
The order of multiple roots of 2 of the equation ${{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8=0$ is
[a] 1
[b] 2
[c] 3
[d] 4
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that if the multiplicity of a root x= a is r in the polynomial p(x), then there exists a polynomial g(x) such that $p\left( x \right)={{\left( x-a \right)}^{r}}g\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( a \right)\ne 0$. Use factor theorem to check that if x-2 is a factor of $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8$. If yes, then write $p\left( x \right)=\left( x-2 \right)g\left( x \right)$ using the long-division method. Apply the same process on g(x). Continue till g(x) is no more divisible by x-2. Hence find the order of the root 2 in the equation ${{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8=0$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8$
Now, we have
$p\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{4}}-5\times {{2}^{3}}+6\times {{2}^{2}}+4\times 2-8=16-40+24+8-8=0$
Hence by factor theorem, x-2 is a factor of p(x).
Dividing p(x) by x-2 using long-division method shown as follows:
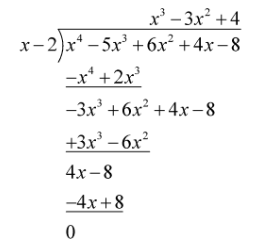
Hence, we have
$p\left( x \right)=\left( x-2 \right)\left( {{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+4 \right)$
Now, we have $g\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+4$
Now, we have
$g\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{3}}-3\times {{2}^{2}}+4=8-12+4=0$
Hence by factor theorem, x-2 is a factor of g(x).
Hence, we have
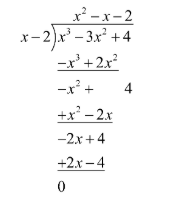
Hence, we have
$\begin{align}
& g\left( x \right)=\left( x-2 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow p\left( x \right)={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-x-2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Let $h\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-x-2$
Hence, we have
$h\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{2}}-2-2=0$
Hence by factor theorem, x-2 is a factor of h(x)
Hence, we have
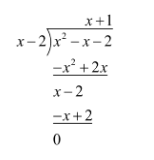
Hence, we have
$\begin{align}
& h\left( x \right)=\left( x-2 \right)\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow p\left( x \right)={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{3}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Let f(x) = x+1
Since $f\left( 2 \right)=1+2\ne 0$, we have
3 is the order of the root 2 of the equation ${{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8=0$
Hence option [c] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution: Best method:
We know that if r is the multiplicity of root x=a in the polynomial p(x), then $p\left( a \right),{{\left. \dfrac{d}{dx}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=a}},{{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{d{{x}^{2}}}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=a}},\cdots ,{{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{r-1}}}{d{{x}^{r-1}}}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=r}}$ are all 0.
Now, we have
$p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8$
Hence, we have
$p\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{4}}-5\times {{2}^{3}}+6\times {{2}^{2}}+4\,\times 2-8=16-40+24+8-8=0$
Now, we have
$\dfrac{d}{dx}p\left( x \right)=4{{x}^{3}}-15{{x}^{2}}+12x+4$
Hence, we have
${{\left. \dfrac{d}{dx}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=2}}=4\times {{2}^{3}}-15\times {{2}^{2}}+12\times 2+4=32-60+24+4=0$
Now, we have
$\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{d{{x}^{2}}}p\left( x \right)=12{{x}^{2}}-30x+12$
Hence, we have
${{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{d{{x}^{2}}}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=2}}=12\times {{2}^{2}}-30\times 2+12=48-60+12=0$
Now, we have
$\dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{d{{x}^{3}}}p\left( x \right)=24x-30$
Hence, we have
${{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{d{{x}^{3}}}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=2}}=24\times 2-30=48-30=18\ne 0$
Hence, the multiplicity of the root x= 2 in p(x) is 2+1 =3.
Hence option [c] is correct.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8$
Now, we have
$p\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{4}}-5\times {{2}^{3}}+6\times {{2}^{2}}+4\times 2-8=16-40+24+8-8=0$
Hence by factor theorem, x-2 is a factor of p(x).
Dividing p(x) by x-2 using long-division method shown as follows:
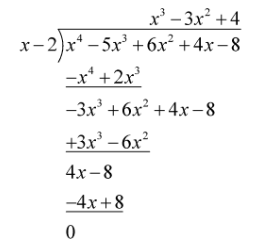
Hence, we have
$p\left( x \right)=\left( x-2 \right)\left( {{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+4 \right)$
Now, we have $g\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+4$
Now, we have
$g\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{3}}-3\times {{2}^{2}}+4=8-12+4=0$
Hence by factor theorem, x-2 is a factor of g(x).
Hence, we have
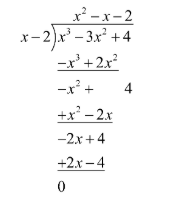
Hence, we have
$\begin{align}
& g\left( x \right)=\left( x-2 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow p\left( x \right)={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}\left( {{x}^{2}}-x-2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Let $h\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-x-2$
Hence, we have
$h\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{2}}-2-2=0$
Hence by factor theorem, x-2 is a factor of h(x)
Hence, we have
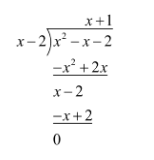
Hence, we have
$\begin{align}
& h\left( x \right)=\left( x-2 \right)\left( x+1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow p\left( x \right)={{\left( x-2 \right)}^{3}}\left( x+1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Let f(x) = x+1
Since $f\left( 2 \right)=1+2\ne 0$, we have
3 is the order of the root 2 of the equation ${{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8=0$
Hence option [c] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution: Best method:
We know that if r is the multiplicity of root x=a in the polynomial p(x), then $p\left( a \right),{{\left. \dfrac{d}{dx}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=a}},{{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{d{{x}^{2}}}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=a}},\cdots ,{{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{r-1}}}{d{{x}^{r-1}}}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=r}}$ are all 0.
Now, we have
$p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}-5{{x}^{3}}+6{{x}^{2}}+4x-8$
Hence, we have
$p\left( 2 \right)={{2}^{4}}-5\times {{2}^{3}}+6\times {{2}^{2}}+4\,\times 2-8=16-40+24+8-8=0$
Now, we have
$\dfrac{d}{dx}p\left( x \right)=4{{x}^{3}}-15{{x}^{2}}+12x+4$
Hence, we have
${{\left. \dfrac{d}{dx}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=2}}=4\times {{2}^{3}}-15\times {{2}^{2}}+12\times 2+4=32-60+24+4=0$
Now, we have
$\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{d{{x}^{2}}}p\left( x \right)=12{{x}^{2}}-30x+12$
Hence, we have
${{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}}{d{{x}^{2}}}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=2}}=12\times {{2}^{2}}-30\times 2+12=48-60+12=0$
Now, we have
$\dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{d{{x}^{3}}}p\left( x \right)=24x-30$
Hence, we have
${{\left. \dfrac{{{d}^{3}}}{d{{x}^{3}}}p\left( x \right) \right|}_{x=2}}=24\times 2-30=48-30=18\ne 0$
Hence, the multiplicity of the root x= 2 in p(x) is 2+1 =3.
Hence option [c] is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




