
The process of asexual reproduction in amoeba is
(a) Binary fission
(b) Budding
(c) Vegetative reproduction
(d) Spore formation
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint:Amoeba divides into two halves to form two daughter cells. In the process of asexual reproduction through which amoeba reproduces parent itself is a reproductive unit and continues to live as two daughter individuals.
Complete answer:
Amoeba reproduces asexually by the process called binary fission. Binary fission occurs in single- celled organisms belonging to Kingdom Monera, and Protista (Amoeba and paramecium). In this process, the parent organism divides into two halves, each half forming an independent daughter organism. It means the parent body as a whole form the reproductive unit, and the parent continues living as two daughter individuals.
Depending on the plane of division, binary fission is of the following types: Simple binary fission: Also known as irregular binary fission. A division can occur through any plane. For example Amoeba. Longitudinal Binary Fission: The plane of division passes along the longitudinal axis of the organism. Example, Euglena Transverse Binary division: The plane of this division runs along the transverse axis of the individual, for example, Bacteria, Paramoecium, Diatoms.
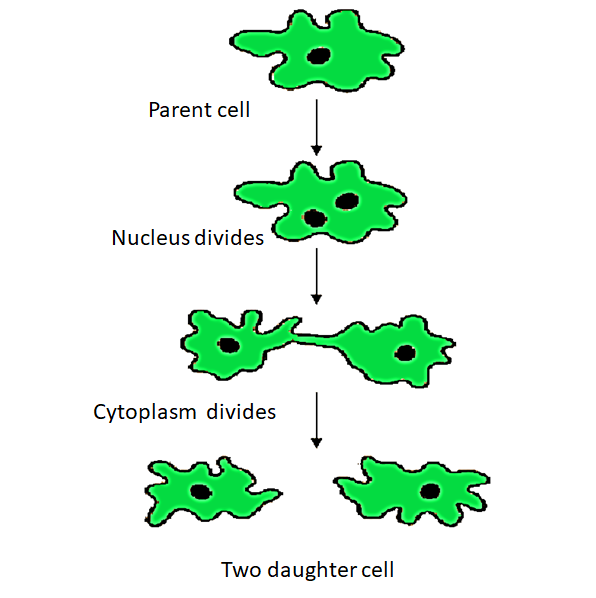
So, the answer is, ‘Binary fission’.
Note: - In binary fission cell division itself is a mode of reproduction. - It involves amitosis in bacteria and mitotic division of the nucleus in yeast and amoeba i.e.,
karyokinesis (a division of the cytoplasm) followed by cytokinesis (a division of the nucleus). - The parent cell in binary fission disappears. - Protuberance like in budding is absent in binary fission. - There is no change in the Chromosome Number of the daughter cells. - Organelles like Mitochondria also divide through binary fission.
Complete answer:
Amoeba reproduces asexually by the process called binary fission. Binary fission occurs in single- celled organisms belonging to Kingdom Monera, and Protista (Amoeba and paramecium). In this process, the parent organism divides into two halves, each half forming an independent daughter organism. It means the parent body as a whole form the reproductive unit, and the parent continues living as two daughter individuals.
Depending on the plane of division, binary fission is of the following types: Simple binary fission: Also known as irregular binary fission. A division can occur through any plane. For example Amoeba. Longitudinal Binary Fission: The plane of division passes along the longitudinal axis of the organism. Example, Euglena Transverse Binary division: The plane of this division runs along the transverse axis of the individual, for example, Bacteria, Paramoecium, Diatoms.

So, the answer is, ‘Binary fission’.
Note: - In binary fission cell division itself is a mode of reproduction. - It involves amitosis in bacteria and mitotic division of the nucleus in yeast and amoeba i.e.,
karyokinesis (a division of the cytoplasm) followed by cytokinesis (a division of the nucleus). - The parent cell in binary fission disappears. - Protuberance like in budding is absent in binary fission. - There is no change in the Chromosome Number of the daughter cells. - Organelles like Mitochondria also divide through binary fission.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




