
The supply voltage to a room is 120 V. The resistance of the lead wires is 6 $\Omega $. A 60 W, 120 V bulb is already switched on. What is the decrease of voltage (in volts) across the bulb, when a 240 W, 120 V heater is switched on in parallel to the bulb?
A. 2.9
B. 13.3
C. 10.4
D. 0
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: First, we need to calculate the resistances of the bulb and the heater, and also find their equivalent resistance in parallel combination. Then by comparing the initial voltage drop for bulb and subtracting the voltage drop after connecting the heater, we can get the required answer.
Formula used:
The power consumed by a circuit is given in the terms of the voltage, the resistance and the current by the following expression.
$P = VI = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Complete answer:
Let us first consider the case of the bulb which is switched on in the room. Its rating is 60W, 120V. Therefore, for the bulb we have
$
V = 120V \\
P = 60W \\
$
From this information we can find out the resistance of the bulb which is given as ${R_b} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{P} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {120} \right)}^2}}}{{60}} = 240\Omega $
Doing the same thing in the case of heater, we have the rating as 240 W, 120 V. Therefore, the resistance of the heater is
${R_h} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {120} \right)}^2}}}{{240}} = 60\Omega $
The bulb and the heater are connected in parallel so their resultant resistance is given as
$R = \dfrac{{{R_b}{R_h}}}{{{R_b} + {R_h}}} = \dfrac{{240 \times 60}}{{240 + 60}} = 48\Omega $
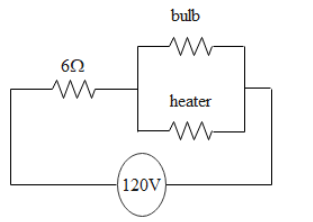
Before connecting the heater to the circuit, the potential drop across the bulb is given as
${V_1} = \dfrac{{{R_b}}}{{{R_b} + 6}} \times V = \dfrac{{240}}{{240 + 6}} \times 120 = 117.07V$
The resistance of the lead wires is 6 $\Omega $.
After we connect the heater to the circuit, the potential drop across the parallel combination of bulb and the heater is given as
${V_2} = \dfrac{R}{{R + 6}} \times V = \dfrac{{48}}{{48 + 6}} \times 120 = 106.67V$
Therefore, change in voltage is given as
${V_1} - {V_2} = 117.07 - 106.67 = 10.4V$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
It should be noted that when only the bulb is connected to the circuit then it is in series with the resistance of the wires. When the heater is attached to the circuit, the parallel combination ensures that the voltage remains the same for bulb and heater.
Formula used:
The power consumed by a circuit is given in the terms of the voltage, the resistance and the current by the following expression.
$P = VI = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R}$
Complete answer:
Let us first consider the case of the bulb which is switched on in the room. Its rating is 60W, 120V. Therefore, for the bulb we have
$
V = 120V \\
P = 60W \\
$
From this information we can find out the resistance of the bulb which is given as ${R_b} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{P} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {120} \right)}^2}}}{{60}} = 240\Omega $
Doing the same thing in the case of heater, we have the rating as 240 W, 120 V. Therefore, the resistance of the heater is
${R_h} = \dfrac{{{{\left( {120} \right)}^2}}}{{240}} = 60\Omega $
The bulb and the heater are connected in parallel so their resultant resistance is given as
$R = \dfrac{{{R_b}{R_h}}}{{{R_b} + {R_h}}} = \dfrac{{240 \times 60}}{{240 + 60}} = 48\Omega $

Before connecting the heater to the circuit, the potential drop across the bulb is given as
${V_1} = \dfrac{{{R_b}}}{{{R_b} + 6}} \times V = \dfrac{{240}}{{240 + 6}} \times 120 = 117.07V$
The resistance of the lead wires is 6 $\Omega $.
After we connect the heater to the circuit, the potential drop across the parallel combination of bulb and the heater is given as
${V_2} = \dfrac{R}{{R + 6}} \times V = \dfrac{{48}}{{48 + 6}} \times 120 = 106.67V$
Therefore, change in voltage is given as
${V_1} - {V_2} = 117.07 - 106.67 = 10.4V$
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
It should be noted that when only the bulb is connected to the circuit then it is in series with the resistance of the wires. When the heater is attached to the circuit, the parallel combination ensures that the voltage remains the same for bulb and heater.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




