
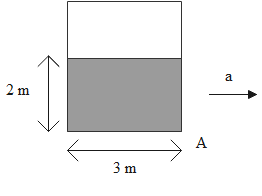
The minimum horizontal acceleration of the container so that the pressure at point A of the container becomes atmospheric is (the tank is of sufficient height)
\[\begin{align}
& A.\,\dfrac{3}{2}g \\
& B.\,\dfrac{4}{3}g \\
& C.\,\dfrac{4}{2}g \\
& D.\,\dfrac{3}{4}g \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
545.4k+ views
Hint: When the external pressure acting on a body/object becomes zero, then, that object/body will have the pressure equal to that of the atmospheric pressure. In this case, because of the liquid, there is some pressure acting on point A. when we tilt the container, the pressure at point A becomes equal to that of the atmospheric pressure.
Formula used:
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opp}}{\text{Adj}}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
The pressure at a point A becomes atmospheric pressure when there will be no liquid present at that point. In order to get the atmospheric pressure at a point A, we need to tilt the container left side such that the point A of the container is left with no liquid.
The diagrammatic representation of the above explanation is given as follows.
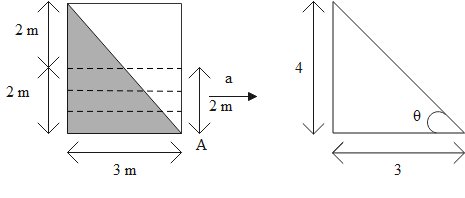
When we tilt the container containing liquid such that the pressure at point A becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure, the liquid present in the container consumes the shape of a triangle.
The triangle has the sides 4 m and 3 m. Using the diagram of the triangle, we can express the equation in terms of the tan function. So, we have,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{4}{3}\]……. (1)
Using the terms, such as the acceleration ‘a’ and the acceleration due to gravity ‘g’, we can express the equation in terms of the tan function. So, we have,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{a}{g}\]……. (2)
Equate the equations (1) and (2), as the LHS of both the equations, is the same. Thus, we get,
\[\dfrac{a}{g}=\dfrac{4}{3}\]
Now, represent the above equation in terms of the acceleration.
\[a=\dfrac{4}{3}g\]
\[\therefore \] The minimum horizontal acceleration of the container so that the pressure at point A of the container becomes atmospheric is \[\dfrac{4}{3}g\], thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: This problem can also be solved by equating the area of a rectangle with the area of the triangle. The area of the rectangle represents the area of the container. The area of the triangle represents the area of the triangular shape formed by tilting the container.
Formula used:
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Opp}}{\text{Adj}}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given information, we have the data as follows.
The pressure at a point A becomes atmospheric pressure when there will be no liquid present at that point. In order to get the atmospheric pressure at a point A, we need to tilt the container left side such that the point A of the container is left with no liquid.
The diagrammatic representation of the above explanation is given as follows.

When we tilt the container containing liquid such that the pressure at point A becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure, the liquid present in the container consumes the shape of a triangle.
The triangle has the sides 4 m and 3 m. Using the diagram of the triangle, we can express the equation in terms of the tan function. So, we have,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{4}{3}\]……. (1)
Using the terms, such as the acceleration ‘a’ and the acceleration due to gravity ‘g’, we can express the equation in terms of the tan function. So, we have,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{a}{g}\]……. (2)
Equate the equations (1) and (2), as the LHS of both the equations, is the same. Thus, we get,
\[\dfrac{a}{g}=\dfrac{4}{3}\]
Now, represent the above equation in terms of the acceleration.
\[a=\dfrac{4}{3}g\]
\[\therefore \] The minimum horizontal acceleration of the container so that the pressure at point A of the container becomes atmospheric is \[\dfrac{4}{3}g\], thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: This problem can also be solved by equating the area of a rectangle with the area of the triangle. The area of the rectangle represents the area of the container. The area of the triangle represents the area of the triangular shape formed by tilting the container.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




