
The product C is ?
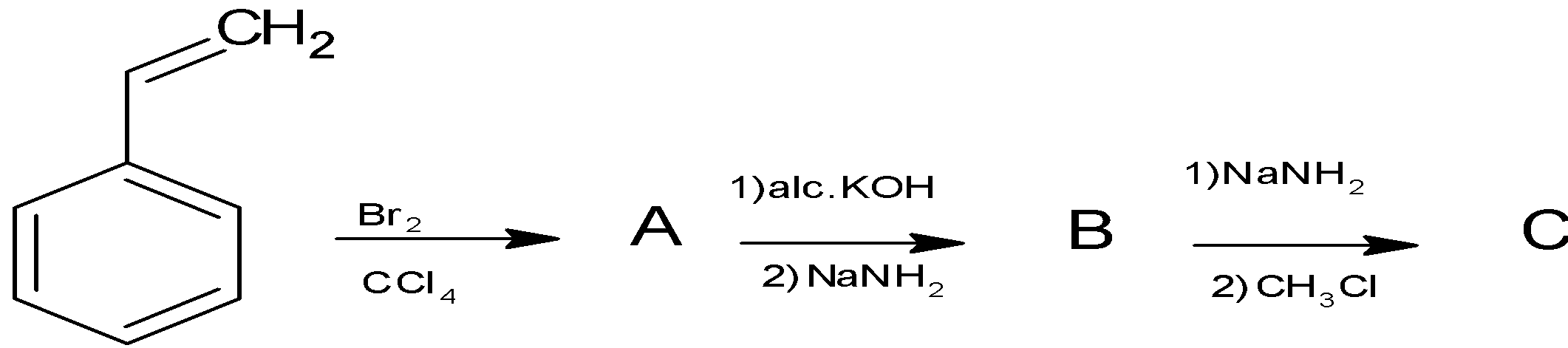
A.
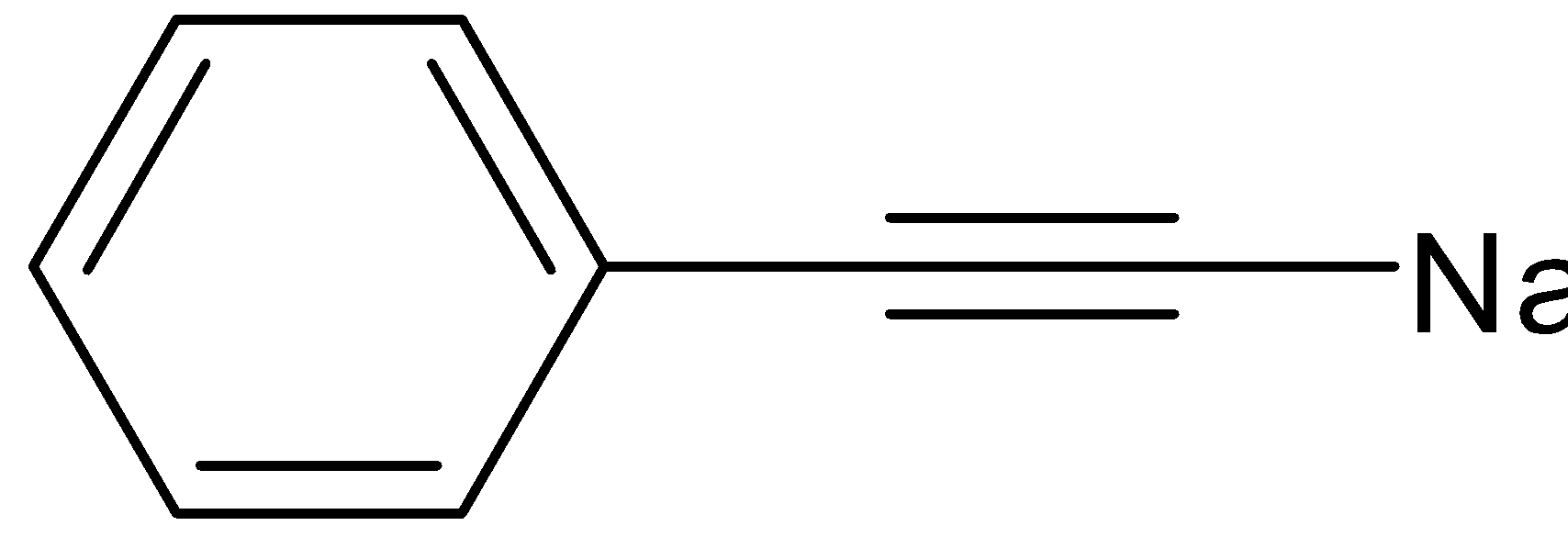
B.
