
The point $ (7,24) $ is on the terminal side of an angle in standard position, how do you determine the exact values of the six trigonometric functions of the angle?
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: In order to determine exact values of all six trigonometric function of the angle in the above question ,calculate $ r = \sqrt {{x^2} + {y^2}} $ where x will be 7 and y will be 24.And then find all the trigonometric ratios considering Hypotenuse as r ,opposite as 24 and adjacent as 7.
Formula:
\[
\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}} \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{Adjacent}} \\
\cos ec\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}} \\
sec\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{Adjacent}} \\
\cot \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}} \\
\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given a point P $ (7,24) $ which is on the terminal side of an angle in standard position.
Let x be 7 and y be 24
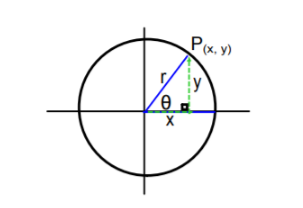
Calculating r using formula $ r = \sqrt {{x^2} + {y^2}} $
$
r = \sqrt {{{(7)}^2} + {{(24)}^2}} \\
r = \sqrt {49 + 576} \\
r = \sqrt {625} \\
r = 25 \;
$
Hence , value of r is $ 25 $
Therefore Calculating all the trigonometric ratios as
\[
\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{y}{r} = \dfrac{{24}}{{25}} \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{x}{r} = \dfrac{7}{{25}} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{Adjacent}} = \dfrac{y}{x} = \dfrac{{24}}{7} \\
\cos ec\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}} = \dfrac{r}{y} = \dfrac{{25}}{{24}} \\
sec\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{Adjacent}} = \dfrac{r}{x} = \dfrac{{25}}{7} \\
\cot \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}} = \dfrac{x}{y} = \dfrac{7}{{24}} \;
\]
Note: 1. Periodic Function= A function $ f(x) $ is said to be a periodic function if there exists a real number T > 0 such that $ f(x + T) = f(x) $ for all x.
If T is the smallest positive real number such that $ f(x + T) = f(x) $ for all x, then T is called the fundamental period of $ f(x) $ .
Since $ \sin \,(2n\pi + \theta ) = \sin \theta $ for all values of $ \theta $ and n $ \in $ N.
2. Even Function – A function $ f(x) $ is said to be an even function ,if $ f( - x) = f(x) $ for all x in its domain.
Odd Function – A function $ f(x) $ is said to be an even function ,if $ f( - x) = - f(x) $ for all x in its domain.
We know that $ \sin ( - \theta ) = - \sin \theta .\cos ( - \theta ) = \cos \theta \,and\,\tan ( - \theta ) = - \tan \theta $
Therefore, $ \sin \theta $ and $ \tan \theta $ and their reciprocals, $ \cos ec\theta $ and $ \cot \theta $ are odd functions whereas \[\cos \theta \] and its reciprocal \[\sec \theta \] are even functions.
Formula:
\[
\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}} \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{Adjacent}} \\
\cos ec\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}} \\
sec\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{Adjacent}} \\
\cot \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}} \\
\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given a point P $ (7,24) $ which is on the terminal side of an angle in standard position.
Let x be 7 and y be 24

Calculating r using formula $ r = \sqrt {{x^2} + {y^2}} $
$
r = \sqrt {{{(7)}^2} + {{(24)}^2}} \\
r = \sqrt {49 + 576} \\
r = \sqrt {625} \\
r = 25 \;
$
Hence , value of r is $ 25 $
Therefore Calculating all the trigonometric ratios as
\[
\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{y}{r} = \dfrac{{24}}{{25}} \\
\cos \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}} = \dfrac{x}{r} = \dfrac{7}{{25}} \\
\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{Adjacent}} = \dfrac{y}{x} = \dfrac{{24}}{7} \\
\cos ec\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}} = \dfrac{r}{y} = \dfrac{{25}}{{24}} \\
sec\theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{Adjacent}} = \dfrac{r}{x} = \dfrac{{25}}{7} \\
\cot \theta = \dfrac{{Adjacent}}{{{\text{Opposite}}}} = \dfrac{x}{y} = \dfrac{7}{{24}} \;
\]
Note: 1. Periodic Function= A function $ f(x) $ is said to be a periodic function if there exists a real number T > 0 such that $ f(x + T) = f(x) $ for all x.
If T is the smallest positive real number such that $ f(x + T) = f(x) $ for all x, then T is called the fundamental period of $ f(x) $ .
Since $ \sin \,(2n\pi + \theta ) = \sin \theta $ for all values of $ \theta $ and n $ \in $ N.
2. Even Function – A function $ f(x) $ is said to be an even function ,if $ f( - x) = f(x) $ for all x in its domain.
Odd Function – A function $ f(x) $ is said to be an even function ,if $ f( - x) = - f(x) $ for all x in its domain.
We know that $ \sin ( - \theta ) = - \sin \theta .\cos ( - \theta ) = \cos \theta \,and\,\tan ( - \theta ) = - \tan \theta $
Therefore, $ \sin \theta $ and $ \tan \theta $ and their reciprocals, $ \cos ec\theta $ and $ \cot \theta $ are odd functions whereas \[\cos \theta \] and its reciprocal \[\sec \theta \] are even functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




