
The strength of sigma bonds formed by the axial overlap of s- or p-orbitals of 2nd shell of participating atoms decreases as:
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: In the formation of any diatomic molecule, there is a minimum energy state while their orbitals undergo partial interpenetration that happens with two atoms coming near it. The partial merging of atomic orbitals leads to the overlapping of atomic orbitals which results in the pairing of electrons.
Complete step by step solution:
When atoms are involved in the overlapping of atomic orbitals, their overlap may be positive, negative or zero depending on the wave function of the orbital and also sign of the orbital.
Depending on the types overlapping of orbitals the covalent bonds are classified into two types of bonds,
(1) sigma bond ( $\sigma $ )
(2) pi bond ( $\pi $ )
sigma bond ( $\sigma $ ): the overlap of bonding orbitals along the internuclear axis by an end to end formation of the covalent bond.
s-s overlapping: this overlapping of two half-filled s-orbitals through the internuclear axis as shown below:
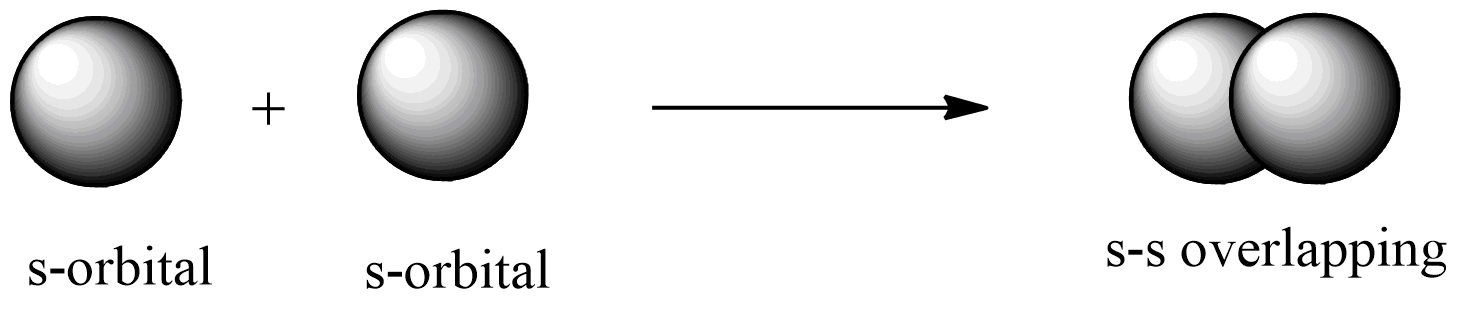
s-p overlapping: this overlapping of two half-filled s-orbital from one atom and p-orbital from another atom.
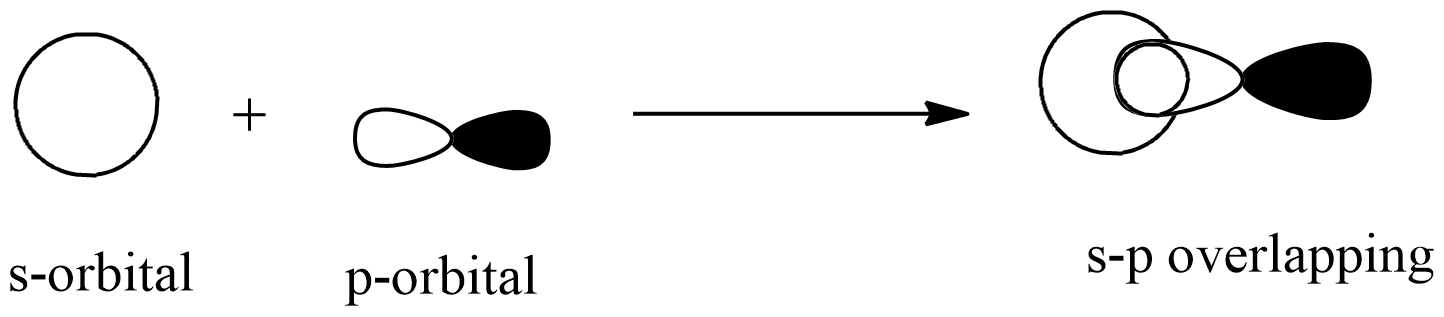
p-p overlapping: this overlapping of two half-filled p-orbitals through the internuclear axis as shown below:

From the above orbitals overlapping, p-orbitals overlap maximum than s-orbital becomes minimum. The strength of the sigma bond depends on its bond length.
Thus, The strength of sigma bonds formed by the axial overlap of s- or p-orbitals of 2nd shell of participating atoms decreases as:
p-p>p-s>s-s.