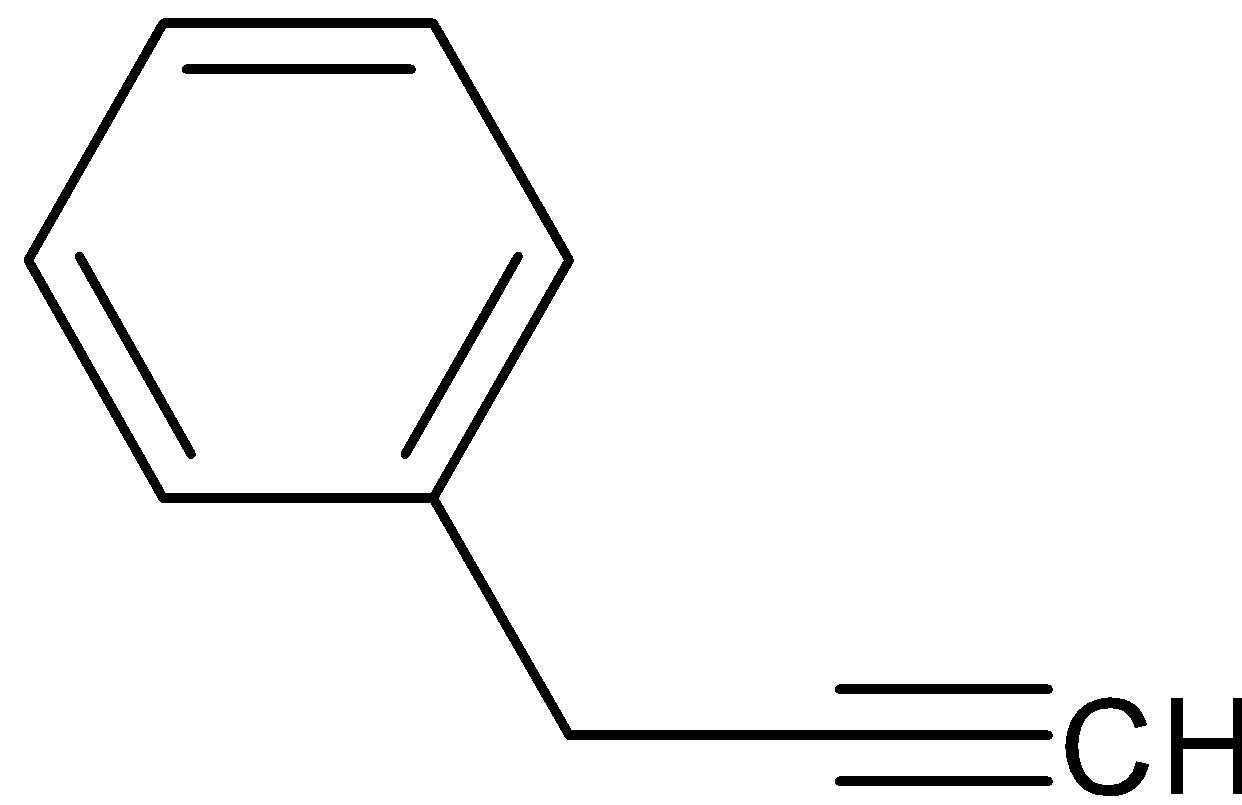
C.
