is ${{H}_{x}}E{{O}_{y}}$ , where E is a non-metal or transition metal and oxygen is directly attached to acidic hydrogen. The determining factor of oxoacid's relative strength is based on the electronegativity of the atom and the number of oxygen atoms around the central atom.
Oxoacids, which have two acidic protons attached to oxygen are known as diprotic acids.
Phosphoric acid - ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}$
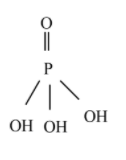
From the above structure, three acidic protons are attached to the oxygen atom. Hence, phosphoric acid is triprotic acid.
Orthophosphoric acid - ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$
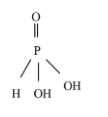
From the above structure, two acidic protons are attached to two oxygen atoms. Hence, Orthophosphorous acid (${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$) is a diprotic acid.
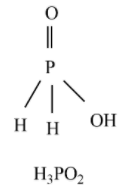
Hypophosphorous acid - ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}}$ is a monoprotic acid
Structures of given oxoacids of sulfur - ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$
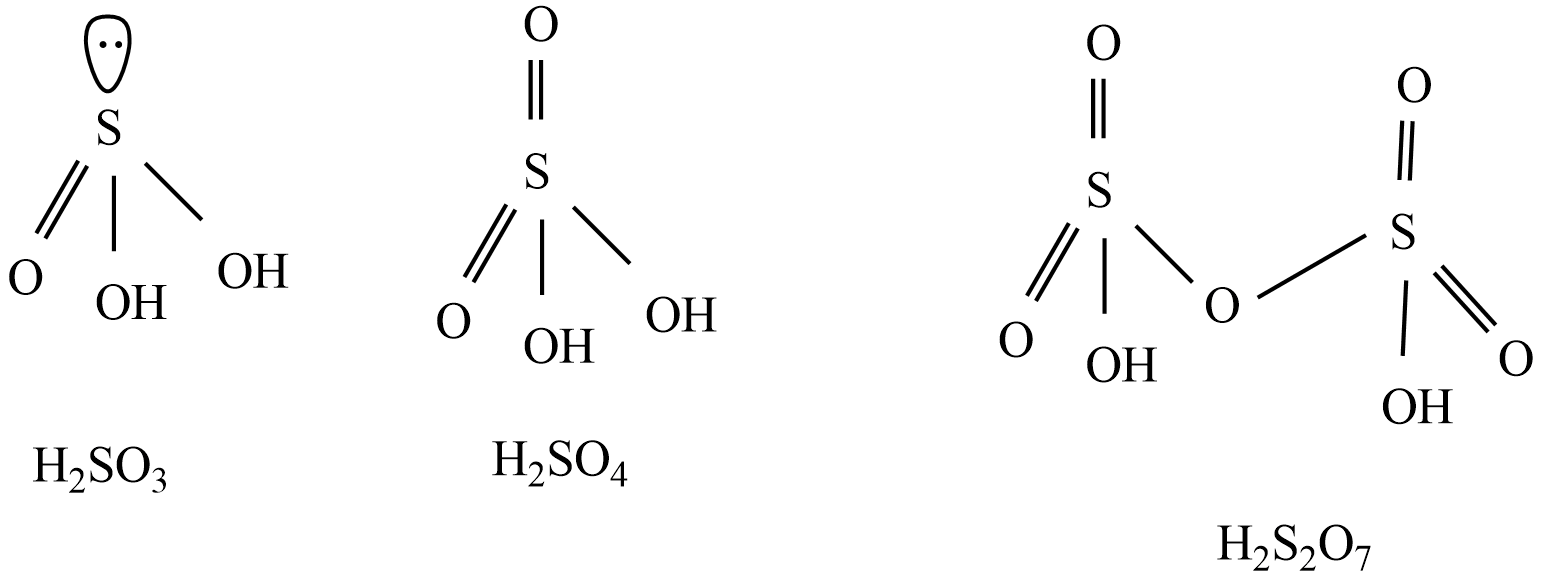
Form the above structures, ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}$ ,${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ , and ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ are diprotic acids, because two protons are attached to oxygen atoms in given oxoacids of sulfurs.
Observe the structures of ${{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}Cr{{O}_{4}}$
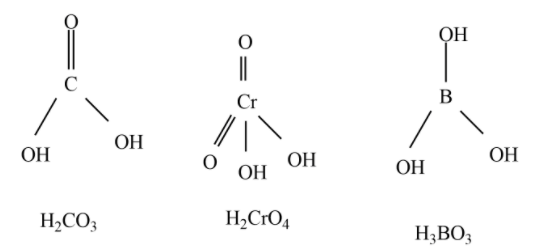
Out of the above three oxoacids, ${{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}Cr{{O}_{4}}$ are diprotic acids.
Hence, among the given oxoacids, six compounds are diprotic acids which are ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}},{{H}_{2}}Cr{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}$ .
Note:
In oxoacids, polyprotic acids contain more than one proton attached to an oxygen atom. There will be a complex equilibrium in polyprotic acids due to the presence of multiple species in solution. Determination of the concentrations of different species at equilibrium can be very difficult due to the variety of possible ionic species in solutions for each acid in polyprotic acids.
Complete answer:
The general formula of oxoacids is ${{H}_{x}}E{{O}_{y}}$ , where E is a non-metal or transition metal and oxygen is directly attached to acidic hydrogen. The determining factor of oxoacid's relative strength is based on the electronegativity of the atom and the number of oxygen atoms around the central atom.
Oxoacids, which have two acidic protons attached to oxygen are known as diprotic acids.
Phosphoric acid - ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{4}}$

From the above structure, three acidic protons are attached to the oxygen atom. Hence, phosphoric acid is triprotic acid.
Orthophosphoric acid - ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$

From the above structure, two acidic protons are attached to two oxygen atoms. Hence, Orthophosphorous acid (${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}}$) is a diprotic acid.
Hypophosphorous acid - ${{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}}$ is a monoprotic acid

Structures of given oxoacids of sulfur - ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$

Form the above structures, ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}$ ,${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ , and ${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$ are diprotic acids, because two protons are attached to oxygen atoms in given oxoacids of sulfurs.
Observe the structures of ${{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}Cr{{O}_{4}}$

Out of the above three oxoacids, ${{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}Cr{{O}_{4}}$ are diprotic acids.
Hence, among the given oxoacids, six compounds are diprotic acids which are ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}},{{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}},{{H}_{2}}Cr{{O}_{4}},{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{3}}$ .
Note:
In oxoacids, polyprotic acids contain more than one proton attached to an oxygen atom. There will be a complex equilibrium in polyprotic acids due to the presence of multiple species in solution. Determination of the concentrations of different species at equilibrium can be very difficult due to the variety of possible ionic species in solutions for each acid in polyprotic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




