
What will be the product when \[{C_6}{H_6}C{l_6}\] is heated with alc. KOH? Explain the mechanism too.
Answer
486k+ views
Hint: A removal response is a kind of natural response wherein substituents are eliminated from a molecule in both a one- or -step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is called the E2 response, and the -step mechanism is called the E1 response. The numbers refer now no longer to the variety of steps withinside the mechanism, however instead to the kinetics of the response: E2 is bimolecular (2d-order) at the same time as E1 is unimolecular (first-order).
Complete answer:
The response will arise if all the atoms are in identical facets i.e. syn and the response will now no longer arise if the atoms are changed syn and anti.
E2 response is an Anti-removal response so see withinside the reaction given below:
1) In the first case the response will arise due to the fact the adjacent and atoms are Anti, so removal is required.
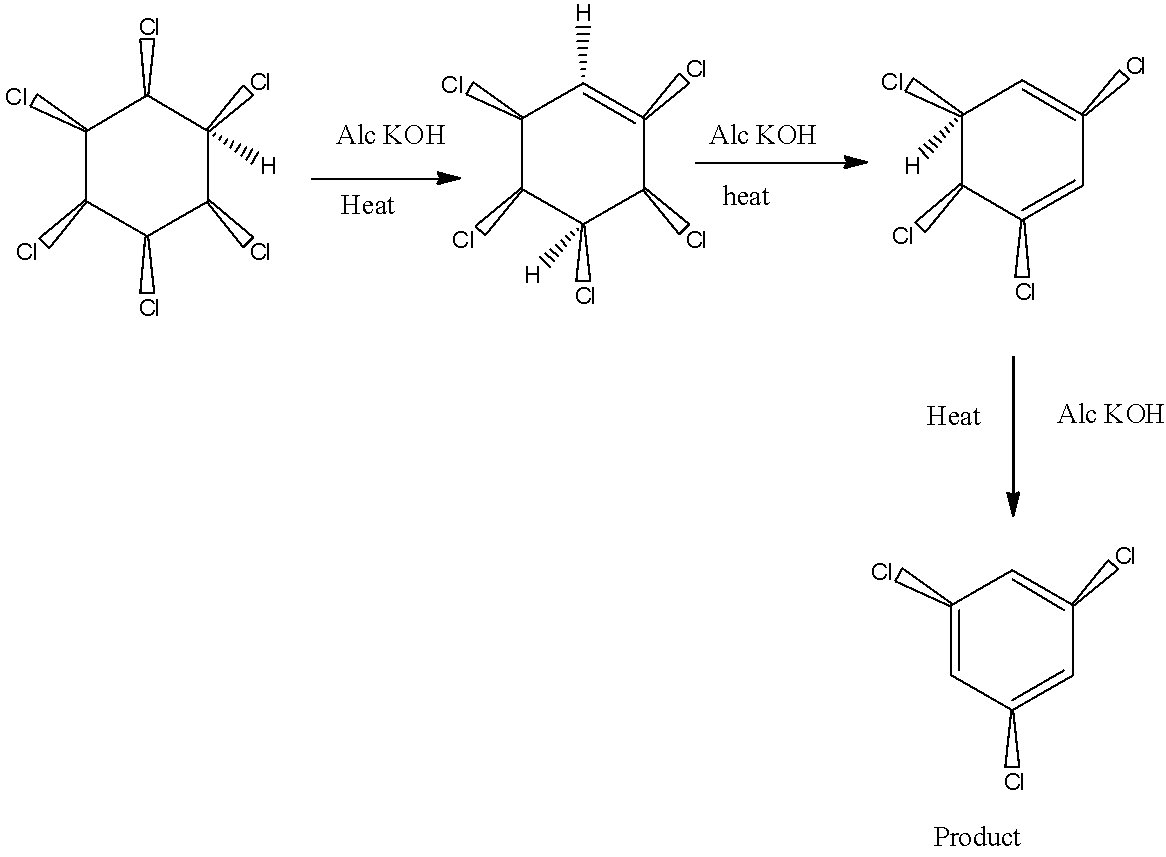
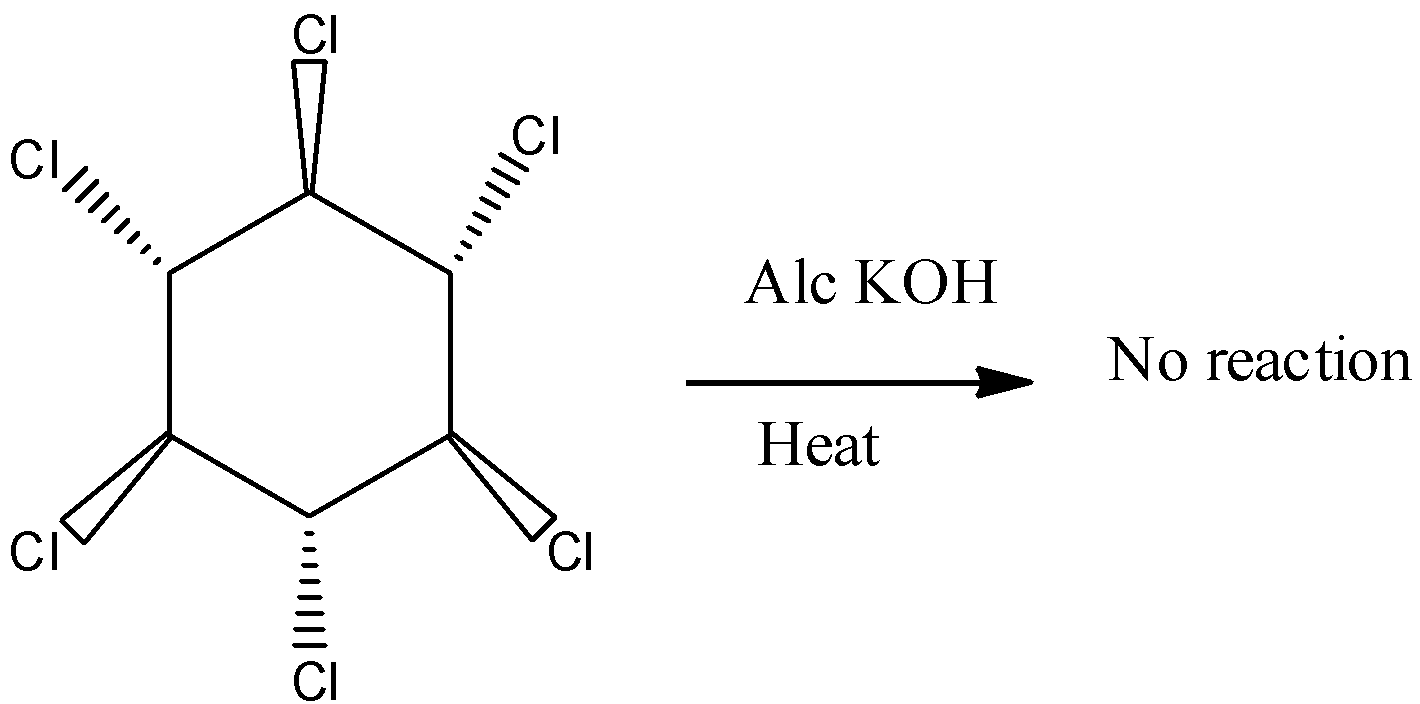
2) In the second case the response will now no longer arise due to the fact the adjacent and atoms are Syn so removal isn't always viable there in 2d case.
Note:
Syn addition is the addition of substituents to the identical facet (or face) of a double bond or triple bond, ensuing in a lower in bond order however a boom in the variety of substituents at the same time as in Anti addition is in direct comparison to syn addition. In anti addition, substituents are introduced to contrary sides (or faces) of a double bond or triple bond, over again ensuing in a lower in bond order and boom in the variety of substituents.
Complete answer:
The response will arise if all the atoms are in identical facets i.e. syn and the response will now no longer arise if the atoms are changed syn and anti.
E2 response is an Anti-removal response so see withinside the reaction given below:
1) In the first case the response will arise due to the fact the adjacent and atoms are Anti, so removal is required.

2) In the second case the response will now no longer arise due to the fact the adjacent and atoms are Syn so removal isn't always viable there in 2d case.

Note:
Syn addition is the addition of substituents to the identical facet (or face) of a double bond or triple bond, ensuing in a lower in bond order however a boom in the variety of substituents at the same time as in Anti addition is in direct comparison to syn addition. In anti addition, substituents are introduced to contrary sides (or faces) of a double bond or triple bond, over again ensuing in a lower in bond order and boom in the variety of substituents.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




