
The relation between edge length (a) and radius of atom (r) for BCC lattice is $\sqrt{3}a=4r$ .
Answer
553.8k+ views
Hint: The pre-knowledge of unit cells and crystal lattice will help us solve this problem. The relationship between atomic radius and the edge length of a unit cell can be derived for BCC structure to illustrate the given data.
Complete answer:
Let us learn about the crystal lattice and its types;
Crystal lattice- The arrangement of atoms or ions in the three-dimensional form in a crystal.
Unit cell- A unit cell is the smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice.
Types of unit cell-
1. Simple cubic structure
2. Body centred cubic structure
3. Face centred cubic structure
Let us concentrate on the second type of a unit cell i.e. BCC structure;
-The BCC unit cell consists of the atoms at all the corners of the crystal and at the centre of the cube.
-Thus, 2 atoms are present in a BCC unit cell. As,
a. Corners of a cube- $8\times \frac{1}{8}=1$ atom.
b. Centre of a cube- 1 atom.
To analyse the relationship of edge length and radius for BCC crystal lattice; focus on the green coloured triangle in the diagram.
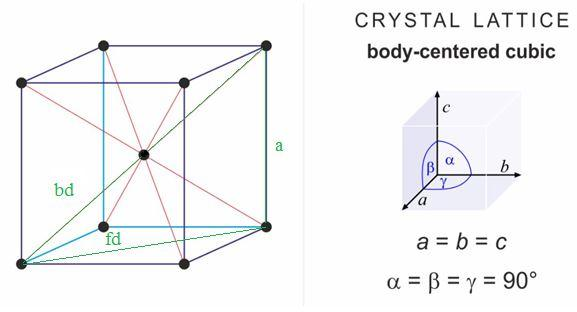
To find the relationship between the edge length of the cube and the radius of an atom, apply Pythagoras theorem to above given figure;
$\begin{align}
& Sid{{e}_{1}}^{2}+Sid{{e}_{2}}^{2}=Hypoteneu{{s}^{2}} \\
& f{{d}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}=b{{d}^{2}} \\
& b{{d}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}} \\
& b{{d}^{2}}=3{{a}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
where,
a = side of a lattice
fd = face diagonal
bd = body diagonal = 4r
Thus,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( 4r \right)}^{2}}=3{{a}^{2}} \\
& 4r=\sqrt{3}a \\
\end{align}$
where,
r = radius of atom
Note:
The relationship between the atomic radius and edge length is different for all types of unit cells; each one has its own significance.
Also, the packing efficiency can be calculated for each type of crystal lattice when we know this relationship.
Complete answer:
Let us learn about the crystal lattice and its types;
Crystal lattice- The arrangement of atoms or ions in the three-dimensional form in a crystal.
Unit cell- A unit cell is the smallest repeating unit of a crystal lattice.
Types of unit cell-
1. Simple cubic structure
2. Body centred cubic structure
3. Face centred cubic structure
Let us concentrate on the second type of a unit cell i.e. BCC structure;
-The BCC unit cell consists of the atoms at all the corners of the crystal and at the centre of the cube.
-Thus, 2 atoms are present in a BCC unit cell. As,
a. Corners of a cube- $8\times \frac{1}{8}=1$ atom.
b. Centre of a cube- 1 atom.
To analyse the relationship of edge length and radius for BCC crystal lattice; focus on the green coloured triangle in the diagram.

To find the relationship between the edge length of the cube and the radius of an atom, apply Pythagoras theorem to above given figure;
$\begin{align}
& Sid{{e}_{1}}^{2}+Sid{{e}_{2}}^{2}=Hypoteneu{{s}^{2}} \\
& f{{d}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}=b{{d}^{2}} \\
& b{{d}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}}+{{a}^{2}} \\
& b{{d}^{2}}=3{{a}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
where,
a = side of a lattice
fd = face diagonal
bd = body diagonal = 4r
Thus,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( 4r \right)}^{2}}=3{{a}^{2}} \\
& 4r=\sqrt{3}a \\
\end{align}$
where,
r = radius of atom
Note:
The relationship between the atomic radius and edge length is different for all types of unit cells; each one has its own significance.
Also, the packing efficiency can be calculated for each type of crystal lattice when we know this relationship.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




