
The terminalization occurs during-
(a)Leptotene to diplotene
(b)Pachytene to diplotene
(c)Zygotene to pachytene
(d)Diplotene to metaphase
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: After pachytene, the fourth stage of the prophase of meiosis, during which the paired chromosomes begin to divide into two pairs of chromatids. It is a step in the cell cycle that condenses all the genetic material into chromosomes. Then these chromosomes become obvious.
Complete answer:
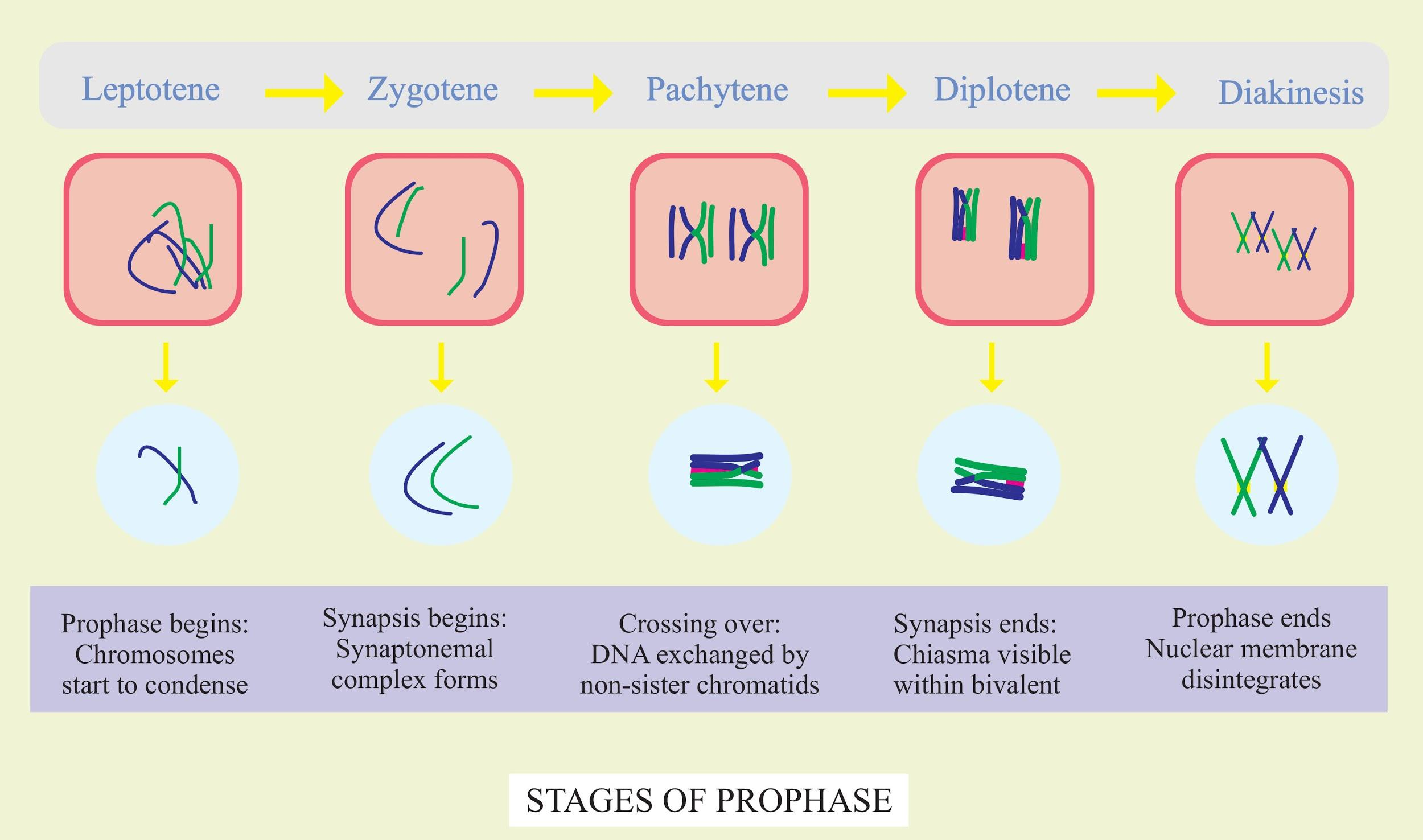
The two homologous chromosomes start to migrate apart during the diplotene process, as the 'synaptonemal complex' disintegrates between the two chromosomal arms and they begin to repel each other. This permits the two chromosomes, retained only by the chiasma, to pass apart. The chromosome starts to uncoil as this process happens, contrary to the normal progression of prophase, but they are still coiled enough to make a separate image of a chiasma formation under a microscope. In a process known as terminalization, the chiasma moves towards the end of the chromatids.
