
The ratio of lateral strain to the linear strain within elastic limit is known as:
A. Young’s modulus
B. Bulk’s modulus
C. Rigidity modulus
D. Poisson’s ratio
Answer
530.1k+ views
Hint: Strain is the change in the dimension of a given body to the original dimension, when a force is applied on the body. Linear strain is a strain that occurs along the direction of the force and lateral strain is a strain that occurs perpendicular to linear strain.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When a force is exerted on a body, the body deforms. Deformation is the change in shape and size of the given body, when a force is applied on it. The degree of deformation depends on the material of the body. Some materials deform largely by a small force whereas some materials need a large force to be deformed.
We understand the extent of deformation in any demission (like length, breadth, height, volume etc.) of a body by the term called strain. Strain is the ratio of the amount of change in dimension of the body to the original dimension of the body.
For example, when we stretch a rubber band, the length of the band expands. Here, strain is the ratio of the change in length (when stretched) to the original length of the band. Suppose the original length of the rubber band is 4cm and the length changes to 8cm when stretched. Therefore, the strain in the length of the band is equal to $\dfrac{\text{change in length}}{\text{original length}}=\dfrac{\text{final length - original length}}{\text{original length}}=\dfrac{8cm-4cm}{4cm}=\dfrac{4cm}{4cm}=1$
Since strain is the ratio of two same quantities, (dimensions), strain has no dimension. Therefore, strain is a dimensional quantity.
There are two types of strains. One is strain along (parallel) the force applied called longitudinal strain or linear strain. Another is strain perpendicular to the force applied called lateral strain. The ratio of lateral strain to the longitudinal strain in a body within its elastic limit is called Poisson’s ratio. Elastic limit is the maximum point where the given body can completely reform into its original shape and size after the force has been removed.
We can understand this better by an example. Consider a regular cylinder. Suppose we stretch this cylinder from both ends. The cylinder expands in such a way that it expands longitudinally as well as laterally (perpendicularly).
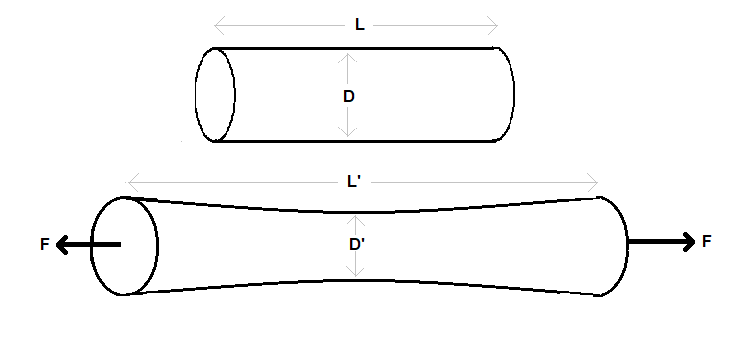
Here, the longitudinal strain is the strain in the length (height) of the cylinder. Lateral strain is the strain is the strain in the diameter of the cylinder. However, the lateral strain is not uniform in this case. Poisson’s ratio for this cylinder will be $\dfrac{\text{lateral strain}}{\text{linear strain}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{D'-D}{D}}{\dfrac{L'-L}{L}}$.
Note: The value of strain can be negative as well as positive. It depends on the direction of the applied force. If the force stretches or expands the given dimension of the body then the strain is positive. If the force compresses the dimension of the body, the strain is negative. In the above example of cylinder, the linear strain is positive but the lateral strain is negative.
Here we can understand that in most of the cases linear and lateral strain happen simultaneously. This means that if one dimension of the given body is elongated or expanded then another dimension compresses like it happened in the discussed example.
Young’s modulus is the ratio of longitudinal stress to the strain in the body.
Bulk’s modulus is the ratio of stress (pressure) to the volumetric strain. Bulk’s is mostly gases.
Rigidity modulus is the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain in the body.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When a force is exerted on a body, the body deforms. Deformation is the change in shape and size of the given body, when a force is applied on it. The degree of deformation depends on the material of the body. Some materials deform largely by a small force whereas some materials need a large force to be deformed.
We understand the extent of deformation in any demission (like length, breadth, height, volume etc.) of a body by the term called strain. Strain is the ratio of the amount of change in dimension of the body to the original dimension of the body.
For example, when we stretch a rubber band, the length of the band expands. Here, strain is the ratio of the change in length (when stretched) to the original length of the band. Suppose the original length of the rubber band is 4cm and the length changes to 8cm when stretched. Therefore, the strain in the length of the band is equal to $\dfrac{\text{change in length}}{\text{original length}}=\dfrac{\text{final length - original length}}{\text{original length}}=\dfrac{8cm-4cm}{4cm}=\dfrac{4cm}{4cm}=1$
Since strain is the ratio of two same quantities, (dimensions), strain has no dimension. Therefore, strain is a dimensional quantity.
There are two types of strains. One is strain along (parallel) the force applied called longitudinal strain or linear strain. Another is strain perpendicular to the force applied called lateral strain. The ratio of lateral strain to the longitudinal strain in a body within its elastic limit is called Poisson’s ratio. Elastic limit is the maximum point where the given body can completely reform into its original shape and size after the force has been removed.
We can understand this better by an example. Consider a regular cylinder. Suppose we stretch this cylinder from both ends. The cylinder expands in such a way that it expands longitudinally as well as laterally (perpendicularly).

Here, the longitudinal strain is the strain in the length (height) of the cylinder. Lateral strain is the strain is the strain in the diameter of the cylinder. However, the lateral strain is not uniform in this case. Poisson’s ratio for this cylinder will be $\dfrac{\text{lateral strain}}{\text{linear strain}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{D'-D}{D}}{\dfrac{L'-L}{L}}$.
Note: The value of strain can be negative as well as positive. It depends on the direction of the applied force. If the force stretches or expands the given dimension of the body then the strain is positive. If the force compresses the dimension of the body, the strain is negative. In the above example of cylinder, the linear strain is positive but the lateral strain is negative.
Here we can understand that in most of the cases linear and lateral strain happen simultaneously. This means that if one dimension of the given body is elongated or expanded then another dimension compresses like it happened in the discussed example.
Young’s modulus is the ratio of longitudinal stress to the strain in the body.
Bulk’s modulus is the ratio of stress (pressure) to the volumetric strain. Bulk’s is mostly gases.
Rigidity modulus is the ratio of shear stress to the shear strain in the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