Note: The overlap of 1-s orbitals of two H-atoms with the covalent bond formed by overlapping of two atomic orbitals from hydrogen molecules. In the case of polyatomic molecules, the bond formation depends on the geometry of molecules. This will be explained by valence bond theory as shape, the formation, and the directional properties of bonds in polyatomic molecules.
Complete step by step solution:
When atoms are involved in the overlapping of atomic orbitals, their overlap may be positive, negative or zero depending on the wave function of the orbital and also sign of the orbital.
Depending on the types overlapping of orbitals the covalent bonds are classified into two types of bonds,
(1) sigma bond ( $\sigma $ )
(2) pi bond ( $\pi $ )
sigma bond ( $\sigma $ ): the overlap of bonding orbitals along the internuclear axis by an end to end formation of the covalent bond.
s-s overlapping: this overlapping of two half-filled s-orbitals through the internuclear axis as shown below:
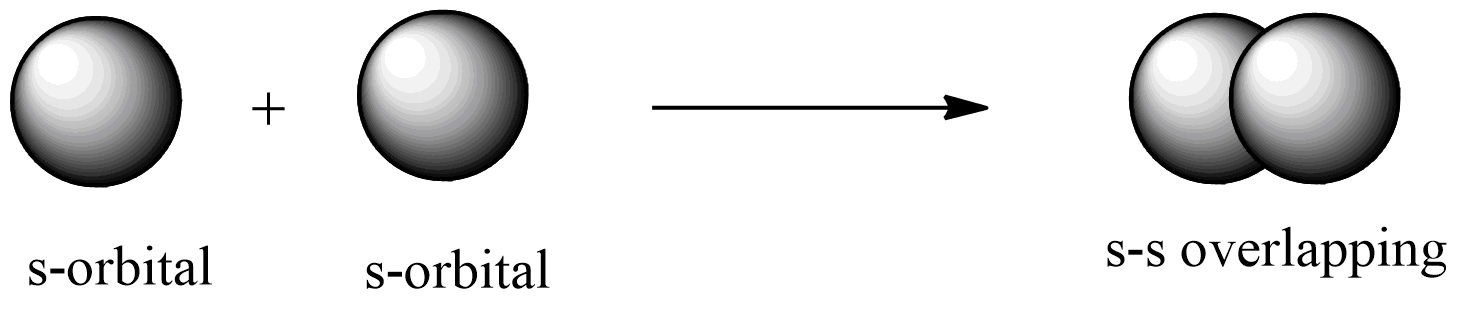
s-p overlapping: this overlapping of two half-filled s-orbital from one atom and p-orbital from another atom.
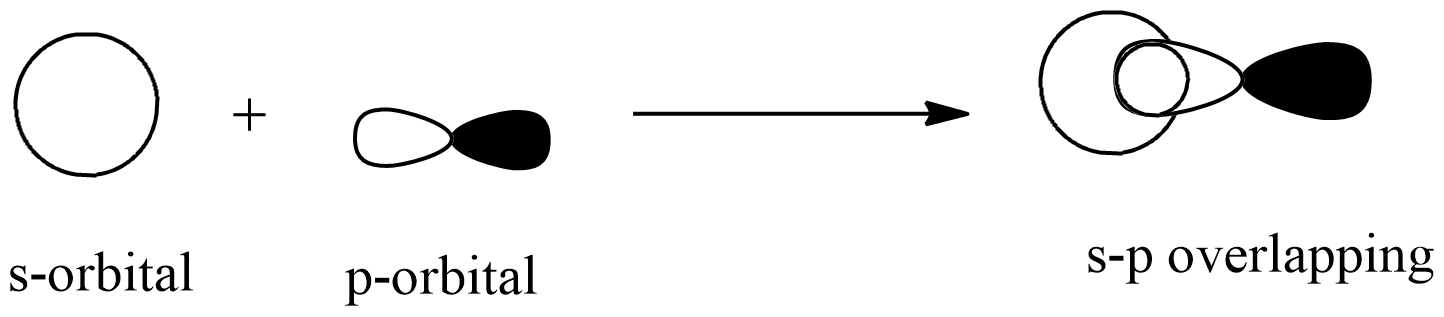
p-p overlapping: this overlapping of two half-filled p-orbitals through the internuclear axis as shown below:

From the above orbitals overlapping, p-orbitals overlap maximum than s-orbital becomes minimum. The strength of the sigma bond depends on its bond length.
Thus, The strength of sigma bonds formed by the axial overlap of s- or p-orbitals of 2nd shell of participating atoms decreases as:
p-p>p-s>s-s.
Note: The overlap of 1-s orbitals of two H-atoms with the covalent bond formed by overlapping of two atomic orbitals from hydrogen molecules. In the case of polyatomic molecules, the bond formation depends on the geometry of molecules. This will be explained by valence bond theory as shape, the formation, and the directional properties of bonds in polyatomic molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




