
The primary building blocks of DNA are
A)Nitrogenous base, phosphorus, and ribose
B)Nitrogenous base, sulphur, and deoxyribose
C)Nitrogenous base, phosphorus, and deoxyribose
D)Nitrogenous base, sulphur, and ribose
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: The DNA is made up of four types of molecules. These molecules are also called the base and they are attached to a sugar-phosphate backbone. DNA has four bases which are Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T). These bases pair across the two strands of the helix i.e Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Cytosine pairs with Guanine.
Complete answer:
The biological instructions that make a species unique are contained in Deoxyribonucleic acid. The instructions are passed from adult organisms to their offspring during reproduction.
-The chemical building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. These nucleotides are made up of three parts - a phosphate group, a sugar group, and one of four types of nitrogen bases.
-the nucleotides linked together to form a strand of DNA, with the phosphate and sugar group.
-The nitrogen bases have four bases which are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The patterns of these bases determine what biological instructions are stored in a strand of DNA
Additional Information: -DNA is found in the cell called nucleus in all the eukaryotic organisms. A DNA molecule is tightly packaged and this package form of DNA is called chromosomes.
-DNA unwinds during the replication which helps make it possible to be copied. It also unwinds so that instructions can be utilized to make proteins.
-DNA is in compact chromosomes form to allow transfer to new cells during cell division.
So, the correct answer is,” Nitrogenous base, phosphorus, and deoxyribose”.
Note: -For the organisms to survive, reproduce, and develop DNA is important because it contains instructions that are needed for all these processes.
-The sequences of each DNA consist of instructions to make protein known as a gene.
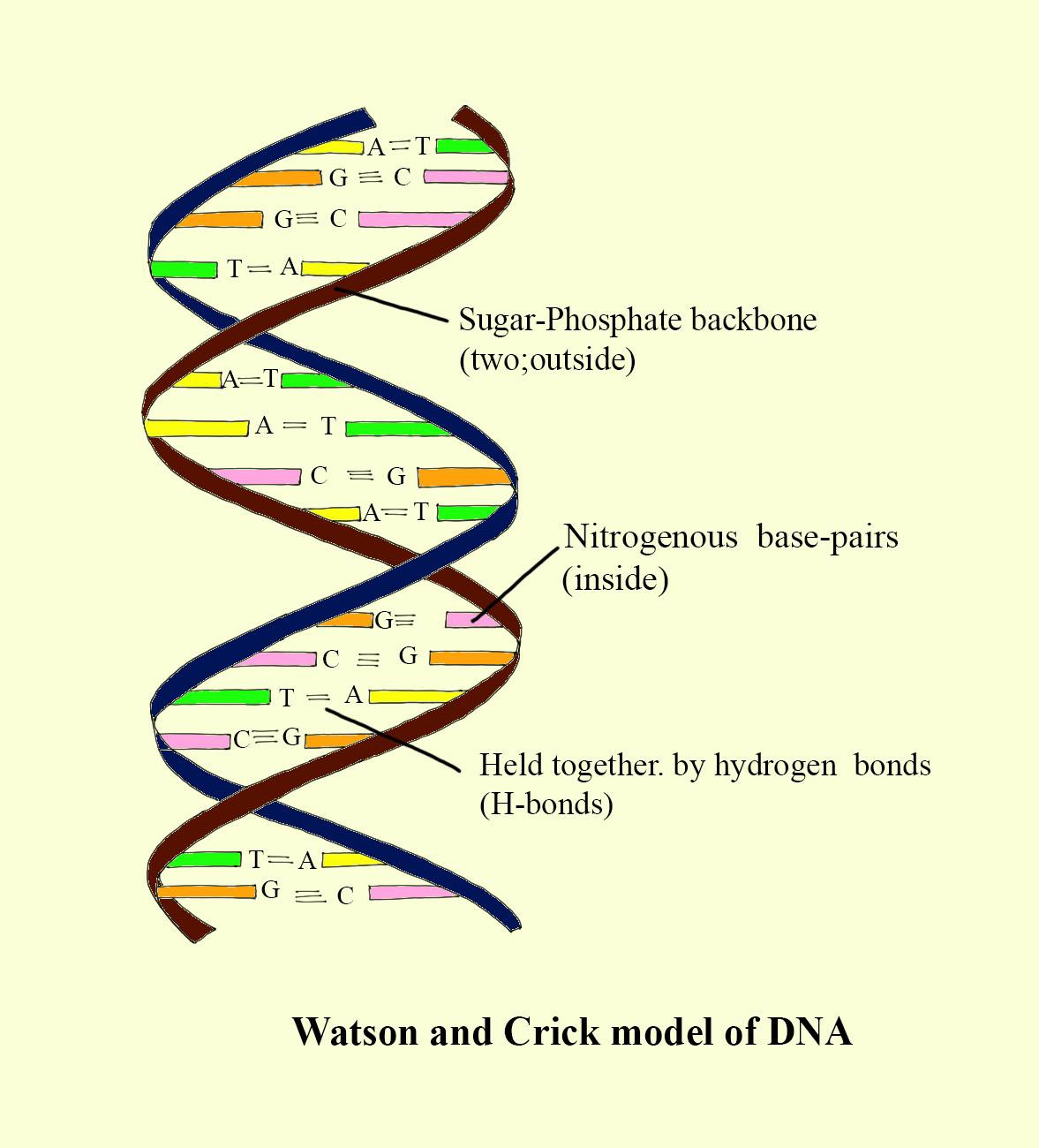
Complete answer:
The biological instructions that make a species unique are contained in Deoxyribonucleic acid. The instructions are passed from adult organisms to their offspring during reproduction.
-The chemical building blocks of DNA are nucleotides. These nucleotides are made up of three parts - a phosphate group, a sugar group, and one of four types of nitrogen bases.
-the nucleotides linked together to form a strand of DNA, with the phosphate and sugar group.
-The nitrogen bases have four bases which are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). The patterns of these bases determine what biological instructions are stored in a strand of DNA
Additional Information: -DNA is found in the cell called nucleus in all the eukaryotic organisms. A DNA molecule is tightly packaged and this package form of DNA is called chromosomes.
-DNA unwinds during the replication which helps make it possible to be copied. It also unwinds so that instructions can be utilized to make proteins.
-DNA is in compact chromosomes form to allow transfer to new cells during cell division.
So, the correct answer is,” Nitrogenous base, phosphorus, and deoxyribose”.
Note: -For the organisms to survive, reproduce, and develop DNA is important because it contains instructions that are needed for all these processes.
-The sequences of each DNA consist of instructions to make protein known as a gene.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