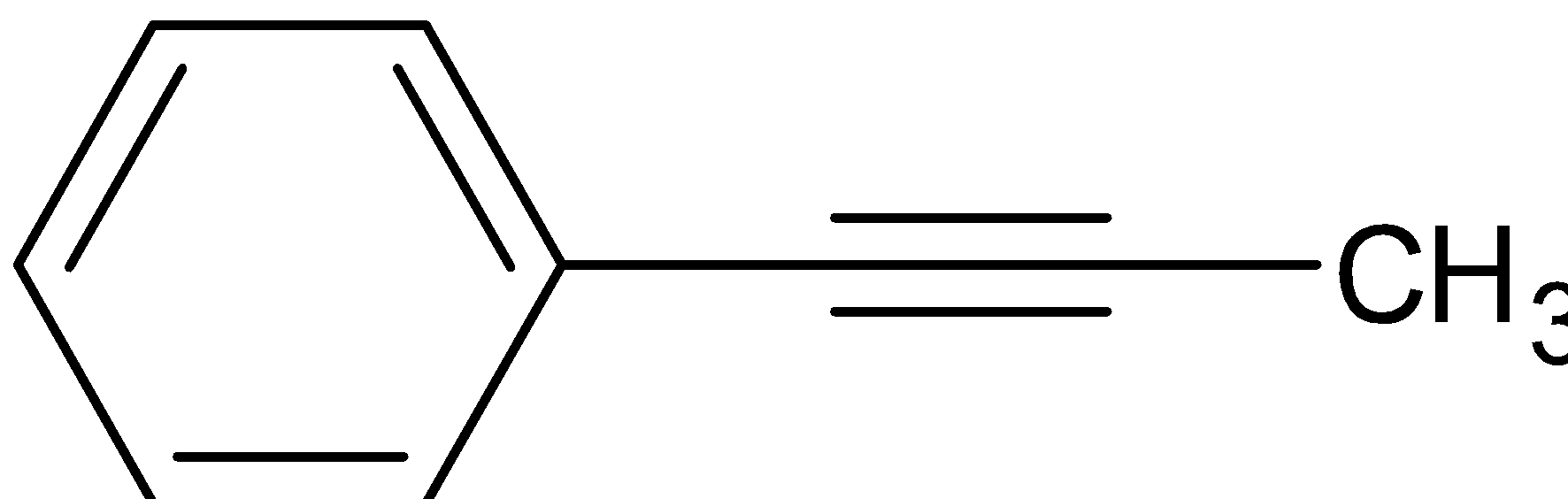
D.
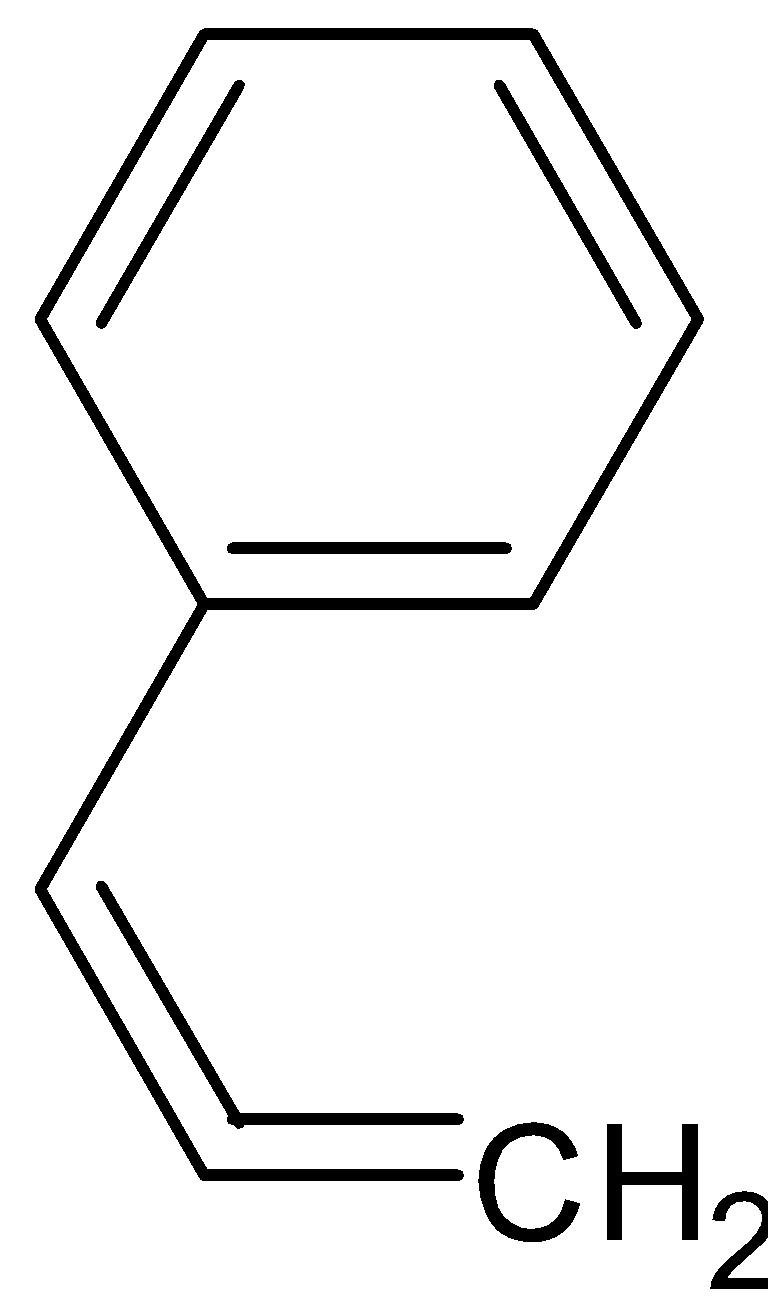





Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint:
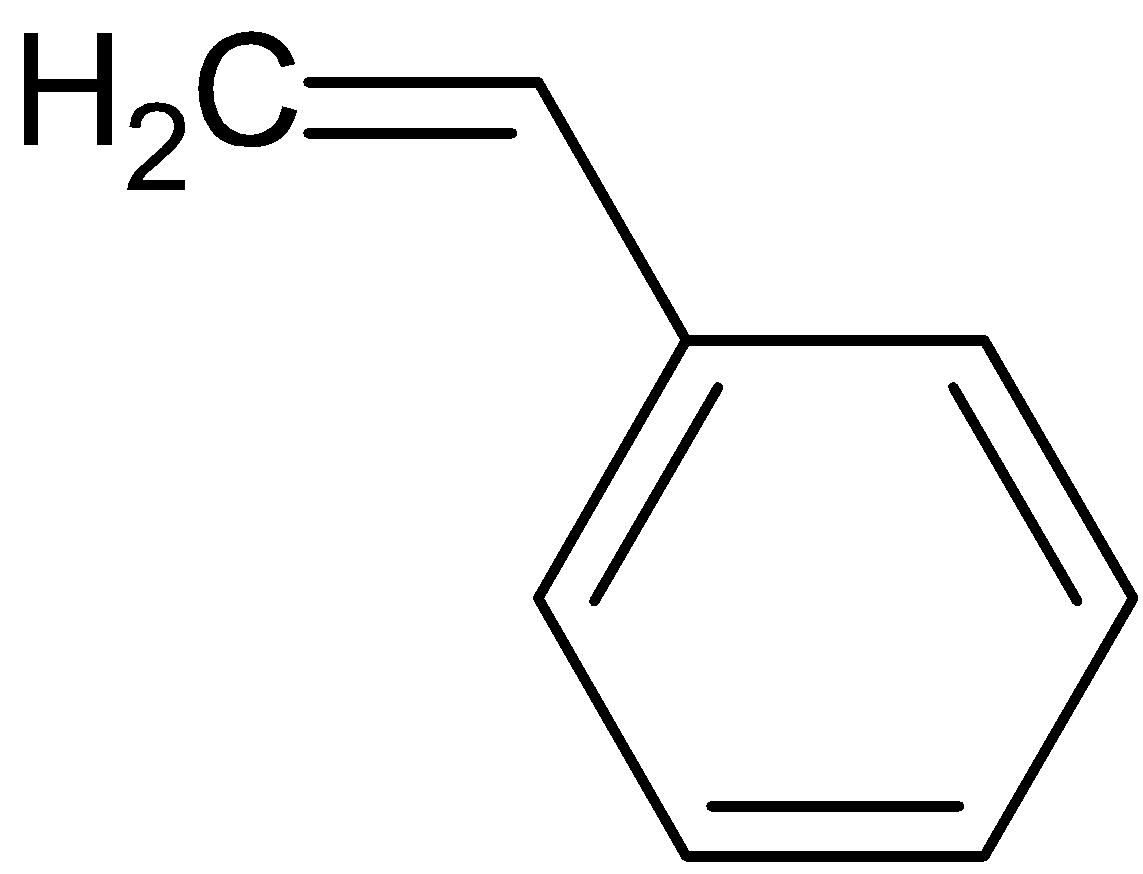
styrene is a liquid hydrocarbon which is highly important because of its marked tendency to undergo polymerization, polymerization is a process in which individual molecules are linked to produce extremely large molecules. Styrene is used in the manufacture of polystyrene which is an important plastic used widely.
