
The shapes of \[I{F_5}\] and \[I{F_7}\] are respectively:
(A) Tetragonal pyramidal and pentagonal bipyramidal
(B) Octahedral and pyramidal
(C) Trigonal bipyramidal and square antiprismatic
(D) Distorted square planar and distorted octahedral
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: Atoms bond together to form molecules that have different sizes and shapes. Molecular shape determines several properties of substances like polarity, reactivity. Physical and chemical properties depend on the geometry of a molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
-Atoms are usually not capable of free existence except noble gases. However, a group of atoms is found to exist together as one species with characteristic properties. Such a group is called a molecule. The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions) together in a molecule is called a chemical bond.
- The shape of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shell electron pairs (bonded and non-bonding electron pairs) is referred to as a bond pair while the unshared/nonbonding pair of electrons on an atom is referred to as a lone pair.
- Electron pair around the central atom exert repulsive force on one another as possible so that the forces of repulsion are minimised the shape of the molecules are different
- \[I{F_5}\] is having tetragonal pyramidal shape and \[I{F_7}\]is having pentagonal bipyramidal shape.The correct answer is option “A” .
- In \[I{F_5}\] the central atom iodine has \[7\] valence electron out of which \[5\] electrons form \[5\]sigma bond with \[F\] atoms and \[2\] electrons form one lone pair. The hybridization of the central atom is \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] Where the geometry of \[I{F_5}\] is octahedral and the shape is tetragonal pyramidal.
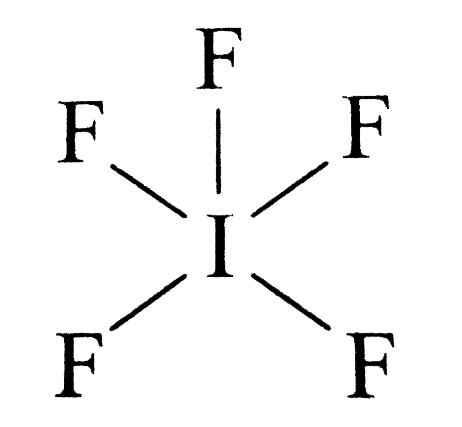
- In \[I{F_7}\] the central atom \[I\] is surrounded by seven bond pairs of electrons. Therefore are the geometry of \[I{F_7}\] is pentagonal bipyramidal as these seven electron pairs try to remain as far apart as possible so the bond angle is \[{72^o}\] and \[{90^o}\].
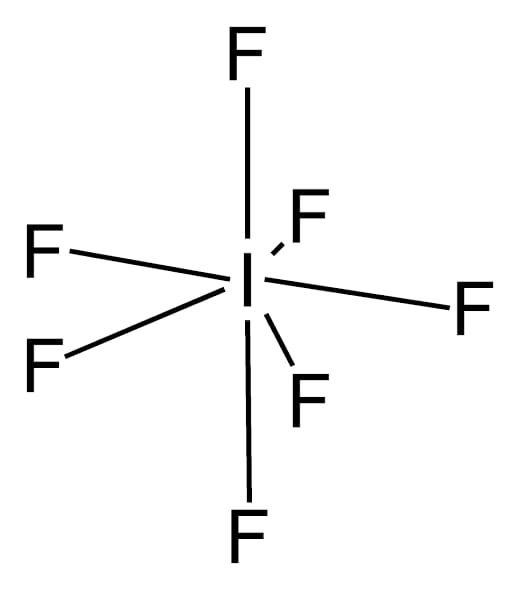
Note: Bond angle- the angle between the lines representing the directions of the bond is called the bond angle. It can be measured by X-ray analysis or by some other spectroscopic methods such as infra-red spectroscopy.
- Number of domains around the central atom determines the geometrical arrangement.
Complete step by step answer:
-Atoms are usually not capable of free existence except noble gases. However, a group of atoms is found to exist together as one species with characteristic properties. Such a group is called a molecule. The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions) together in a molecule is called a chemical bond.
- The shape of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shell electron pairs (bonded and non-bonding electron pairs) is referred to as a bond pair while the unshared/nonbonding pair of electrons on an atom is referred to as a lone pair.
- Electron pair around the central atom exert repulsive force on one another as possible so that the forces of repulsion are minimised the shape of the molecules are different
- \[I{F_5}\] is having tetragonal pyramidal shape and \[I{F_7}\]is having pentagonal bipyramidal shape.The correct answer is option “A” .
- In \[I{F_5}\] the central atom iodine has \[7\] valence electron out of which \[5\] electrons form \[5\]sigma bond with \[F\] atoms and \[2\] electrons form one lone pair. The hybridization of the central atom is \[s{p^3}{d^2}\] Where the geometry of \[I{F_5}\] is octahedral and the shape is tetragonal pyramidal.

- In \[I{F_7}\] the central atom \[I\] is surrounded by seven bond pairs of electrons. Therefore are the geometry of \[I{F_7}\] is pentagonal bipyramidal as these seven electron pairs try to remain as far apart as possible so the bond angle is \[{72^o}\] and \[{90^o}\].

Note: Bond angle- the angle between the lines representing the directions of the bond is called the bond angle. It can be measured by X-ray analysis or by some other spectroscopic methods such as infra-red spectroscopy.
- Number of domains around the central atom determines the geometrical arrangement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




