
The soap molecule has:
(A) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
(B) hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
(C) hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
(D) hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Soaps are the sodium and potassium salts of fatty acids. Their one of the major applications is the cleansing action of soap based on the principle of micelle formation. Soaps have relatively weak cleansing action in comparison with detergents.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been asked about the soap molecule,
The molecule of soap constitutes sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acid.
They are used in the cleansing action,
Sodium stearate is an example of soap with molecular formula: ${C_ {18}} {H_ {35}} Na{O_2} $,

In the case of soaps, the carbon chain dissolves in oil and the ionic end dissolves in water.
Soaps in the form of micelles clean the dirt and oil as the oil will be collected at the centre of micelle. This property of soap makes it an emulsifier. The dirt suspended in micelles is easily rinsed away. This is known as the cleansing action of soap.
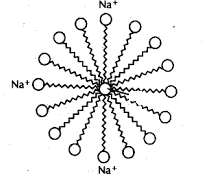
While coming to the structure of soap,
The basic structure of all soaps is essentially the same, consisting of a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon tail and a hydrophilic head.
The hydrophilic head contains polar anion such as carboxylate ion and is water-soluble.
The hydrophobic tail contains a nonpolar carbon chain and is oil soluble.
So, we can say that the soap molecule contains a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail.
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Note: The soap molecules have a general formula: $RCO {O^ -} N {a^ +} $. When mixed with water, it dissociates into positive ($N {a^ +} $) and negative $(RCO {O^ -}) $ ions. The $RCO {O^ -} $ ions consists of two polar and non -polar groups, R and $CO {O^ -} $.
Complete step by step solution:
We have been asked about the soap molecule,
The molecule of soap constitutes sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acid.
They are used in the cleansing action,
Sodium stearate is an example of soap with molecular formula: ${C_ {18}} {H_ {35}} Na{O_2} $,

In the case of soaps, the carbon chain dissolves in oil and the ionic end dissolves in water.
Soaps in the form of micelles clean the dirt and oil as the oil will be collected at the centre of micelle. This property of soap makes it an emulsifier. The dirt suspended in micelles is easily rinsed away. This is known as the cleansing action of soap.

While coming to the structure of soap,
The basic structure of all soaps is essentially the same, consisting of a long hydrophobic hydrocarbon tail and a hydrophilic head.
The hydrophilic head contains polar anion such as carboxylate ion and is water-soluble.
The hydrophobic tail contains a nonpolar carbon chain and is oil soluble.
So, we can say that the soap molecule contains a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail.
Therefore, option (A) is correct.
Note: The soap molecules have a general formula: $RCO {O^ -} N {a^ +} $. When mixed with water, it dissociates into positive ($N {a^ +} $) and negative $(RCO {O^ -}) $ ions. The $RCO {O^ -} $ ions consists of two polar and non -polar groups, R and $CO {O^ -} $.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