Complete step by step solution:
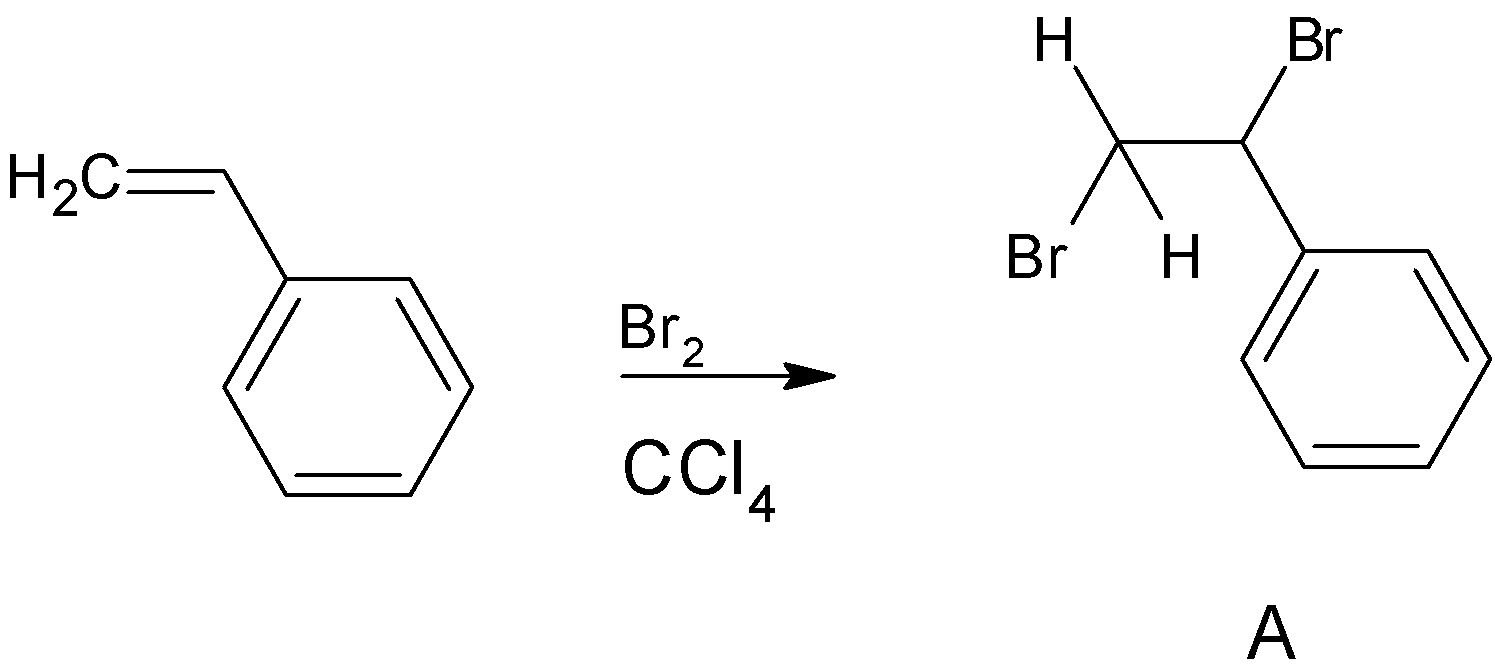
Since styrene has alkene in its side chain it can undergo most of the reactions which are given by alkene. Firstly styrene undergoes bromination in presence of the solvent $CCl_4$. So here the alkene side chain will undergo bromination reaction giving vicinal dibromides. Bromine s add to opposite faces of the double bond that is anti addition takes place here. Solvent $CCl_4$ has no effect on the reaction. We can write the reaction as
