
The product formed in Gattermann-Koch reaction from benzene is:
A)Chloro benzene
B)Benzol chloride
C)Benzaldehyde
D)Acetophenone
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: We must know that Gattermann Koch Reaction Mechanism starts with the formation of the reactive species with the help of an acid. The overall purpose of the reaction is to attach a formyl group (-CHO group) to an aromatic system, thus forming an aromatic aldehyde as product.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When benzene is treated with carbon monoxide in an acidic medium in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it results in the production of benzaldehyde. This reaction is a name reaction, popularly known as Gattermann-Koch reaction. Anhydrous aluminium chloride acts as a catalyst in this reaction. We can call it as an electrophilic substitution reaction.
We can write the reaction as:

Let us discuss the mechanism of this reaction.
First step: Carbon monoxide acts as a Lewis base and accepts a proton from the hydrochloric acid forming a positively charged molecule which has different resonance structures. One of it displays a positive charge on the carbon and act as an electrophile while reacting with the aromatic ring. However, it is the target of a nucleophilic attack from the chloride ion in the hydrochloric acid.
The reaction starts with the interaction of carbon monoxide with hydrochloric acid such that it forms formyl chloride. We can write the reaction as:

Second step: The formed formyl chloride then reacts with anhydrous aluminium chloride which is a catalyst, and forms an electrophile or aldehyde intermediate. We can write this reaction as:
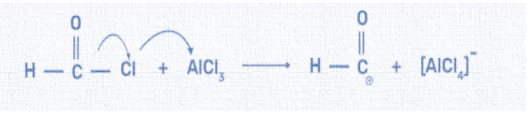
Third step: At last, the electrophile or the aldehyde group reacts with the benzene ring and forms the final product i.e. benzaldehyde. The aromatic ring behaves as a nucleophile and donates an electron pair to the formyl cation. The temporary loss of aromaticity is resolved by the expulsion of a proton simultaneously. This reaction results in the elimination of hydrochloric acid and aluminium chloride. We can write this reaction as:
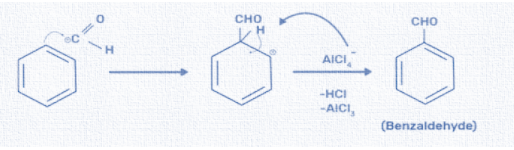
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: In Gattermann-Koch reaction, phenol and phenol ether substrates are not applicable. If we use zinc chloride as a catalyst in the Gattermann – Koch reaction, traces of copper(I) chloride are also necessary to be added since it works as a co-catalyst which enhance the action of catalysts.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When benzene is treated with carbon monoxide in an acidic medium in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it results in the production of benzaldehyde. This reaction is a name reaction, popularly known as Gattermann-Koch reaction. Anhydrous aluminium chloride acts as a catalyst in this reaction. We can call it as an electrophilic substitution reaction.
We can write the reaction as:

Let us discuss the mechanism of this reaction.
First step: Carbon monoxide acts as a Lewis base and accepts a proton from the hydrochloric acid forming a positively charged molecule which has different resonance structures. One of it displays a positive charge on the carbon and act as an electrophile while reacting with the aromatic ring. However, it is the target of a nucleophilic attack from the chloride ion in the hydrochloric acid.
The reaction starts with the interaction of carbon monoxide with hydrochloric acid such that it forms formyl chloride. We can write the reaction as:

Second step: The formed formyl chloride then reacts with anhydrous aluminium chloride which is a catalyst, and forms an electrophile or aldehyde intermediate. We can write this reaction as:

Third step: At last, the electrophile or the aldehyde group reacts with the benzene ring and forms the final product i.e. benzaldehyde. The aromatic ring behaves as a nucleophile and donates an electron pair to the formyl cation. The temporary loss of aromaticity is resolved by the expulsion of a proton simultaneously. This reaction results in the elimination of hydrochloric acid and aluminium chloride. We can write this reaction as:

Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: In Gattermann-Koch reaction, phenol and phenol ether substrates are not applicable. If we use zinc chloride as a catalyst in the Gattermann – Koch reaction, traces of copper(I) chloride are also necessary to be added since it works as a co-catalyst which enhance the action of catalysts.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




