
The number of structural isomers of pentene is:
A.3
B.4
C.5
D.6
Answer
551.1k+ views
Hint: It can have chain isomers, position isomers, and ring chain isomers. But do not possess functional group isomers. The number of isomers can be determined by changing the position of methyl groups w.r.t. the double bond.
Complete step-by-step answer:Isomers are those molecules which have the same molecular formula but physical, chemical and biological properties can be different. Structural isomers are those having the same molecular formula but different properties due to different structures such as chain, position, functional group, linking property, etc. Functional group isomers are those structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but different functional groups. Chain isomers are those structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but have different lengths of principle carbon chain or parent carbon chain as per IUPAC. Position isomers are those structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but are different in position of functional group, multiple bond or substituent. Ring chain isomers are those structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but have either multiple bonds or ring with respect to its isomer.
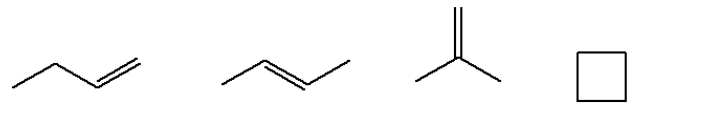
For example structural isomers possible for \[{{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}\] are 5. These are as follow:
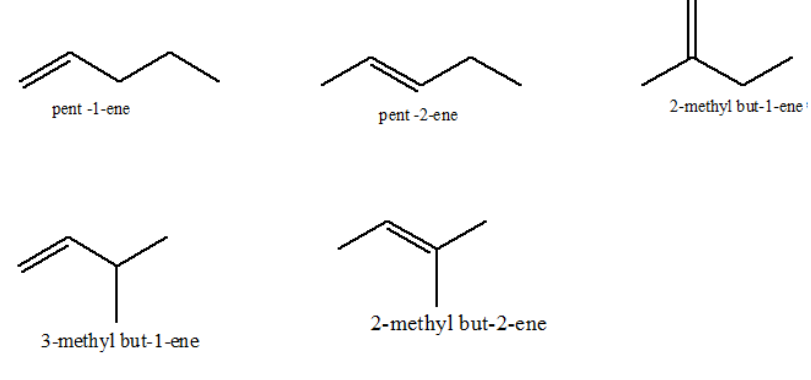
Similarly, possible structural isomers for pentene are 5:
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note: As changing the position of double bond in an organic compound containing alkene makes a different isomer. Other isomers of pentene can be drawn by changing the way that the carbon atoms are joined to each other or by changing the place of double bond. Isomers have the same chemical formula but different properties, like straight chain compounds have higher surface area than branched alkanes and thus have higher Vander Waal force of attraction and higher boiling and melting point.
Complete step-by-step answer:Isomers are those molecules which have the same molecular formula but physical, chemical and biological properties can be different. Structural isomers are those having the same molecular formula but different properties due to different structures such as chain, position, functional group, linking property, etc. Functional group isomers are those structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but different functional groups. Chain isomers are those structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but have different lengths of principle carbon chain or parent carbon chain as per IUPAC. Position isomers are those structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but are different in position of functional group, multiple bond or substituent. Ring chain isomers are those structural isomers which have the same molecular formula but have either multiple bonds or ring with respect to its isomer.
For example structural isomers possible for \[{{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_8}\] are 5. These are as follow:

Similarly, possible structural isomers for pentene are 5:

Thus, the correct option is C.
Note: As changing the position of double bond in an organic compound containing alkene makes a different isomer. Other isomers of pentene can be drawn by changing the way that the carbon atoms are joined to each other or by changing the place of double bond. Isomers have the same chemical formula but different properties, like straight chain compounds have higher surface area than branched alkanes and thus have higher Vander Waal force of attraction and higher boiling and melting point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




