
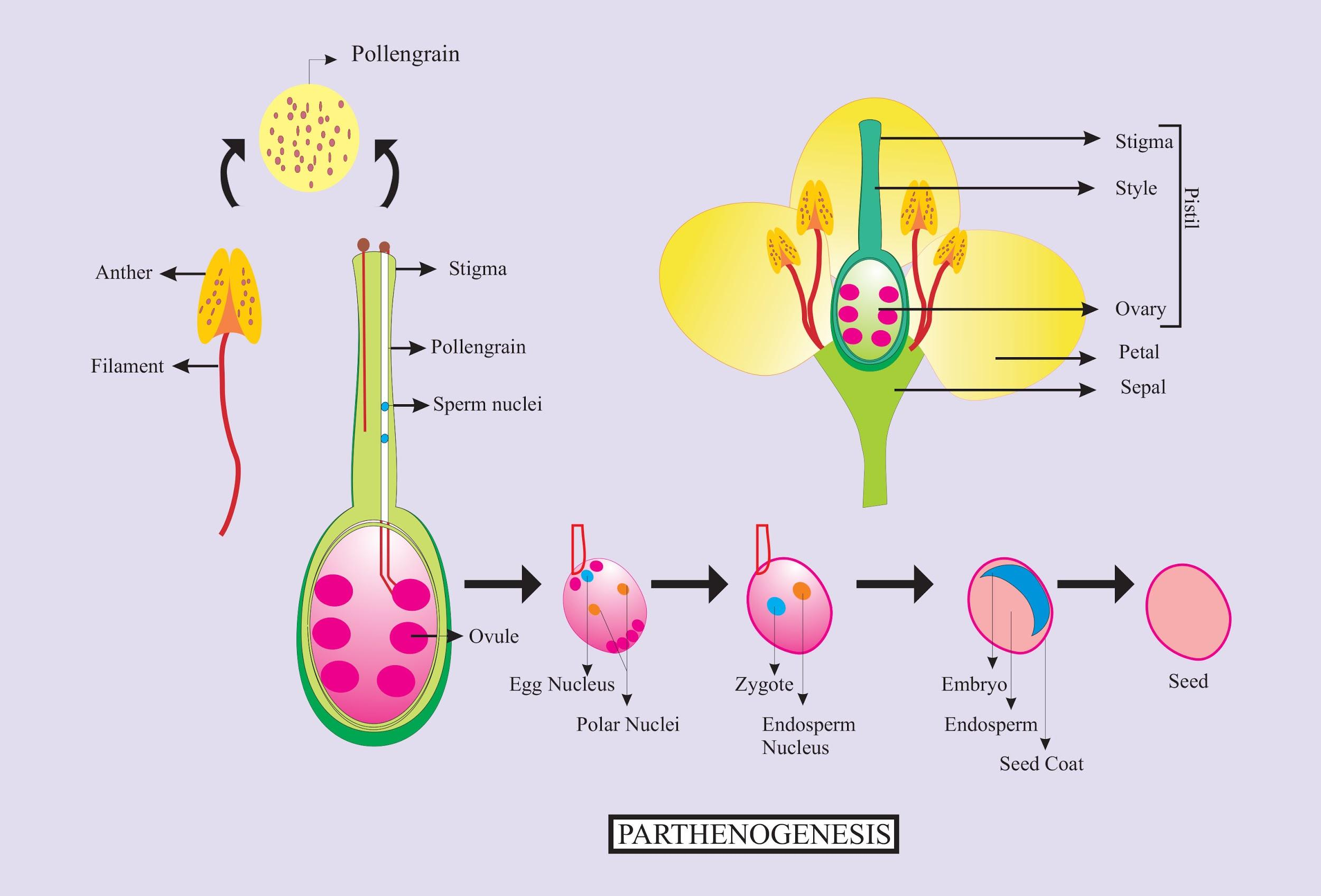
The process in which an embryo develops from unfertilized oosphere is called as
(a)Parthenogenesis
(b)Apospory
(c)Apogamy
(d)None of the above
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: It's a reproductive strategy that involves the event of a female (rarely a male) gamete (sex cell) without fertilization. It happens normally among lower plants and invertebrate creatures (especially rotifers, ants, wasps, aphids, and honey bees) and inconsistently among higher vertebrates.
Complete answer:
Apospory is the development of gametophyte without meiosis forming haploid spores.
Apogamy is the development of sporophyte without the standard syngamy of gametes. The apogamous sporophyte is going to be haploid sporophyte as against normal diploid sporophyte. Parthenogenesis is the development of an embryo without fertilization from an unfertilized egg.
Additional Information:
Parthenogenesis is typically viewed as an asexual sort of reproduction; be that as it may, it will be all the more precisely depicted as an "incomplete kind of amphimixis," since offspring of parthenogenic species creates from gametes. Gametes are reproductive cells that result from meiosis (or decrease division)— in which a particular cell with a (diploid) twofold arrangement of chromosomes goes through two splittings of its nucleus.
Meiosis gives rise to four gametes, or sex cells, which are haploid—in that everyone possesses half the amount of chromosomes of the first cell.
Parthenogenesis can operate either haploid or a diploid cell. In haploid parthenogenesis, a rare sort of parthenogenesis that happens during a few species of bees, nematodes, and plants, offspring develop from haploid eggs to supply haploid adults. On the contrary hand, the strategy for diploid parthenogenesis, a more normal and fluctuated kind of phenomenon, may continue along two pathways.
So the correct answer is ‘Parthenogenesis’.
Note: The variety of parthenogenic variations are observed. Some aphids and water fleas undergo a kind of parthenogenesis called heterogony or cyclic parthenogenesis. In these species, the ages of offspring delivered from treated eggs may substitute with those created from unfertilized ones. Such an alternation of generations in both groups of insects is assumed to result partly from seasonal temperature changes, with eggs produced through amphimixis having a greater ability to face up to the winter cold. They lie dormant until temperatures rise.
Complete answer:
Apospory is the development of gametophyte without meiosis forming haploid spores.
Apogamy is the development of sporophyte without the standard syngamy of gametes. The apogamous sporophyte is going to be haploid sporophyte as against normal diploid sporophyte. Parthenogenesis is the development of an embryo without fertilization from an unfertilized egg.
Additional Information:
Parthenogenesis is typically viewed as an asexual sort of reproduction; be that as it may, it will be all the more precisely depicted as an "incomplete kind of amphimixis," since offspring of parthenogenic species creates from gametes. Gametes are reproductive cells that result from meiosis (or decrease division)— in which a particular cell with a (diploid) twofold arrangement of chromosomes goes through two splittings of its nucleus.
Meiosis gives rise to four gametes, or sex cells, which are haploid—in that everyone possesses half the amount of chromosomes of the first cell.
Parthenogenesis can operate either haploid or a diploid cell. In haploid parthenogenesis, a rare sort of parthenogenesis that happens during a few species of bees, nematodes, and plants, offspring develop from haploid eggs to supply haploid adults. On the contrary hand, the strategy for diploid parthenogenesis, a more normal and fluctuated kind of phenomenon, may continue along two pathways.
So the correct answer is ‘Parthenogenesis’.
Note: The variety of parthenogenic variations are observed. Some aphids and water fleas undergo a kind of parthenogenesis called heterogony or cyclic parthenogenesis. In these species, the ages of offspring delivered from treated eggs may substitute with those created from unfertilized ones. Such an alternation of generations in both groups of insects is assumed to result partly from seasonal temperature changes, with eggs produced through amphimixis having a greater ability to face up to the winter cold. They lie dormant until temperatures rise.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




