
The percentage of free $S{{O}_{3}}$ in oleum sample which is labelled as 106% is:
A. 55%
B. 26.67%
C. 38%
D. 43.33%
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: As we know that the molecular formula of oleum is ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}.S{{O}_{3}}$, which is produced by contact process. It is found that oleum acts as an intermediate in production of sulphuric acid. The structure of Fuming sulphuric acid is:
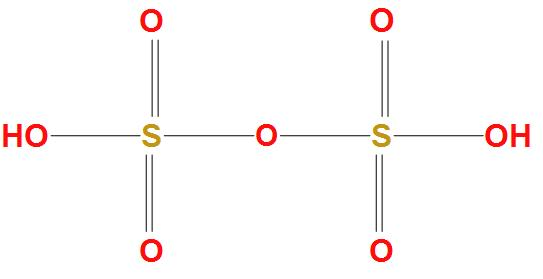
Complete answer:
- As we know that the formula of oleum is ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}.S{{O}_{3}}$ .
- When we will add water in ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}.S{{O}_{3}}$ it will form ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ as the water molecule is found to react with $S{{O}_{3}}$, and will give ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$.
- 106% labelled oleum means 100 g oleum will react with ${{H}_{2}}O$ to form 106% ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$.
- Therefore, we can say that the mass of ${{H}_{2}}O$ = 106 g - 100 g = 6 g.
- Actually, as we have discussed that water molecule is found to react with $S{{O}_{3}}$, and will give ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$. Here, 1 mole of $S{{O}_{3}}$ reacts with 1 mole of water to form 1 mole of sulphuric acid.
The molar mass of $S{{O}_{3}}$ , ${{H}_{2}}O$ and ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ is 80 g, 18 g , 98 g. We can calculate them as: molar mass of $S{{O}_{3}}$:
\[\begin{align}
& S{{O}_{3}} \\
& =32+3\times \left( 16 \right) \\
& =32+48 \\
& =80 \\
\end{align}\]
molar mass of ${{H}_{2}}O$:
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{2}}O \\
& =2\times \left( 1 \right)+16 \\
& =2+16 \\
& =18 \\
\end{align}\]
molar mass of ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$:
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} \\
& =2\times \left( 1 \right)+32+4\times (16) \\
& =2+32+64 \\
& =98 \\
\end{align}\]
- This means that 80 g $S{{O}_{3}}$will react with 18 g water to form 98 g ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$.
- Now, as 80 g $S{{O}_{3}}$ will react with 18 g water, we can say that 6 g ${{H}_{2}}O$ reacts with :
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{80}{18}\times 6\text{ }g \\
& =26.67\text{ }g \\
\end{align}$
- Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is (b), that is the percentage of free $S{{O}_{3}}$ in an oleum sample which is labelled as 106% is 26.67% .
Note: - We must note here that oleum (${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$) is also called as fuming sulphuric acid, these terms basically refer to solutions of various compositions of sulphur trioxide in sulphuric acid or we can say sometimes more specifically to disulfuric acid.

Complete answer:
- As we know that the formula of oleum is ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}.S{{O}_{3}}$ .
- When we will add water in ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}.S{{O}_{3}}$ it will form ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ as the water molecule is found to react with $S{{O}_{3}}$, and will give ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$.
- 106% labelled oleum means 100 g oleum will react with ${{H}_{2}}O$ to form 106% ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$.
- Therefore, we can say that the mass of ${{H}_{2}}O$ = 106 g - 100 g = 6 g.
- Actually, as we have discussed that water molecule is found to react with $S{{O}_{3}}$, and will give ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$. Here, 1 mole of $S{{O}_{3}}$ reacts with 1 mole of water to form 1 mole of sulphuric acid.
The molar mass of $S{{O}_{3}}$ , ${{H}_{2}}O$ and ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ is 80 g, 18 g , 98 g. We can calculate them as: molar mass of $S{{O}_{3}}$:
\[\begin{align}
& S{{O}_{3}} \\
& =32+3\times \left( 16 \right) \\
& =32+48 \\
& =80 \\
\end{align}\]
molar mass of ${{H}_{2}}O$:
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{2}}O \\
& =2\times \left( 1 \right)+16 \\
& =2+16 \\
& =18 \\
\end{align}\]
molar mass of ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$:
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}} \\
& =2\times \left( 1 \right)+32+4\times (16) \\
& =2+32+64 \\
& =98 \\
\end{align}\]
- This means that 80 g $S{{O}_{3}}$will react with 18 g water to form 98 g ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$.
- Now, as 80 g $S{{O}_{3}}$ will react with 18 g water, we can say that 6 g ${{H}_{2}}O$ reacts with :
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{80}{18}\times 6\text{ }g \\
& =26.67\text{ }g \\
\end{align}$
- Hence, we can conclude that the correct option is (b), that is the percentage of free $S{{O}_{3}}$ in an oleum sample which is labelled as 106% is 26.67% .
Note: - We must note here that oleum (${{H}_{2}}{{S}_{2}}{{O}_{7}}$) is also called as fuming sulphuric acid, these terms basically refer to solutions of various compositions of sulphur trioxide in sulphuric acid or we can say sometimes more specifically to disulfuric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




