
The positively charged center in an atom is called as:
A. Nucleus
B. Neutrons
C. Protons
D. Electrons
Answer
615.6k+ views
Hint- In order to deal with this question first we will understand the terms atom, proton, neutron then according to the atomic particle diagram we will try to find out our answer.
Complete answer:
Atom: The smallest volume of matter that nevertheless maintains its status as a chemical element and it constitutes of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.
Atomic Particles
Atoms are composed of three elementary particles: protons, electrons , and neutrons. Atom nucleus (center) includes the protons (positively charged) and the neutrons (without charge). The atom's outermost regions are called electron shells and have the electrons (negative charged).
Proton: Positively charged subatomic particle forms part of an atom's nucleus, and decides an element's atomic number. Weighing 1 amu.
Neutron: A subatomic particle that forms part of an atomic nucleus. There's no charge to it. It is equal to a proton in mass, or weights 1 amu.
Figure:
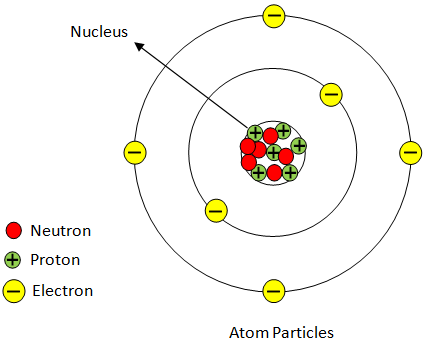
Hence, positively charged center in an atom is called as nucleus.
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note- An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter constituent which constitutes a chemical element. Each solid , liquid, gas, and plasma consists of either neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small , usually approximately 100 picometers across. There are various models of atom, some of them are: Dalton model (Billiard ball model), Thomson model (Plum pudding model), Lewis model (Cubical atom model), Nagaoka model (Saturnian model), Rutherford model (Planetary model), Bohr model (Rutherford–Bohr model).
Complete answer:
Atom: The smallest volume of matter that nevertheless maintains its status as a chemical element and it constitutes of a nucleus surrounded by electrons.
Atomic Particles
Atoms are composed of three elementary particles: protons, electrons , and neutrons. Atom nucleus (center) includes the protons (positively charged) and the neutrons (without charge). The atom's outermost regions are called electron shells and have the electrons (negative charged).
Proton: Positively charged subatomic particle forms part of an atom's nucleus, and decides an element's atomic number. Weighing 1 amu.
Neutron: A subatomic particle that forms part of an atomic nucleus. There's no charge to it. It is equal to a proton in mass, or weights 1 amu.
Figure:

Hence, positively charged center in an atom is called as nucleus.
So, the correct answer is option A.
Note- An atom is the smallest unit of ordinary matter constituent which constitutes a chemical element. Each solid , liquid, gas, and plasma consists of either neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are extremely small , usually approximately 100 picometers across. There are various models of atom, some of them are: Dalton model (Billiard ball model), Thomson model (Plum pudding model), Lewis model (Cubical atom model), Nagaoka model (Saturnian model), Rutherford model (Planetary model), Bohr model (Rutherford–Bohr model).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




