
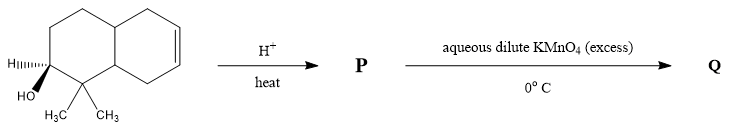
The number of hydroxyl group(s) in Q is ?

Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint :This step is the multiple reaction in which the intermediate product is formed. The final product of the reaction is phyrophosperic acid. Phyrophosperic acid molecular structure is $ {H_4}{O_7}{P_2} $
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The first step is the acid catalyzed dehydration reaction in which the alcoholic group is converted to an alkene group. A dehydration reaction is a reaction in which an organic compound undergoes loss of water molecules to form an alkene group with a carbon-carbon double bond. The primary carbocation form is the carbon group with a positive ion charge. The secondary carbocation rearranges itself into tertiary carbocation to form a more stable alkene group.
In the next step dihydroxylation reaction takes place in which an alkene group is converted into a vicinal diol in presence of excess potassium permanganate $ KMn{O_4} $ . It is done by oxidation of transition metal. The metal acts as a catalyst to complete the reaction and double bond is hydrolyzed attaching the $ 4 - OH $ groups to the compound.
Pyrophosphoric acid is also known as diphosphoric acid. It is a colorless, odorless, hygroscopic and is soluble compound in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol.
As stated in the reaction that $ 4 - OH $ groups are being attached. The total number of hydroxyl groups in pyrophosphoric acid is $ 4 $ .
Therefore, the number of hydroxyl group(s) in Q is $ 4 $
Note :
Anions, salts, and esters of pyrophosphoric acid are known as pyrophosphates. It is an acyclic phosphorus acid anhydride obtained by condensation of two molecules of phosphoric acid.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The first step is the acid catalyzed dehydration reaction in which the alcoholic group is converted to an alkene group. A dehydration reaction is a reaction in which an organic compound undergoes loss of water molecules to form an alkene group with a carbon-carbon double bond. The primary carbocation form is the carbon group with a positive ion charge. The secondary carbocation rearranges itself into tertiary carbocation to form a more stable alkene group.
In the next step dihydroxylation reaction takes place in which an alkene group is converted into a vicinal diol in presence of excess potassium permanganate $ KMn{O_4} $ . It is done by oxidation of transition metal. The metal acts as a catalyst to complete the reaction and double bond is hydrolyzed attaching the $ 4 - OH $ groups to the compound.
Pyrophosphoric acid is also known as diphosphoric acid. It is a colorless, odorless, hygroscopic and is soluble compound in water, diethyl ether, and ethyl alcohol.

As stated in the reaction that $ 4 - OH $ groups are being attached. The total number of hydroxyl groups in pyrophosphoric acid is $ 4 $ .
Therefore, the number of hydroxyl group(s) in Q is $ 4 $
Note :
Anions, salts, and esters of pyrophosphoric acid are known as pyrophosphates. It is an acyclic phosphorus acid anhydride obtained by condensation of two molecules of phosphoric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




