
The moment of inertia of a cube of mass m and side (a) about one of its edges is equal to:
A. $\dfrac{2}{3}m{a^2}$
B. $\dfrac{4}{3}m{a^2}$
C. $3m{a^2}$
D. $\dfrac{8}{3}m{a^2}$
Answer
583.5k+ views
Hint: The perpendicular axis theorem is defined as that moment of inertia of a planar lamina about an axis perpendicular to the lamina which is equal to the sum of the moment inertia of the Lamina about the two axes at the right angle to each other in its own plane of intersection to each other.
Complete answer:
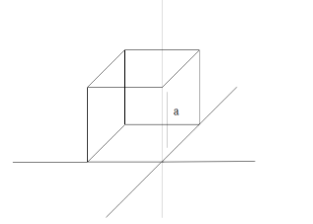
According to perpendicular axis:
$I = {I_C} + m{(\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 2 }})^2}$
$ \Rightarrow (\dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{{12}} - \dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{{12}}) + \dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{2} = \dfrac{2}{3}m{a^2}$
$I = \dfrac{2}{3}m{a^2}$
The term moment of inertia is also known as mass moment of inertia. It is defined as the ratio of net angular momentum of a system to its angular velocity around the principal axis. Moment of inertia plays a very important role in physics which means that in physics problems that involve the mass in rotation motion and that are calculated by angular momentum.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
THERE ARE THREE TYPES OF INERTIA:
a. INERTIA OF REST
b. INERTIA OF MOTION
C.INERTIA OF DIRECTION
If the moment of inertia is increased there will be a slowing down process of speed of rotation. We can also say that the moment of inertia of the body is directly proportional to the mass and it increases as the mass moves further from the axis of rotation.
Note:
Don’t get confused in saying that the moment of inertia and the inertia is the same in nature in physics. No it is not inertia means just the state of the body either it is in motion or rest whereas the moment of inertia is the measurement of resistances of the object against the rotation.
Complete answer:

According to perpendicular axis:
$I = {I_C} + m{(\dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 2 }})^2}$
$ \Rightarrow (\dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{{12}} - \dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{{12}}) + \dfrac{{m{a^2}}}{2} = \dfrac{2}{3}m{a^2}$
$I = \dfrac{2}{3}m{a^2}$
The term moment of inertia is also known as mass moment of inertia. It is defined as the ratio of net angular momentum of a system to its angular velocity around the principal axis. Moment of inertia plays a very important role in physics which means that in physics problems that involve the mass in rotation motion and that are calculated by angular momentum.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
THERE ARE THREE TYPES OF INERTIA:
a. INERTIA OF REST
b. INERTIA OF MOTION
C.INERTIA OF DIRECTION
If the moment of inertia is increased there will be a slowing down process of speed of rotation. We can also say that the moment of inertia of the body is directly proportional to the mass and it increases as the mass moves further from the axis of rotation.
Note:
Don’t get confused in saying that the moment of inertia and the inertia is the same in nature in physics. No it is not inertia means just the state of the body either it is in motion or rest whereas the moment of inertia is the measurement of resistances of the object against the rotation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




