
The part of the ear which distinguishes different pitches of sound is
A. Auditory nerve
B. Semicircular canal
C. Organ of Corti
D. Scala media
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. The organs of hearing and equilibrium convert mechanical energy to receptor(action) potential. Therefore they are called mechanoreceptors. The ears are located on the sides of the head.
The ears show three parts: external, middle, and internal.
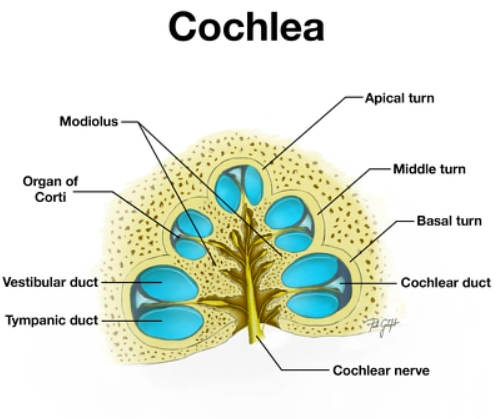
Complete answer: The ear not only detects sound but also notes its direction judges its loudness and determines its pitch (frequency).
1. The vibration of the fluid (endolymph) of the middle chamber (cohealr duct) causes the floor to vibrate. The vibration of the floor makes the sensory hair of receptor cells in the organ of Corti move in the overlying gelatinous membrane and gets distorted.
2. This stimulation causes depolarization of the receptor cells and initiation of receptor (action) potential in the fibres of the auditory nerve.
3. The latter carries the impulses to the cerebral cortex, which interprets the impulses as sound.
4. The receptor cells in different regions of the organ of Corti are sensitive to the sounds of different pitches.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Additional Information: The parts of ear include:
1. External ear – The external ear has two regions pinna, auricle or ear lobe, and external auditory canal or meatus
2. Internal ear- It is a delicate, irregular organ called a membranous labyrinth.
It is surrounded by an almost similarly shaped bony labyrinth.
3. Middle chamber: It is called scala media.
It is actually the cochlear duct and is an outgrowth from the saccule.
The floor of scala media is called the basilar membrane.
Note: The basilar membrane on it’s an organ of hearing called the organ of Corti.
The latter consists of receptor cells and supporting cells.
The receptor cells also called hair cells bear hair at the surface and have synaptic contact with the dendrites of neurons at the bases.
The ears show three parts: external, middle, and internal.
Complete answer: The ear not only detects sound but also notes its direction judges its loudness and determines its pitch (frequency).
1. The vibration of the fluid (endolymph) of the middle chamber (cohealr duct) causes the floor to vibrate. The vibration of the floor makes the sensory hair of receptor cells in the organ of Corti move in the overlying gelatinous membrane and gets distorted.
2. This stimulation causes depolarization of the receptor cells and initiation of receptor (action) potential in the fibres of the auditory nerve.
3. The latter carries the impulses to the cerebral cortex, which interprets the impulses as sound.
4. The receptor cells in different regions of the organ of Corti are sensitive to the sounds of different pitches.

So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Additional Information: The parts of ear include:
1. External ear – The external ear has two regions pinna, auricle or ear lobe, and external auditory canal or meatus
2. Internal ear- It is a delicate, irregular organ called a membranous labyrinth.
It is surrounded by an almost similarly shaped bony labyrinth.
3. Middle chamber: It is called scala media.
It is actually the cochlear duct and is an outgrowth from the saccule.
The floor of scala media is called the basilar membrane.
Note: The basilar membrane on it’s an organ of hearing called the organ of Corti.
The latter consists of receptor cells and supporting cells.
The receptor cells also called hair cells bear hair at the surface and have synaptic contact with the dendrites of neurons at the bases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




