
What will be the minimum height $h$ from which the system should be released when the spring is un stretched because of that after a perfectly inelastic collision $\left( e=0 \right)$ with the ground, $B$ will be lifted off the ground$\left( \text{spring constant}=k \right)$.
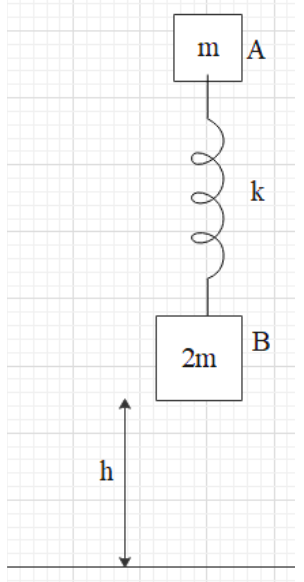
$\begin{align}
& A.\dfrac{mg}{2k} \\
& B.\dfrac{4mg}{k} \\
& C.\dfrac{mg}{4k} \\
& D.\dfrac{2mg}{k} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: The velocity can be found by taking the square root of the product of twice the acceleration due to gravity and height of the system. Apply the conservation of energy equation in this system and substitute the equation of velocity in it. Simplifying this equation will give the value of height. This will help you in answering this question.
Complete step by step answer:
The velocity can be found by taking the square root of the product of twice the acceleration due to gravity and height of the system. That is we can write that,
$u=\sqrt{2gh}$
In order to lift the block $B$, the extension in the spring, $x$ can be written as,
$x=\dfrac{2mg}{k}$
By the method of conservation of energy we can write that,
$0-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{u}^{2}}=-mgx-\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
The extension in the spring can be substituted in this equation as,
$\dfrac{1}{2}m{{u}^{2}}=mg\times \dfrac{2mg}{k}+\dfrac{1}{2}k{{\left( \dfrac{2mg}{k} \right)}^{2}}$
Rearranging this equation and then simplifying it can be shown as,
$\dfrac{1}{2}m{{u}^{2}}=\dfrac{2{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}+\dfrac{2{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}=\dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}$
Substituting the value of the velocity in this equation can be shown as,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}m\times 2gh=\dfrac{2{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}+\dfrac{2{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}=\dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k} \\
& \therefore h=\dfrac{4mg}{k} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the height from which the system should be released when the spring is un-stretched because of that after a perfectly inelastic collision with the ground, $B$ will be lifted off the ground.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: According to the theorem of conservation of energy, the energy cannot be created by ourselves and cannot be destroyed by ourselves. It can only be transferred one form to any other form. That is in rotating a fan the electrical energy has been converted to mechanical energy. This way only the conversion of energy is only possible.
Complete step by step answer:
The velocity can be found by taking the square root of the product of twice the acceleration due to gravity and height of the system. That is we can write that,
$u=\sqrt{2gh}$
In order to lift the block $B$, the extension in the spring, $x$ can be written as,
$x=\dfrac{2mg}{k}$
By the method of conservation of energy we can write that,
$0-\dfrac{1}{2}m{{u}^{2}}=-mgx-\dfrac{1}{2}k{{x}^{2}}$
The extension in the spring can be substituted in this equation as,
$\dfrac{1}{2}m{{u}^{2}}=mg\times \dfrac{2mg}{k}+\dfrac{1}{2}k{{\left( \dfrac{2mg}{k} \right)}^{2}}$
Rearranging this equation and then simplifying it can be shown as,
$\dfrac{1}{2}m{{u}^{2}}=\dfrac{2{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}+\dfrac{2{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}=\dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}$
Substituting the value of the velocity in this equation can be shown as,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}m\times 2gh=\dfrac{2{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}+\dfrac{2{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k}=\dfrac{4{{m}^{2}}{{g}^{2}}}{k} \\
& \therefore h=\dfrac{4mg}{k} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore the height from which the system should be released when the spring is un-stretched because of that after a perfectly inelastic collision with the ground, $B$ will be lifted off the ground.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: According to the theorem of conservation of energy, the energy cannot be created by ourselves and cannot be destroyed by ourselves. It can only be transferred one form to any other form. That is in rotating a fan the electrical energy has been converted to mechanical energy. This way only the conversion of energy is only possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




