
The molecular formula of glucose is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$. Calculate its molecular mass. (Atomic mass: C = 12u, H = 1u, O = 16u.)
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: Let us first see what is the atomic mass. The atomic weight or atomic mass of an element can be calculated by taking the weighted average of all the isotopes of that element that exist in nature, considering their abundance.
Complete answer:
The mass of one mole of the substance is said to be the molar mass of that substance. It is usually expressed in g/mol but its SI base unit is kg/mol. It is not a molecular property of a substance but its bulk property.
A mole of any substance has exactly $6.022\times {{10}^{23}}$ particles which can be ions, atoms, electrons, or molecules.
Now, the molecular mass of one mole of a compound can be calculated by taking the sum of atomic masses of all the elements present in the molecule.
It is given to us that the atomic masses of elements present in glucose are
C = 12 u
H = 1 u
O = 16 u
Since the molecular formula of glucose is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$, it has 6 atoms of carbon element, 12 atoms of hydrogen element, and 6 atoms of oxygen element
So, its molecular mass will be
\[\begin{align}
& {{M}_{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}}=6\times {{M}_{C}}+12\times {{M}_{H}}+6\times {{M}_{O}} \\
& {{M}_{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}}=6\times 12+12\times 1+6\times 16 \\
& {{M}_{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}}=180g/mol \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the molecular mass of glucose having molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$ is 180 g/mol.
Additional information:
Glucose is a type of carbohydrate. It is the most abundant monosaccharide which is obtained mainly from algae and plants that synthesize it during photosynthesis. Glucose serves as the main source of energy in all organisms. Its structure is as follows.
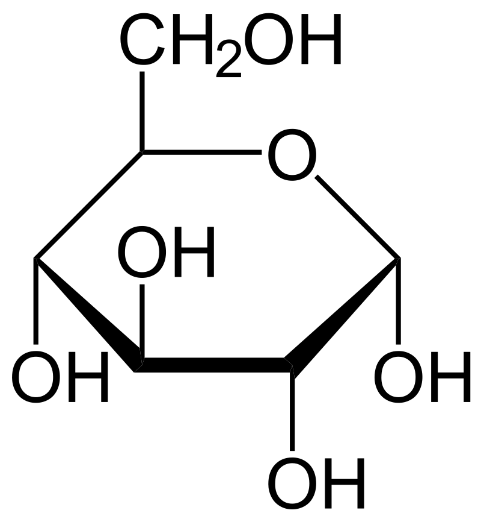
Note:
Let us determine the mass percentage compositions of elements in glucose.
\[(C)=\dfrac{12\times 6}{180}\times 100=40\]%
\[(H)=\dfrac{1\times 12}{180}\times 100=6.67\]%
\[(O)=\dfrac{6\times 16}{180}\times 100=53.33\]%
So, one mole of glucose contains 40% carbon atom, 6.67% hydrogen atom, and 53.33% oxygen atom by mass.
Complete answer:
The mass of one mole of the substance is said to be the molar mass of that substance. It is usually expressed in g/mol but its SI base unit is kg/mol. It is not a molecular property of a substance but its bulk property.
A mole of any substance has exactly $6.022\times {{10}^{23}}$ particles which can be ions, atoms, electrons, or molecules.
Now, the molecular mass of one mole of a compound can be calculated by taking the sum of atomic masses of all the elements present in the molecule.
It is given to us that the atomic masses of elements present in glucose are
C = 12 u
H = 1 u
O = 16 u
Since the molecular formula of glucose is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$, it has 6 atoms of carbon element, 12 atoms of hydrogen element, and 6 atoms of oxygen element
So, its molecular mass will be
\[\begin{align}
& {{M}_{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}}=6\times {{M}_{C}}+12\times {{M}_{H}}+6\times {{M}_{O}} \\
& {{M}_{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}}=6\times 12+12\times 1+6\times 16 \\
& {{M}_{{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}}}=180g/mol \\
\end{align}\]
Hence the molecular mass of glucose having molecular formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{12}}{{O}_{6}}$ is 180 g/mol.
Additional information:
Glucose is a type of carbohydrate. It is the most abundant monosaccharide which is obtained mainly from algae and plants that synthesize it during photosynthesis. Glucose serves as the main source of energy in all organisms. Its structure is as follows.

Note:
Let us determine the mass percentage compositions of elements in glucose.
\[(C)=\dfrac{12\times 6}{180}\times 100=40\]%
\[(H)=\dfrac{1\times 12}{180}\times 100=6.67\]%
\[(O)=\dfrac{6\times 16}{180}\times 100=53.33\]%
So, one mole of glucose contains 40% carbon atom, 6.67% hydrogen atom, and 53.33% oxygen atom by mass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