I have the following stages of meiosis-Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Prophase I consists of leptotene, zygotene, diplotene, diakinesis, pachytene.
During diplotene, terminalization of chiasma takes place after crossing over at pachytene, and completion of terminalization takes place in diakinesis.
Additional Information: Chromosomes begin to condense in the first stage of Prophase I, leptotene (from the Greek for "delicate"). Every chromosome is in a haploid state and consists of two sister chromatids, but the sister chromatids' chromatin is not yet sufficiently condensed to be microscopically resolvable. Homologous regions start to interact with each other within homologous chromosome pairs.
Both maternally and paternally derived chromosomes have met their homologous partner in the second step of prophase I, zygotene (from the Greek for 'conjugation'). The homologous pairs then undergo synapsis, a process by which the synaptonemal complex (a proteinaceous structure) aligns the corresponding genetic information regions with the non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosome pairs that are maternally and paternally derived.
At the end of synapsis, the third step of prophase I, pachytene (from the Greek for 'thick'), begins. Chromatin has condensed so that in microscopy, chromosomes can now be resolved. On the synaptonemal complex of bivalents, structures called recombination nodules form.
So, the correct answer is ‘diplotene to metaphase’.
Note: In genetics, a chiasma is a physical connexion between two chromatids belonging to homologous chromosomes, the point of contact. There can be an exchange of genetic material between both chromatids at a given chiasma, which is called a chromosomal crossover, but this is much more common than mitosis during meiosis.
Complete answer:
The two homologous chromosomes start to migrate apart during the diplotene process, as the 'synaptonemal complex' disintegrates between the two chromosomal arms and they begin to repel each other. This permits the two chromosomes, retained only by the chiasma, to pass apart. The chromosome starts to uncoil as this process happens, contrary to the normal progression of prophase, but they are still coiled enough to make a separate image of a chiasma formation under a microscope. In a process known as terminalization, the chiasma moves towards the end of the chromatids.
I have the following stages of meiosis-Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase. Prophase I consists of leptotene, zygotene, diplotene, diakinesis, pachytene.
During diplotene, terminalization of chiasma takes place after crossing over at pachytene, and completion of terminalization takes place in diakinesis.
Additional Information: Chromosomes begin to condense in the first stage of Prophase I, leptotene (from the Greek for "delicate"). Every chromosome is in a haploid state and consists of two sister chromatids, but the sister chromatids' chromatin is not yet sufficiently condensed to be microscopically resolvable. Homologous regions start to interact with each other within homologous chromosome pairs.
Both maternally and paternally derived chromosomes have met their homologous partner in the second step of prophase I, zygotene (from the Greek for 'conjugation'). The homologous pairs then undergo synapsis, a process by which the synaptonemal complex (a proteinaceous structure) aligns the corresponding genetic information regions with the non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosome pairs that are maternally and paternally derived.
At the end of synapsis, the third step of prophase I, pachytene (from the Greek for 'thick'), begins. Chromatin has condensed so that in microscopy, chromosomes can now be resolved. On the synaptonemal complex of bivalents, structures called recombination nodules form.
So, the correct answer is ‘diplotene to metaphase’.
Note: In genetics, a chiasma is a physical connexion between two chromatids belonging to homologous chromosomes, the point of contact. There can be an exchange of genetic material between both chromatids at a given chiasma, which is called a chromosomal crossover, but this is much more common than mitosis during meiosis.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




