
The reaction of ethanol with conc. \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\]gives ethane
A. True
B. False
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: We know the reaction of ethanol with conc. \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\] is a process of dehydration. Sulphuric acid is a dehydration agent. Therefore, the dehydration process is the removal of water. Hence ethanol converted into ethane.
Complete answer:
Ethanol when heated with concentrated sulphuric acid (acts as a catalyst); gases produced are passed through sodium hydroxide solution to remove the carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide produced as side products. Ethene is the main product collected over water. Hence, dehydration of ethanol to give ethene, not ethane.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
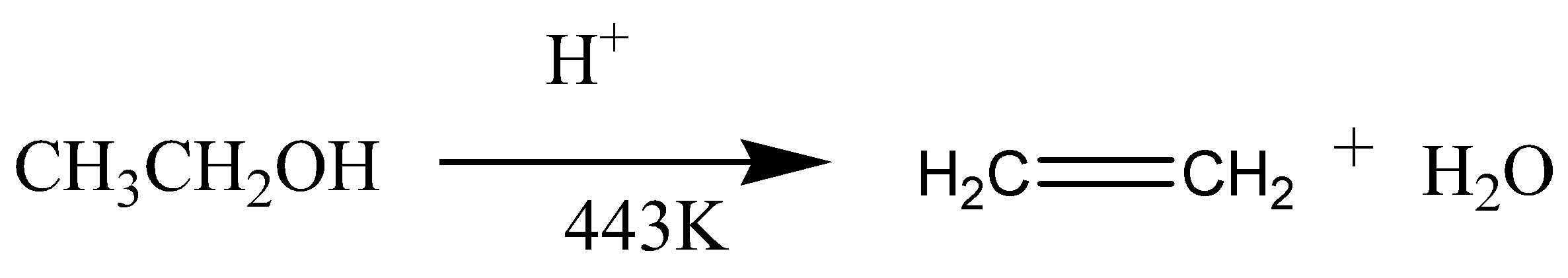
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - OH}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]
Mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol:-
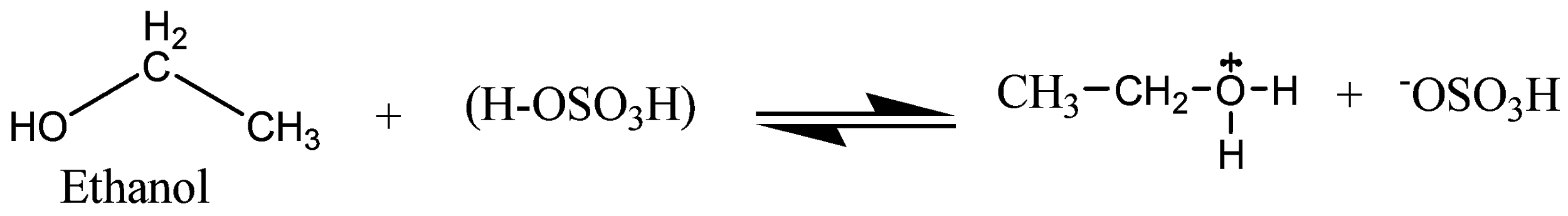
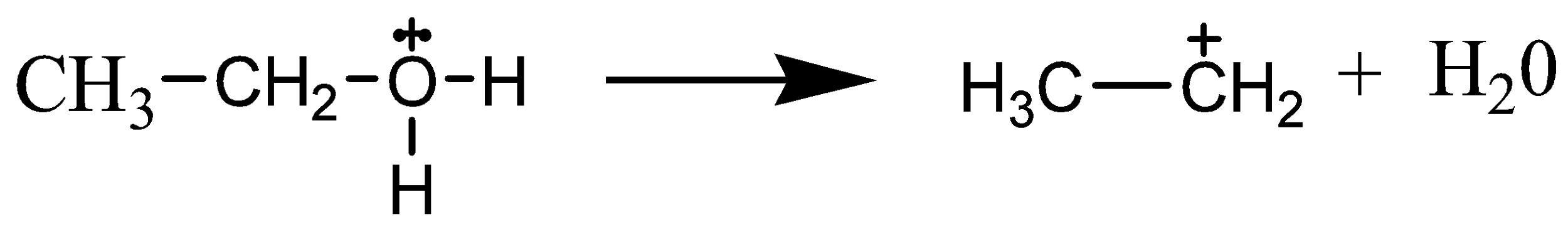
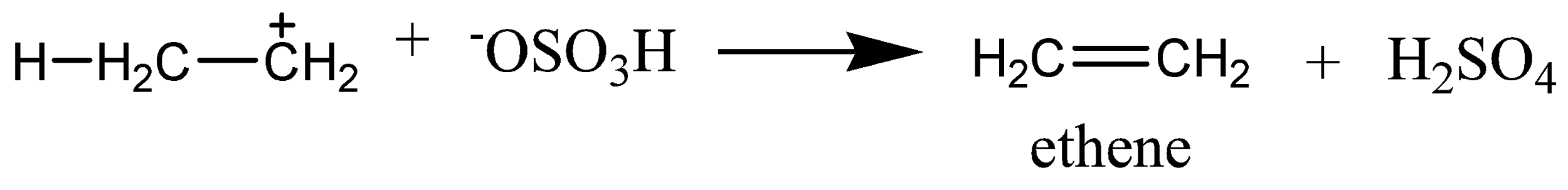
The mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene is shown below. In the first step is the protonation of oxygen atom of \[{\text{ - OH}}\] group by \[{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}\]. In the second step, there is loss of a molecule of water leading to the formation of a carbocation. While the last step involves the deprotonation to form a carbon-carbon double bond.
Acid dehydration of ethanol
Mechanism:
Additional Information:
1. Ethene is the IUPAC name for ethylene.
2. Ethene is a very important raw material used in the manufacture of polymers such as polyethylene (PE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polystyrene (PS) as well as fibers and other organic chemicals.
3. It finds application as a plant growth regulator.
4. The lamps made of ethene are useful for color development and ripening of fruits such as banana, mango, apple, etc.
Note:
We must know that the formation of the carbocation is the rate-determining step. In this step, the \[{\text{C - O}}\] bond breaks to generate a carbocation. This step is the slowest step in the mechanism of dehydration of an alcohol. Hence, the formation of the carbocation is considered as the rate-determining step.
Complete answer:
Ethanol when heated with concentrated sulphuric acid (acts as a catalyst); gases produced are passed through sodium hydroxide solution to remove the carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide produced as side products. Ethene is the main product collected over water. Hence, dehydration of ethanol to give ethene, not ethane.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
\[{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - OH}}\xrightarrow{{{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ = C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\]
Mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol:-
The mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene is shown below. In the first step is the protonation of oxygen atom of \[{\text{ - OH}}\] group by \[{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}\]. In the second step, there is loss of a molecule of water leading to the formation of a carbocation. While the last step involves the deprotonation to form a carbon-carbon double bond.
Acid dehydration of ethanol

Mechanism:



Additional Information:
1. Ethene is the IUPAC name for ethylene.
2. Ethene is a very important raw material used in the manufacture of polymers such as polyethylene (PE), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polystyrene (PS) as well as fibers and other organic chemicals.
3. It finds application as a plant growth regulator.
4. The lamps made of ethene are useful for color development and ripening of fruits such as banana, mango, apple, etc.
Note:
We must know that the formation of the carbocation is the rate-determining step. In this step, the \[{\text{C - O}}\] bond breaks to generate a carbocation. This step is the slowest step in the mechanism of dehydration of an alcohol. Hence, the formation of the carbocation is considered as the rate-determining step.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




