
The radius of a circle is \[16cm\]. The midpoint of a chord of the circle lies on the diameter perpendicular to the chord and its distance from the near end of the diameter is $3cm$. If the length of that chord is $m\sqrt {87} cm$, find the value of $m$.
A) 4
B) $8$
C) $2$
D) $1$
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: We can solve this problem using Pythagoras theorem. Since the diameter is perpendicular to the chord and bisects the chord, we can consider a right angled triangle. The hypotenuse will be the radius and other sides can be calculated with the given information.
Formula used:
Pythagoras theorem:
For a right angled triangle, \[{\text{bas}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}} + {\text{altitud}}{{\text{e}}^2} = {\text{hypotenuse}}{{\text{e}}^2}\], where hypotenuse is the side opposite to ${90^ \circ }$ angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that radius of the circle is $16cm$.
And also the midpoint of a chord of the circle lies on the diameter perpendicular to the chord.
So we can construct a right angled triangle.
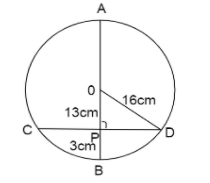
Here, $AB$ represents the diameter and $CD$ represents the chord perpendicular to it.
$ \Rightarrow AB = 16 \times 2 = 32,CD = m\sqrt {87} $
So we have, $PC = PD$ (since diameter passes through the midpoint)
$OD$ is the radius of the circle gives $OD = 16cm$
$OB$ is also radius to the circle and $PB = 3cm$ (given)
So we have, $OP = OB - PB = 16cm - 3cm = 13cm$
Now $\vartriangle OPD$ is a right triangle with hypotenuse $OD$.
For a right angled triangle, \[{\text{bas}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}} + {\text{altitud}}{{\text{e}}^2} = {\text{hypotenuse}}{{\text{e}}^2}\], where hypotenuse is the side opposite to ${90^ \circ }$ angle.
So, we have, $O{P^2} + P{D^2} = O{D^2}$
$ \Rightarrow P{D^2} = O{D^2} - O{P^2}$
Substituting the values we get,
$ \Rightarrow P{D^2} = {16^2} - {13^2} = 256 - 169 = 87$
Taking square root on both sides we get,
$ \Rightarrow PD = \sqrt {87} cm$
Since $PD$ is half the chord, length of the chord, $CD = 2\sqrt {87} cm$
But it is given that $CD = m\sqrt {87} cm$
Comparing we get, $m = 2$.
$\therefore $ The answer is option C.
Note: A diameter drawn perpendicular to any chord will bisect the chord. If as in the figure, $AB$ is the diameter and $CD$ is the chord perpendicular to it, then then $PC = PD$. Also we have $PA \times PB = P{C^2}$. Using this result too we can solve for $m$.
Formula used:
Pythagoras theorem:
For a right angled triangle, \[{\text{bas}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}} + {\text{altitud}}{{\text{e}}^2} = {\text{hypotenuse}}{{\text{e}}^2}\], where hypotenuse is the side opposite to ${90^ \circ }$ angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given that radius of the circle is $16cm$.
And also the midpoint of a chord of the circle lies on the diameter perpendicular to the chord.
So we can construct a right angled triangle.

Here, $AB$ represents the diameter and $CD$ represents the chord perpendicular to it.
$ \Rightarrow AB = 16 \times 2 = 32,CD = m\sqrt {87} $
So we have, $PC = PD$ (since diameter passes through the midpoint)
$OD$ is the radius of the circle gives $OD = 16cm$
$OB$ is also radius to the circle and $PB = 3cm$ (given)
So we have, $OP = OB - PB = 16cm - 3cm = 13cm$
Now $\vartriangle OPD$ is a right triangle with hypotenuse $OD$.
For a right angled triangle, \[{\text{bas}}{{\text{e}}^{\text{2}}} + {\text{altitud}}{{\text{e}}^2} = {\text{hypotenuse}}{{\text{e}}^2}\], where hypotenuse is the side opposite to ${90^ \circ }$ angle.
So, we have, $O{P^2} + P{D^2} = O{D^2}$
$ \Rightarrow P{D^2} = O{D^2} - O{P^2}$
Substituting the values we get,
$ \Rightarrow P{D^2} = {16^2} - {13^2} = 256 - 169 = 87$
Taking square root on both sides we get,
$ \Rightarrow PD = \sqrt {87} cm$
Since $PD$ is half the chord, length of the chord, $CD = 2\sqrt {87} cm$
But it is given that $CD = m\sqrt {87} cm$
Comparing we get, $m = 2$.
$\therefore $ The answer is option C.
Note: A diameter drawn perpendicular to any chord will bisect the chord. If as in the figure, $AB$ is the diameter and $CD$ is the chord perpendicular to it, then then $PC = PD$. Also we have $PA \times PB = P{C^2}$. Using this result too we can solve for $m$.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




