
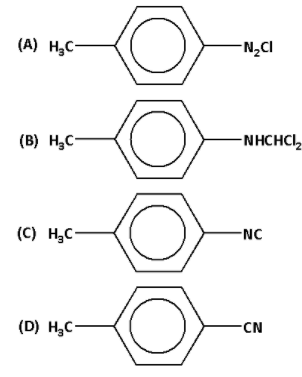
The reaction of chloroform with alcoholic \[{\text{KOH}}\] and p-toluidine forms:

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: The reaction of chloroform with alcoholic KOH and p-toluidine is known as a carbylamine reaction. It is a specific reaction for aliphatic and aromatic primary amines.
Complete step by step answer:
The molecular formula for chloroform is ${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$.
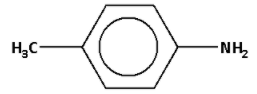
The structure of o-toluidine is as follows:
The reaction is known as carbylamine reaction or Hofmann isocyanide synthesis. The reaction mechanism involves the addition of amine to an intermediator formed by the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform. The intermediate is known as dichlorocarbene.
The reaction occurs between a primary amine, chloroform and a base. Isocyanides are synthesized in the reaction. The reaction cannot occur with secondary or tertiary amines.
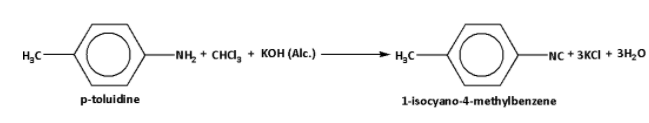
The reaction of chloroform with alcoholic \[{\text{KOH}}\] and p-toluidine is as follows:
Thus, the reaction of chloroform with alcohol \[{\text{KOH}}\] and p-toluidine form 1-isocyano-4-methylbenzene.
Thus, the reaction can be used for the synthesis of isocyanides from primary amines with chloroform and a strong base. The reaction can also be used to detect the presence of primary amines in a given sample.
Thus, the correct option is (D).
Note: We know that the carbylamine reaction occurs only with primary amines. Thus, the reaction can be used as a chemical test to detect the presence of primary amines. The carbylamine reaction is known as Hofmann’s isocyanide test when it is used as a test. In the test, the sample substance is heated with chloroform and alcohol \[{\text{KOH}}\]. If primary amine is present in the sample, isocyanide is produced which can be detected by its foul smell. If the sample contains secondary or tertiary amines, no foul smell is detected.
Complete step by step answer:
The molecular formula for chloroform is ${\text{CHC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}$.
The structure of o-toluidine is as follows:

The reaction is known as carbylamine reaction or Hofmann isocyanide synthesis. The reaction mechanism involves the addition of amine to an intermediator formed by the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform. The intermediate is known as dichlorocarbene.
The reaction occurs between a primary amine, chloroform and a base. Isocyanides are synthesized in the reaction. The reaction cannot occur with secondary or tertiary amines.
The reaction of chloroform with alcoholic \[{\text{KOH}}\] and p-toluidine is as follows:

Thus, the reaction of chloroform with alcohol \[{\text{KOH}}\] and p-toluidine form 1-isocyano-4-methylbenzene.
Thus, the reaction can be used for the synthesis of isocyanides from primary amines with chloroform and a strong base. The reaction can also be used to detect the presence of primary amines in a given sample.
Thus, the correct option is (D).
Note: We know that the carbylamine reaction occurs only with primary amines. Thus, the reaction can be used as a chemical test to detect the presence of primary amines. The carbylamine reaction is known as Hofmann’s isocyanide test when it is used as a test. In the test, the sample substance is heated with chloroform and alcohol \[{\text{KOH}}\]. If primary amine is present in the sample, isocyanide is produced which can be detected by its foul smell. If the sample contains secondary or tertiary amines, no foul smell is detected.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




