
The parallelogram ABCD shows the points P and Q dividing each of the line AD and DC in the ratio 1:4. What is the ratio in which R divides DB? What is the ratio in which R divides PQ?
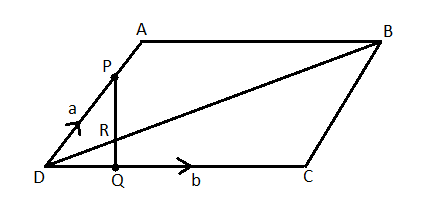

Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint: First construct the line AQ parallel to PQ. Using similar triangles DPQ and DAQ. There are many types of theorems like cevian theorem to get the ratio of the DB and PQ which pass through R.
Complete step by step answer:
Let $\left| {ABC} \right|$ denote area of $\vartriangle ABC$
Let $\left| {ABCD} \right| = 10x$,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {ABC} \right| = \left| {ADC} \right| = \left| {ABD} \right| = \left| {CBD} \right| = \dfrac{{10x}}{2} = 5x$
Given, $DQ:QC = 1:4$,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {ADQ} \right|:\left| {AQC} \right| = \left| {BDQ} \right|\left| {BQC} \right| = 1:4$,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {ABP} \right| = x,\left| {PBD} \right| = 4x$,
And, $\left| {AQP} \right| = \dfrac{1}{5}x,\left| {PQD} \right| = \dfrac{4}{5}x$
$\left| {PDQB} \right| = \left| {PBD} \right| + \left| {BDQ} \right| = 4x + x = 5x$
$ \Rightarrow \left| {PQB} \right| = \left| {PDQB} \right| - \left| {PDQ} \right| = 5x - \dfrac{4}{5}x = \dfrac{{21}}{5}x$
$ \Rightarrow DR:RB = \left| {PDQ} \right|:\left| {PQB} \right| = \dfrac{4}{5}x:\dfrac{{21}}{5}x = 4:21$
$\therefore PR:RQ = \left| {BPD} \right|:\left| {BDQ} \right| = 4x:x = 4:1$
Note: One may note that there are certain quadrilaterals whose diagonals bisect each other but here we have assumed the quadrilateral as a parallelogram because this is the basic property of a parallelogram.
Complete step by step answer:
Let $\left| {ABC} \right|$ denote area of $\vartriangle ABC$
Let $\left| {ABCD} \right| = 10x$,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {ABC} \right| = \left| {ADC} \right| = \left| {ABD} \right| = \left| {CBD} \right| = \dfrac{{10x}}{2} = 5x$
Given, $DQ:QC = 1:4$,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {ADQ} \right|:\left| {AQC} \right| = \left| {BDQ} \right|\left| {BQC} \right| = 1:4$,
$ \Rightarrow \left| {ABP} \right| = x,\left| {PBD} \right| = 4x$,
And, $\left| {AQP} \right| = \dfrac{1}{5}x,\left| {PQD} \right| = \dfrac{4}{5}x$
$\left| {PDQB} \right| = \left| {PBD} \right| + \left| {BDQ} \right| = 4x + x = 5x$
$ \Rightarrow \left| {PQB} \right| = \left| {PDQB} \right| - \left| {PDQ} \right| = 5x - \dfrac{4}{5}x = \dfrac{{21}}{5}x$
$ \Rightarrow DR:RB = \left| {PDQ} \right|:\left| {PQB} \right| = \dfrac{4}{5}x:\dfrac{{21}}{5}x = 4:21$
$\therefore PR:RQ = \left| {BPD} \right|:\left| {BDQ} \right| = 4x:x = 4:1$
Note: One may note that there are certain quadrilaterals whose diagonals bisect each other but here we have assumed the quadrilateral as a parallelogram because this is the basic property of a parallelogram.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Who is known as the "Little Master" in Indian cricket history?

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

Who Won 36 Oscar Awards? Record Holder Revealed

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




