
The three vertices of a parallelogram are (3, 4), (3, 8) and (9, 8). Find the fourth vertex.
Answer
613.8k+ views
Hint: Assume the coordinate of the fourth vertex of parallelogram ABCD to be (x,y). We know that the diagonal of a parallelogram bisects each other. Since ABCD is a parallelogram, the diagonals must bisect each other. We know that the midpoint(x,y) of A \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and B \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] is \[x=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}\] , \[y=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2}\] . Using the midpoint formula, find the coordinate of the midpoint of the diagonal BD. Similarly, find the midpoint of the coordinate of the diagonal AC. Since the diagonals meet at a point O. So, the midpoint of the diagonal AC and the diagonal BD must coincide. Now, solve it further and get the values of x and y.
Complete step-by-step answer:
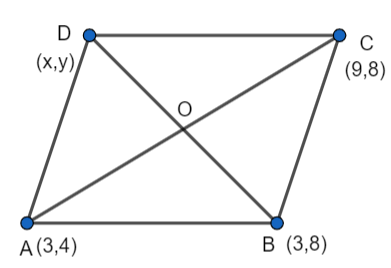
Let the coordinate of the fourth vertex D be (x,y).
We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. Since ABCD is a parallelogram, the diagonals must bisect each other.
For diagonal AC, O is its midpoint.
We know the formula that the midpoint(x,y) of A \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and B \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] is \[x=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}\] , \[y=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2}\] .
As O is the midpoint of the diagonal AC, we can find its coordinates using the midpoint formula.
We have, A = (3,4) and C = (9,8),
O = \[\left( \dfrac{3+9}{2},\dfrac{4+8}{2} \right)\] = \[\left( 6,6 \right)\] ……………………….(1)
As O is the midpoint of the diagonal BD, we can find its coordinates using the midpoint formula.
We have, B = (3,8) and D = (x,y),
O = \[\left( \dfrac{3+x}{2},\dfrac{8+y}{2} \right)\] …………………….(2)
Comparing equation (1) and equation (2), we get
\[6=\dfrac{3+x}{2}\] ………………….(3)
\[6=\dfrac{8+y}{2}\] ………………….(4)
Solving equation (3), we get
\[\begin{align}
& 6=\dfrac{3+x}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow 12=3+x \\
& \Rightarrow 9=x \\
\end{align}\]
Solving equation (4), we get
\[\begin{align}
& 6=\dfrac{8+y}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow 12=8+y \\
& \Rightarrow 4=y \\
\end{align}\]
The values of x and y are 4 and 9 respectively.
So, D = (9,4).
Hence, the fourth vertex is (9,4).
Note: We can also solve this question using the distance formula.
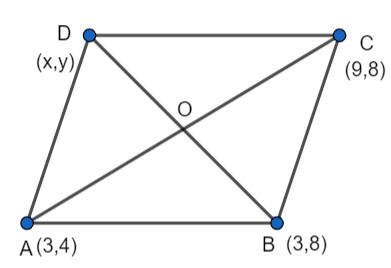
Let the fourth vertex of the parallelogram be (x,y).
We know that the opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal to each other.
So, AB = CD and BC = AD.
AB = \[\sqrt{{{(3-3)}^{2}}+{{(4-8)}^{2}}}=4\] …………………(1)
BC = \[\sqrt{{{(3-9)}^{2}}+{{(8-8)}^{2}}}=6\] ……………………..(2)
CD = \[\sqrt{{{(9-x)}^{2}}+{{(8-y)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-18x-16y+145}\] ………………………(3)
AD = \[\sqrt{{{(3-x)}^{2}}+{{(4-y)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x-8y+25}\] ……………………..(4)
From equation (1) and equation (3), we get
\[A{{B}^{2}}=C{{D}^{2}}\]
\[{{4}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-18x-16y+145\] …………………..(5)
From equation (2) and equation (4), we get
\[B{{C}^{2}}=A{{D}^{2}}\]
\[{{6}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x-8y+25\] …………………..(6)
We have two equations and two variables. On solving equation (5) and equation (6), we get
x=9 and y=4.
Hence, the fourth vertex is (9,4).
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let the coordinate of the fourth vertex D be (x,y).
We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. Since ABCD is a parallelogram, the diagonals must bisect each other.
For diagonal AC, O is its midpoint.
We know the formula that the midpoint(x,y) of A \[({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}})\] and B \[({{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}})\] is \[x=\dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}}{2}\] , \[y=\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}}{2}\] .
As O is the midpoint of the diagonal AC, we can find its coordinates using the midpoint formula.
We have, A = (3,4) and C = (9,8),
O = \[\left( \dfrac{3+9}{2},\dfrac{4+8}{2} \right)\] = \[\left( 6,6 \right)\] ……………………….(1)
As O is the midpoint of the diagonal BD, we can find its coordinates using the midpoint formula.
We have, B = (3,8) and D = (x,y),
O = \[\left( \dfrac{3+x}{2},\dfrac{8+y}{2} \right)\] …………………….(2)
Comparing equation (1) and equation (2), we get
\[6=\dfrac{3+x}{2}\] ………………….(3)
\[6=\dfrac{8+y}{2}\] ………………….(4)
Solving equation (3), we get
\[\begin{align}
& 6=\dfrac{3+x}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow 12=3+x \\
& \Rightarrow 9=x \\
\end{align}\]
Solving equation (4), we get
\[\begin{align}
& 6=\dfrac{8+y}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow 12=8+y \\
& \Rightarrow 4=y \\
\end{align}\]
The values of x and y are 4 and 9 respectively.
So, D = (9,4).
Hence, the fourth vertex is (9,4).
Note: We can also solve this question using the distance formula.

Let the fourth vertex of the parallelogram be (x,y).
We know that the opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal to each other.
So, AB = CD and BC = AD.
AB = \[\sqrt{{{(3-3)}^{2}}+{{(4-8)}^{2}}}=4\] …………………(1)
BC = \[\sqrt{{{(3-9)}^{2}}+{{(8-8)}^{2}}}=6\] ……………………..(2)
CD = \[\sqrt{{{(9-x)}^{2}}+{{(8-y)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-18x-16y+145}\] ………………………(3)
AD = \[\sqrt{{{(3-x)}^{2}}+{{(4-y)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x-8y+25}\] ……………………..(4)
From equation (1) and equation (3), we get
\[A{{B}^{2}}=C{{D}^{2}}\]
\[{{4}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-18x-16y+145\] …………………..(5)
From equation (2) and equation (4), we get
\[B{{C}^{2}}=A{{D}^{2}}\]
\[{{6}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-6x-8y+25\] …………………..(6)
We have two equations and two variables. On solving equation (5) and equation (6), we get
x=9 and y=4.
Hence, the fourth vertex is (9,4).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