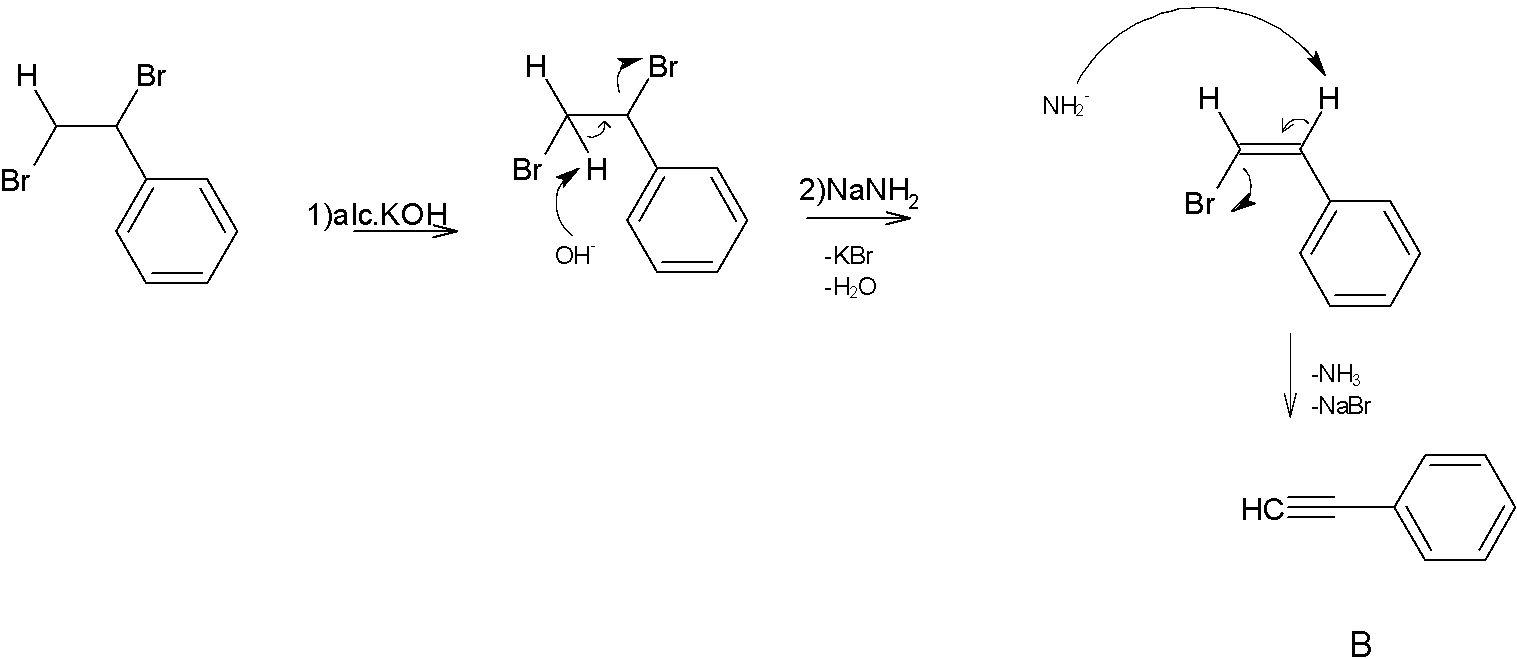
Next step the product A reacts with $NaNH_2$ in presence of alcoholic $KOH$. Where $NaNH_2$ is a strong base and excellent nucleophile which is used for deprotonation of weak acids and also for elimination reactions.one of the most common applications of $NaNH_2$ is formation of alkynes from halogens. That is treatment of geminal dihalides and vicinal dihalides with $NaNH_2$ gives corresponding alkynes.
