
The three components of a nucleotide are _________, _________ and __________.
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Nucleotides are organic molecules which consist of a phosphate and a nucleoside. They act as monomeric units of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleic acid polymers, both of which are important biomolecules in all life forms on Earth.
Complete answer:
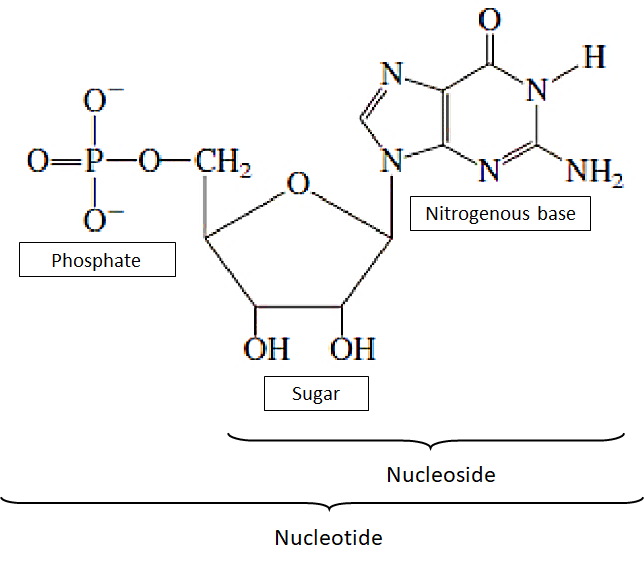
Three subunit molecules are composed of nucleotides: a nitrogen base (also known as nucleobase), a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a group of phosphates consisting of one to three phosphates. Guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA; uracil is used instead of thymine in RNA.
At a fundamental, cellular level, nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism. In the form of nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP), and uridine triphosphate (UTP), they provide chemical energy throughout the cell for the many cellular functions that require energy, including synthesis of amino acid, protein and cell membrane, movement of cell and cell parts (both internally and intracellularly), cellular functions. In addition, nucleotides (cyclic guanosine monophosphate or cGMP and cyclic adenosine monophosphate or cAMP) are involved in cell signaling and are incorporated into essential enzymatic reaction cofactors (e.g., coenzyme A, FAD, FMN, NAD, and NADP+).
Additional Information:
Three distinctive chemical subunits form a nucleotide: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nitrogen base, two of which together are called a nucleoside, and a phosphate group. Depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate group, a nucleotide is often called a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate" with all three joined.
Note: The nucleic acid is a major class of macromolecules that are present in both viruses and cells. The functions of nucleic acids are related to genetic information storage and expression. The information the cell requires to make proteins is encoded by deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
Complete answer:
Three subunit molecules are composed of nucleotides: a nitrogen base (also known as nucleobase), a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a group of phosphates consisting of one to three phosphates. Guanine, adenine, cytosine, and thymine are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA; uracil is used instead of thymine in RNA.
At a fundamental, cellular level, nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism. In the form of nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP), and uridine triphosphate (UTP), they provide chemical energy throughout the cell for the many cellular functions that require energy, including synthesis of amino acid, protein and cell membrane, movement of cell and cell parts (both internally and intracellularly), cellular functions. In addition, nucleotides (cyclic guanosine monophosphate or cGMP and cyclic adenosine monophosphate or cAMP) are involved in cell signaling and are incorporated into essential enzymatic reaction cofactors (e.g., coenzyme A, FAD, FMN, NAD, and NADP+).
Additional Information:
Three distinctive chemical subunits form a nucleotide: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nitrogen base, two of which together are called a nucleoside, and a phosphate group. Depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate group, a nucleotide is often called a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate" with all three joined.
Note: The nucleic acid is a major class of macromolecules that are present in both viruses and cells. The functions of nucleic acids are related to genetic information storage and expression. The information the cell requires to make proteins is encoded by deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




