
The monomers of nucleic acids are held together by:
A. Phosphoester linkage
B. Amide linkage
C. Glycosidic linkage
D. Ester linkage
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: A monomer is a molecule that forms the basic unit of a polymer , which are the building blocks of proteins. Monomers bind to other monomers to form repeating chain molecules through a process known as polymerization. All nucleic acids are made up of the same building blocks (monomers) known as “ nucleotides”
Complete step by step answer:
The monomers of the nucleic acid are linked by a link known as N- glycosidic linkage or glycosidic linkage.
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
In this, one water molecule is produced during formation of a glycosidic bond.
The reverse reaction, the breakage of a glycosidic bond, is a hydrolysis reaction.
There are two types of glycosidic bonds 1,4 alpha and 1, 4 beta glycosidic bonds.
1, 4 alpha glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH on the carbon-1 is below the glucose ring, while 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH is above the plane.
These linkages are commonly found in carbohydrates, such as sugars and starches.
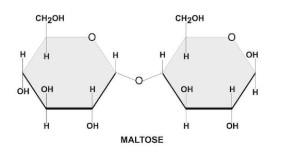
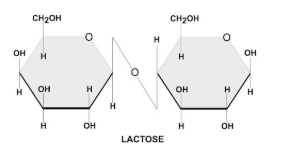
Hence, option C is correct.
Additional information
There are more linkage in monomers of DNA like
-Ionic bonding
-Vander waal force of attraction
-Disulphide linkage
-Phosphodiester linkage
In proteins peptide bonds are formed. Proteins are made up of amino acids that form polypeptide chains.
Note:
Glycosidic bonds are labeled according to the identity of the atom on the second carbohydrate or functional group. It can be broken by hydrolysis, which is the addition of water molecules, to form two monosaccharides.
Complete step by step answer:
The monomers of the nucleic acid are linked by a link known as N- glycosidic linkage or glycosidic linkage.
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
In this, one water molecule is produced during formation of a glycosidic bond.
The reverse reaction, the breakage of a glycosidic bond, is a hydrolysis reaction.
There are two types of glycosidic bonds 1,4 alpha and 1, 4 beta glycosidic bonds.
1, 4 alpha glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH on the carbon-1 is below the glucose ring, while 1,4 beta glycosidic bonds are formed when the OH is above the plane.
These linkages are commonly found in carbohydrates, such as sugars and starches.


Hence, option C is correct.
Additional information
There are more linkage in monomers of DNA like
-Ionic bonding
-Vander waal force of attraction
-Disulphide linkage
-Phosphodiester linkage
In proteins peptide bonds are formed. Proteins are made up of amino acids that form polypeptide chains.
Note:
Glycosidic bonds are labeled according to the identity of the atom on the second carbohydrate or functional group. It can be broken by hydrolysis, which is the addition of water molecules, to form two monosaccharides.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