When product B is treated with $NaNH_2$ and $CH_3Cl$, The strong base $NaNH_2$ will take the hydrogen atom from the terminal carbon atom to make it electron rich, which attracts the carbocation $CH_3^+$.
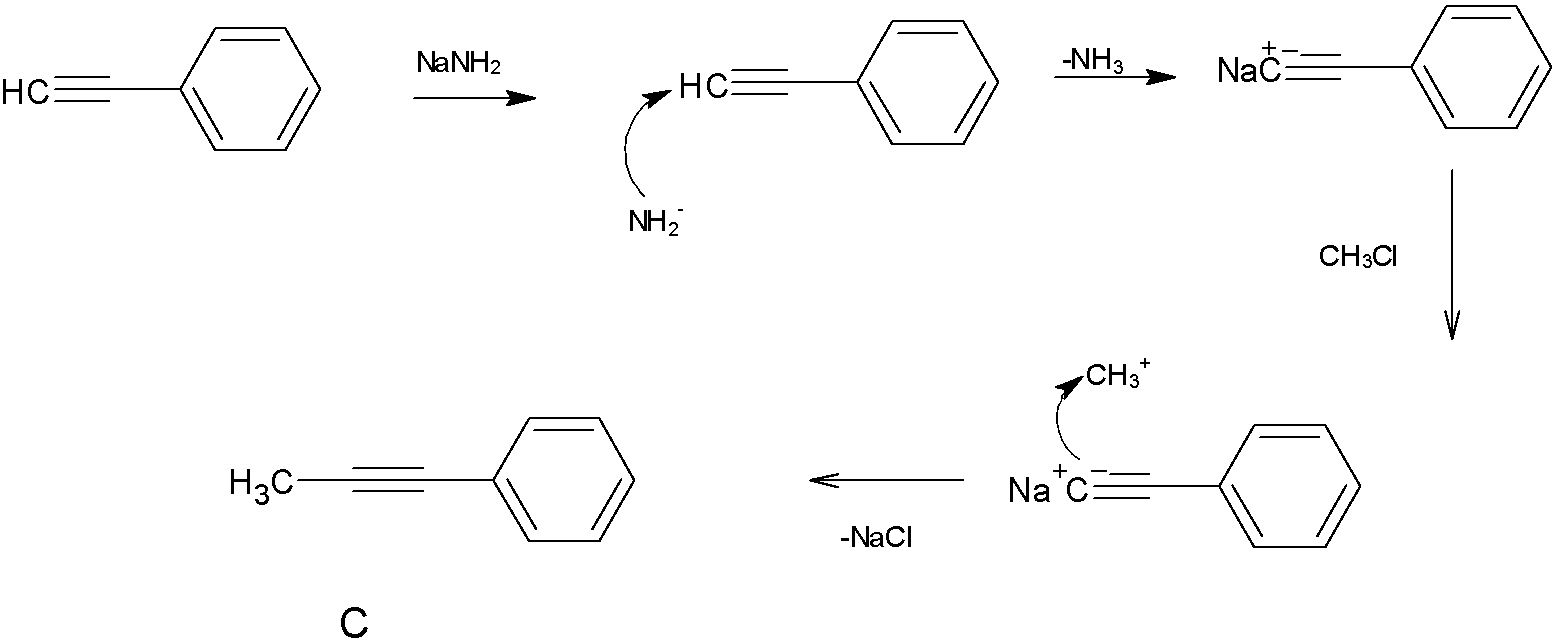
So here we get the product,its structure is given below
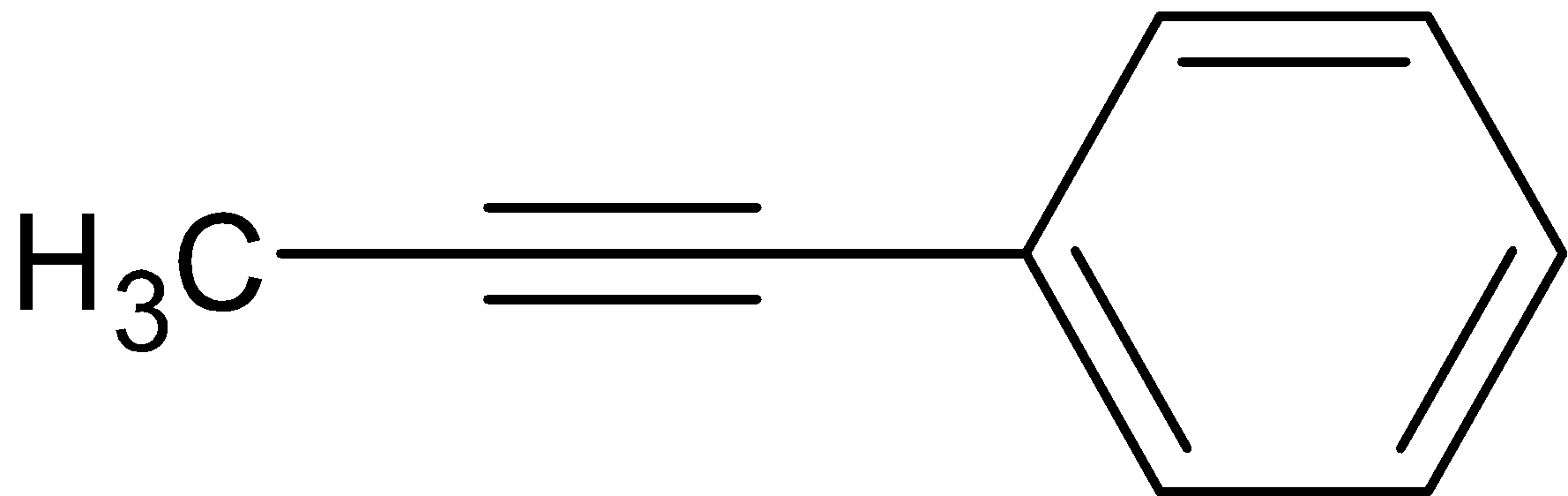
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Here the elimination reaction of di-bromides using $NaNH_2$ to make alkenes require the presence of bases because it is $E_2$ elimination. Formation of the product B is done by the elimination of H and bromine,which is an anti elimination that eliminates atoms are anti direction to each other, by which the product formed is an alkene with still a halide attached. This halide too can be removed to get the alkyne. Again the same $E_2$ elimination mechanism is followed for this.

styrene is a liquid hydrocarbon which is highly important because of its marked tendency to undergo polymerization, polymerization is a process in which individual molecules are linked to produce extremely large molecules. Styrene is used in the manufacture of polystyrene which is an important plastic used widely.
Complete step by step solution:
Since styrene has alkene in its side chain it can undergo most of the reactions which are given by alkene. Firstly styrene undergoes bromination in presence of the solvent $CCl_4$. So here the alkene side chain will undergo bromination reaction giving vicinal dibromides. Bromine s add to opposite faces of the double bond that is anti addition takes place here. Solvent $CCl_4$ has no effect on the reaction. We can write the reaction as

Next step the product A reacts with $NaNH_2$ in presence of alcoholic $KOH$. Where $NaNH_2$ is a strong base and excellent nucleophile which is used for deprotonation of weak acids and also for elimination reactions.one of the most common applications of $NaNH_2$ is formation of alkynes from halogens. That is treatment of geminal dihalides and vicinal dihalides with $NaNH_2$ gives corresponding alkynes.

When product B is treated with $NaNH_2$ and $CH_3Cl$, The strong base $NaNH_2$ will take the hydrogen atom from the terminal carbon atom to make it electron rich, which attracts the carbocation $CH_3^+$.

So here we get the product,its structure is given below

Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note: Here the elimination reaction of di-bromides using $NaNH_2$ to make alkenes require the presence of bases because it is $E_2$ elimination. Formation of the product B is done by the elimination of H and bromine,which is an anti elimination that eliminates atoms are anti direction to each other, by which the product formed is an alkene with still a halide attached. This halide too can be removed to get the alkyne. Again the same $E_2$ elimination mechanism is followed for this.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




