
The source of nitrogen in Gabriel synthesis of amines is:
A. Sodium azide $Na{N_3}$
B. Sodium nitrite $NaN{O_2}$
C. Potassium cyanide $ KCN $
D. Potassium phthalimide ${C_6}{H_4}(C{O_2}){N^ - }{K^ + }$
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: the Gabriel synthesis is a method used to prepare primary amines.
Complete step by step solution: while preparing amines when ammonia is reacted with alkyl halides it results in multiple alkylations which can be reduced by using a large excess of ammonia. Hence phthalimide can be used. It is quite acidic in nature so it is converted to potassium phthalide by reacting it with potassium hydroxide.
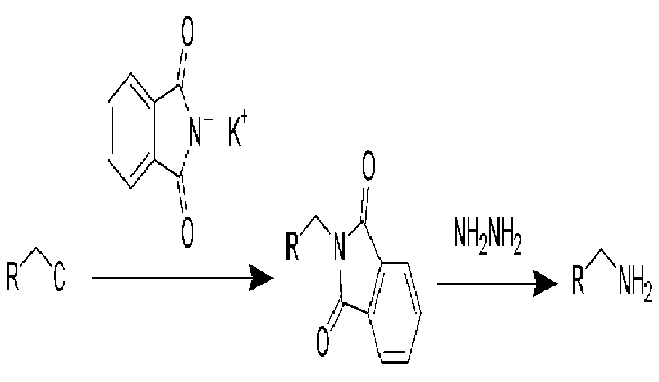
The phthalimide anion is a strong nucleophile and it reacts with an alkyl halide by a nucleophilic reaction of SN2 to give N-alkyl phthalimide. At this point the N-alkyl phthalimide can be hydrolyzed by with aqueous acid or base but the hydrolysis is often difficult it is often more convenient to treat the N-alkyl phthalimide with hydrazine () in refluxing ethanol to give a primary amine and phthalazine-1, 4-dione. Synthesis of amines using the Gabriel synthesis is, as we might expect restricted to the use of methyl, primary and secondary alkyl halides. The use of tertiary halides leads almost exclusively to eliminations.
Hence the correct option is option D as potassium phthalimide is used in Gabriel synthesis.
Additional information: Multiple alkylations are not a problem when tertiary amines are alkylated with methyl or primary amines. Such reactions take place in good yield
Note: This method is used to avoid multiple alkylations that occur while treating amines with alkyl halides.
Complete step by step solution: while preparing amines when ammonia is reacted with alkyl halides it results in multiple alkylations which can be reduced by using a large excess of ammonia. Hence phthalimide can be used. It is quite acidic in nature so it is converted to potassium phthalide by reacting it with potassium hydroxide.

The phthalimide anion is a strong nucleophile and it reacts with an alkyl halide by a nucleophilic reaction of SN2 to give N-alkyl phthalimide. At this point the N-alkyl phthalimide can be hydrolyzed by with aqueous acid or base but the hydrolysis is often difficult it is often more convenient to treat the N-alkyl phthalimide with hydrazine () in refluxing ethanol to give a primary amine and phthalazine-1, 4-dione. Synthesis of amines using the Gabriel synthesis is, as we might expect restricted to the use of methyl, primary and secondary alkyl halides. The use of tertiary halides leads almost exclusively to eliminations.
Hence the correct option is option D as potassium phthalimide is used in Gabriel synthesis.
Additional information: Multiple alkylations are not a problem when tertiary amines are alkylated with methyl or primary amines. Such reactions take place in good yield
Note: This method is used to avoid multiple alkylations that occur while treating amines with alkyl halides.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




